绚丽的loading动效的实现
最近看到有个gif动画效果挺不错的,可以拿来当项目的LoadingView,所以就花点时间做了下。先来看下效果图:
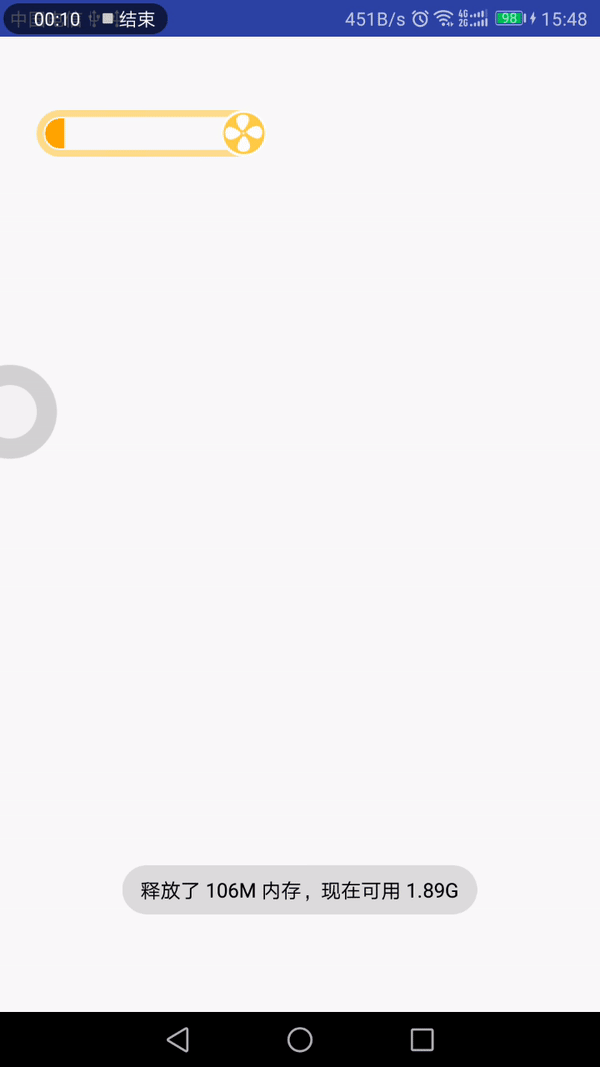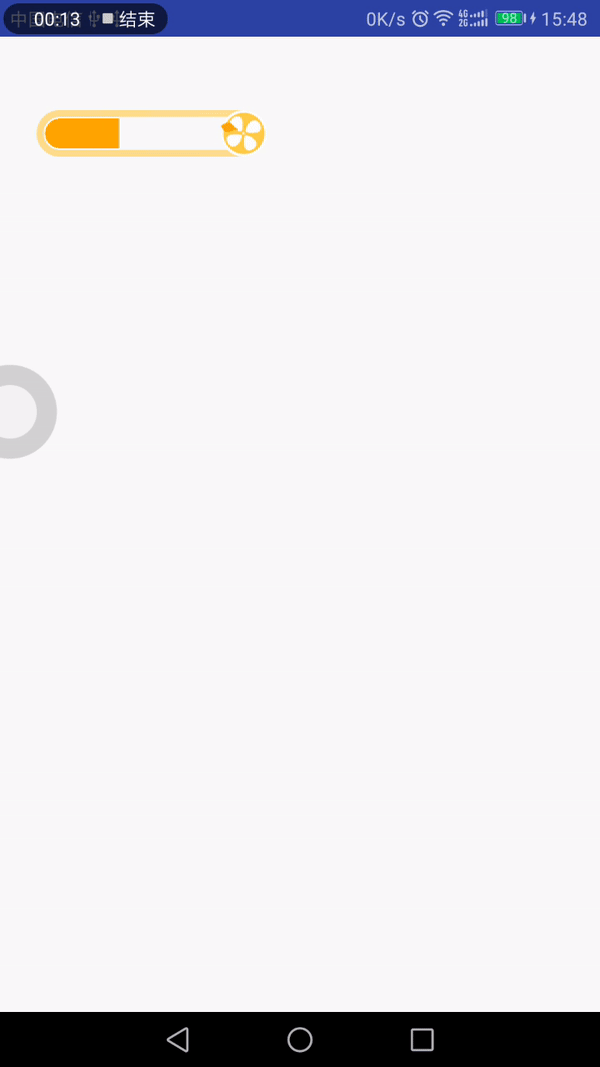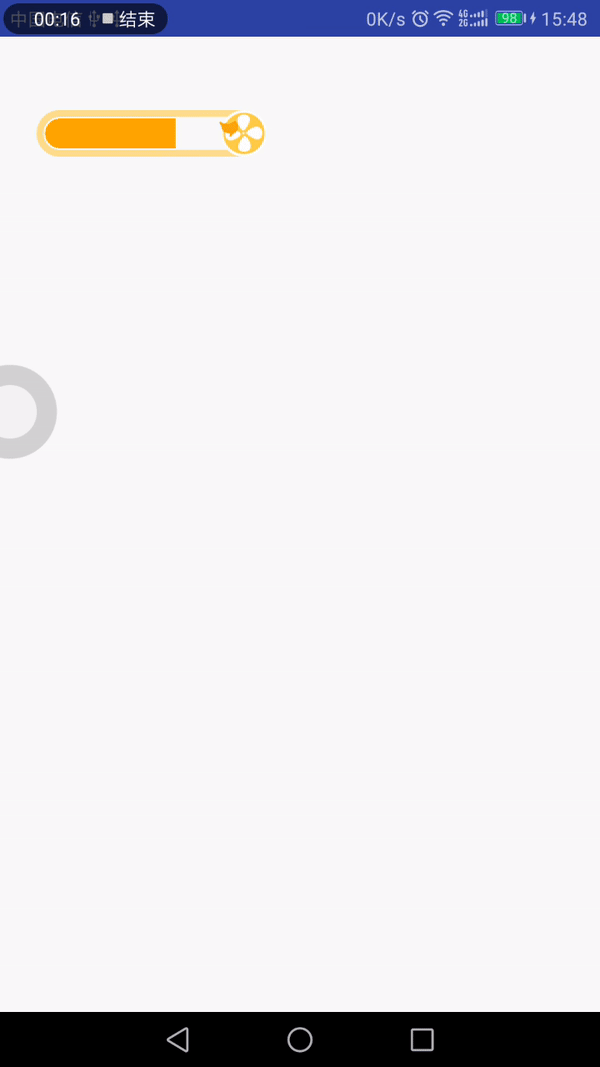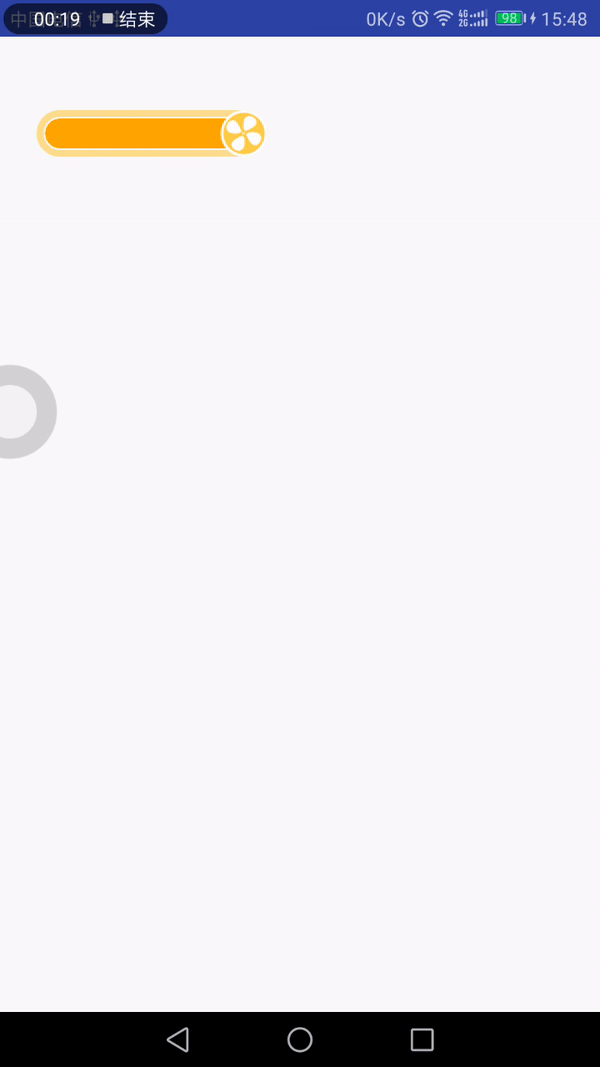
分析
从效果上看,我们可以将其拆分成以下几部分:
(1)底部框:带有黄色边框的圆角矩形和右边的圆形,为了方便,整个底部框切了,不需要我们去绘制圆角矩形和圆形了;

(2)进度框:带有进度值和色值的圆角矩形框,特殊的是它的圆角只有左上角和左下角是,另外的两个角是直角;
(3)风扇:在底部框的圆形位置中,绘制风扇,它可以旋转,直至进度加载完毕;
(4)叶子:从风扇处飘出,有多个叶子,按照一定的曲线和频率飘荡,遇到了进度框,看起来似乎融入进去了。
我们需要考虑的有几个问题:
1:叶子是随机产生的;
2:叶子遇到进度框,像是融进去了,不在显示了;
3:叶子是随着一条正余弦曲线移动;
4:叶子飘出的角度是不一样的,而且移动的振幅也不一样,比较有美感。
这样子,我们需要处理的有以下几部分:
一是,绘制底部框;
二是,不断往前绘制的进度条;
三是,不断旋转的风扇;
最后,不断飘出的叶子。
=========================================================
我们先处理第一部分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | private void drawBackground(Canvas canvas){ Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(mContext.getResources(), R.mipmap.leaf_kuang); mPicWidth = bitmap.getWidth(); mPicHeight = bitmap.getHeight(); canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap,0,0,mBgPaint); mTotalProgressWidth = mPicWidth - 76; } |
第二部分
利用Path的addRoundRect方法绘制可定制圆角的圆角矩形。绘制进度值,它的宽度的计算是进度值/100*总进度的宽度。因为,我们刚刚先绘制了底部框,然后绘制进度框,两者会有相交的地方,遵循上层覆盖下层原则,会出现相交的部分显示在底部框之上,不符合我们的效果。所以给它设置下图片混合效果DST_OVER,就可以了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | private void drawProgress(Canvas canvas){ mProgressWidth = mProgress/100 * mTotalProgressWidth; RectF rectF = new RectF(); rectF.left = 16; rectF.top = 16; rectF.right = mProgressWidth; rectF.bottom = mPicHeight-16; float[] radius = new float[8]; radius[0] = 40; radius[1] = 40; radius[2] = 0; radius[3] = 0; radius[4] = 0; radius[5] = 0; radius[6] = 40; radius[7] = 40; Path path = new Path(); path.addRoundRect(rectF,radius, Path.Direction.CW); //SRC 上层 DST 下层 mProgressPaint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.DST_OVER));//设置图片混合显示效果 canvas.drawPath(path,mProgressPaint); } |
第三部分
