简单介绍递归算法以及应用场景
递归就是程序自己调用自己( recursion)
一般来说,递归需要有边界条件、递归前进段和递归返回段。当边界条件不满足时,递归前进;当边界条件满足时,递归返回。
1.趣味问题——年龄。
有5个人坐在一起,问第五个人多少岁?他说比第4个人大2岁。问第4个人岁数,他说比第3个人大2岁。问第三个人,又说比第2人大两岁。问第2个人,说比第一个人大两岁。最后问第一个人,他说是10岁。请问第五个人多大?用递归算法实现。
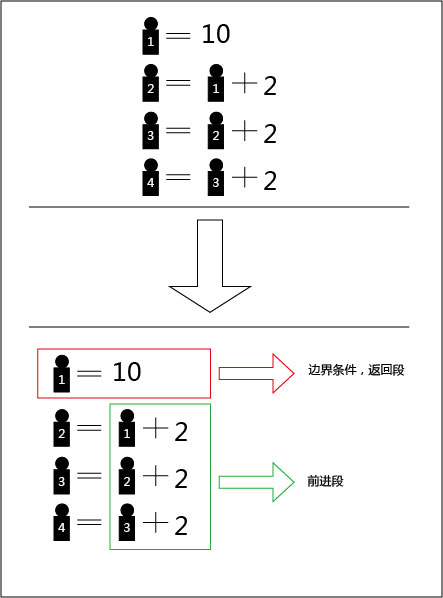
可以用循环解释这道题
static int GetAge(int num) { int age = 10; while (num>1) { age += 2; num -= 1; } return age; }
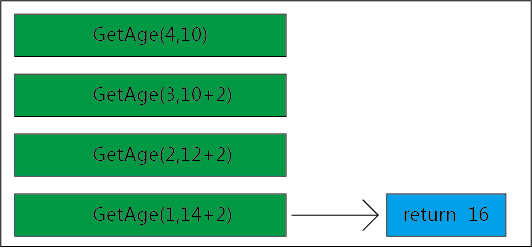
换成递归
static int GetAge(int num) { if (num==1) return 10;
return GetAge(num-1)+2; }

如果换成尾递归
static int GetAge(int num,int acc) { if (num == 1) return acc; return GetAge(num-1,acc+2); }
3.应用场景
删除指定路径下的文件夹里内容以及子文件夹以及子文件夹内容
static void DeleteFolder(string dir) { foreach (string d in Directory.GetFileSystemEntries(dir)) { //判断路径是否存在 if (File.Exists(d)) { FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(d); //去除文件夹的只读属性 if (fi.Attributes.ToString().IndexOf("ReadOnly") != -1) fi.Attributes = FileAttributes.Normal; File.Delete(d);//直接删除其中的文件 } else { DirectoryInfo d1 = new DirectoryInfo(d); if (d1.GetFiles().Length != 0) { DeleteFolder(d1.FullName);////递归删除子文件夹 } Directory.Delete(d); } } }
4.结
一般树状结构的都可以使用递归查询,比如 查询地区,树状的菜单等等,递归比普通的算法耗内存,谨慎使用。还有一种叫作“尾递归”就是把上一个方法的返回值当作参数传给下一个方法,不用像递归再向上返回。




