『PyTorch』第三弹_自动求导
torch.autograd 包提供Tensor所有操作的自动求导方法。
数据结构介绍
autograd.Variable 这是这个包中最核心的类。 它包装了一个Tensor,并且几乎支持所有的定义在其上的操作。一旦完成了你的运算,你可以调用 .backward()来自动计算出所有的梯度,Variable有三个属性:
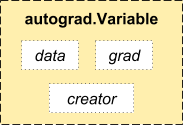
访问原始的tensor使用属性.data;
关于这一Variable的梯度则集中于 .grad;
.creator反映了创建者,标识了是否由用户使用.Variable直接创建(None)。
1 import torch 2 from torch.autograd import Variable 3 4 5 '''求导数''' 6 7 x = Variable(torch.ones(2,2),requires_grad=True) 8 y = x + 2 9 print(x.creator) # None,用户直接创建没有creater属性 10 print(y.creator) # <torch.autograd._functions.basic_ops.AddConstant object at 0x7fb9b4d4b208>
返回:
None
<torch.autograd._functions.basic_ops.AddConstant object at 0x7fb9b4d4b208>
求导运算
如果你想要进行求导计算,你可以在Variable上调用.backward()。
-
如果Variable是一个标量(例如它包含一个单元素数据),你无需对backward()指定任何参数
1 z = y*y*3 2 out = z.mean() 3 4 out.backward() 5 6 print(x,y,z) 7 print(x.grad) # 输出对out对x求倒结果 8 print(y.grad) # y不是自动求导变量
Variable containing: 1 1 1 1 [torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2] Variable containing: 3 3 3 3 [torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2] Variable containing: 27 27 27 27 [torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2] Variable containing: 4.5000 4.5000 4.5000 4.5000 [torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2] None
最终得出的结果应该是一个全是4.5的矩阵。设置输出的变量为o。我们通过这一公式来计算:
,
,
,因此,
,最后有
-
如果它有更多的元素(矢量),你需要指定一个和tensor的形状匹配的grad_output参数(y在指定方向投影对x的导数)
1 x = torch.randn(3) 2 x = Variable(x, requires_grad = True) 3 y = x * 2 4 while y.data.norm() < 1000: 5 y = y * 2 6 gradients = torch.FloatTensor([0.1, 1.0, 0.0001]) 7 y.backward(gradients) 8 x.grad
Variable containing: -0.8143 -1.5852 -0.8598 [torch.FloatTensor of size 3] Variable containing: -1.6286 -3.1704 -1.7195 [torch.FloatTensor of size 3] 3.9573325720437613 Variable containing: 51.2000 512.0000 0.0512 [torch.FloatTensor of size 3]
测试传入向量的意义:
1 x = torch.randn(3) 2 x = Variable(x,requires_grad=True) 3 y = x*2 4 5 gradients = torch.FloatTensor([0.5,0.5,1]) 6 y.backward(gradients) # 沿着某方向的梯度 7 print(x.grad) 8 9 # Variable containing: 10 # 1 11 # 1 12 # 2 13 # [torch.FloatTensor of size 3]
1 x = torch.randn(3) 2 x = Variable(x,requires_grad=True) 3 y = x*2 4 5 gradients = torch.FloatTensor([1,1,1]) 6 y.backward(gradients) # 沿着某方向的梯度 7 print(x.grad) 8 9 # Variable containing: 10 # 2 11 # 2 12 # 2 13 # [torch.FloatTensor of size 3]