我们通过Matrix矩阵操作图片,可以让图片旋转,缩放。首先,风扇图片是显示在底部框最右边的圆形位置(称为R位置),所以需要先位移坐标。原来的坐标原点是在(0,0),现在图片是要在R位置旋转,缩放,所以通过setTranslate设置图片的坐标位置,然后在进度未达到100%时,让图片需要不停的旋转;达到95%以上,这时图片会进行缩放;达到100%时,就显示文本。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | private void drawFan(Canvas canvas){ int centerX = (int) mTotalProgressWidth; int centerY = 8; if(mProgress == 100){ String text = "100%"; canvas.drawText(text,centerX,mPicHeight/2+getTextHeight(text)/2,mFanPaint); }else{ Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(mContext.getResources(), R.mipmap.fengshan); int bitmapWidth = bitmap.getWidth(); int bitmapHeight = bitmap.getHeight(); Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); matrix.setTranslate(centerX, centerY); //设置图片的原点坐标 if (this.mProgress >= 95 && this.mProgress < 100){ float scale = Math.abs(this.mProgress - 100) * 0.2f; //缩放 参数1:X轴缩放倍数,参数2:Y轴缩放倍数 参数3,4:缩放中心点 matrix.preScale(scale,scale,(float)bitmapWidth/2, (float)bitmapHeight/2); }else{ //旋转 参数1:角度,参数2,3:旋转中心点 matrix.preRotate(mAngle, (float)bitmapWidth/2, (float)bitmapHeight/2); } canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, matrix, mFanPaint); if (this.mProgress != 100){ mAngle += 60; } } } |
最后一部分
首先根据效果情况基本确定出曲线函数,标准函数方程为:y = A(wx+Q)+h,其中w影响周期,A影响振幅 ,周期T= 2 * Math.PI/w;
根据效果可以看出,周期T大致为总进度长度,所以确定w=(float) ((float) 2 * Math.PI /mTotalProgressWidth);
由以上的分析可知,叶子是有位置(x,y),有振幅的幅度type(低等幅度,中等幅度,高等幅度),有旋转的角度和方向rotateAngle和rotateDirection,它是随机产生的,有个起始时间startTime。
叶子Leaf类就此产生:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | private enum StartType { LITTLE, MIDDLE, BIG } /** * 叶子对象,用来记录叶子主要数据 * */ private class Leaf { // 在绘制部分的位置 float x, y; // 控制叶子飘动的幅度 StartType type; // 旋转角度 int rotateAngle; // 旋转方向--0代表顺时针,1代表逆时针 int rotateDirection; // 起始时间(ms) long startTime; } |
叶子是可以随机产生一个或多个的,所以我们提供了一个LeafFactory类来生产叶子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | private class LeafFactory { private static final int MAX_LEAFS = 8; Random random = new Random(); // 生成一个叶子信息 public Leaf generateLeaf() { Leaf leaf = new Leaf(); int randomType = random.nextInt(3); // 随时类型- 随机振幅 StartType type = StartType.MIDDLE; switch (randomType) { case 0: break; case 1: type = StartType.LITTLE; break; case 2: type = StartType.BIG; break; default: break; } leaf.type = type; // 随机起始的旋转角度 leaf.rotateAngle = random.nextInt(360); // 随机旋转方向(顺时针或逆时针) leaf.rotateDirection = random.nextInt(2); // 为了产生交错的感觉,让开始的时间有一定的随机性 mLeafFloatTime = mLeafFloatTime <= 0 ? LEAF_FLOAT_TIME : mLeafFloatTime; mAddTime += random.nextInt((int) (mLeafFloatTime)); leaf.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + mAddTime; return leaf; } // 根据最大叶子数产生叶子信息 public List<Leaf> generateLeafs() { return generateLeafs(MAX_LEAFS); } // 根据传入的叶子数量产生叶子信息 public List<Leaf> generateLeafs(int leafSize) { List<Leaf> leafs = new LinkedList<Leaf>(); for (int i = 0; i < leafSize; i++) { leafs.add(generateLeaf()); } return leafs; } } |
接下来,我们就可以获取到叶子的Y坐标了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | // 通过叶子信息获取当前叶子的Y值 private int getLocationY(Leaf leaf) { // y = A(wx+Q)+h float w = (float) ((float) 2 * Math.PI / mTotalProgressWidth); float a = mMiddleAmplitude; switch (leaf.type) { case LITTLE: // 小振幅 = 中等振幅 - 振幅差 a = mMiddleAmplitude - mAmplitudeDisparity; break; case MIDDLE: a = mMiddleAmplitude; break; case BIG: // 小振幅 = 中等振幅 + 振幅差 a = mMiddleAmplitude + mAmplitudeDisparity; break; default: break; } return (int) (a * Math.sin(w * leaf.x)) + 40 * 2 / 3;//40是圆角半径 } |
接下来,开始绘制叶子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | /** * 绘制叶子 * * @param canvas */ private void drawLeaf(Canvas canvas) { mLeafRotateTime = mLeafRotateTime <= 0 ? LEAF_ROTATE_TIME : mLeafRotateTime; long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < mLeafInfos.size(); i++) { Leaf leaf = mLeafInfos.get(i); if (currentTime > leaf.startTime && leaf.startTime != 0) { // 绘制叶子--根据叶子的类型和当前时间得出叶子的(x,y) getLeafLocation(leaf, currentTime); // 根据时间计算旋转角度 canvas.save(); // 通过Matrix控制叶子旋转 Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); float transX = leaf.x; float transY = leaf.y; Log.e("(x,y)=","("+transX+","+transY+")"); if (transX > mProgressWidth) {//叶子遇到进度框,就融入了不再显示 matrix.postTranslate(transX, transY); // 通过时间关联旋转角度,则可以直接通过修改LEAF_ROTATE_TIME调节叶子旋转快慢 float rotateFraction = ((currentTime - leaf.startTime) % mLeafRotateTime) / (float) mLeafRotateTime; int angle = (int) (rotateFraction * 360); // 根据叶子旋转方向确定叶子旋转角度 int rotate = leaf.rotateDirection == 0 ? angle + leaf.rotateAngle : -angle + leaf.rotateAngle; matrix.postRotate(rotate, transX + mLeafWidth / 2, transY + mLeafHeight / 2); canvas.drawBitmap(mLeafBitmap, matrix, mLeafPaint); canvas.restore(); } } else { continue; } } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | /** * 获取叶子的x,y * @param leaf * @param currentTime */ private void getLeafLocation(Leaf leaf, long currentTime) { long intervalTime = currentTime - leaf.startTime; mLeafFloatTime = mLeafFloatTime <= 0 ? LEAF_FLOAT_TIME : mLeafFloatTime; if (intervalTime < 0) { return; } else if (intervalTime > mLeafFloatTime) { leaf.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + new Random().nextInt((int) mLeafFloatTime); } float fraction = (float) intervalTime / mLeafFloatTime; leaf.x = (int) (mTotalProgressWidth - mTotalProgressWidth * fraction); leaf.y = getLocationY(leaf); } |
最后,向外暴露几个方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | /** * 设置进度 * @param progress */ public void setProgress(float progress){ mProgress = progress; invalidate(); } /** * 进度框颜色 * @param color */ public void setProgressColor(int color){ this.mProgressColor = color; } /** * 设置中等幅度值 * @param amplitude */ public void setAmplitude(int amplitude){ this.mMiddleAmplitude = amplitude; } /** * 设置幅度差 * @param amplitudeDisparity */ public void setAmplitudeDisparity(int amplitudeDisparity){ this.mAmplitudeDisparity = amplitudeDisparity; } |
使用方式
(1)Activity:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private final int REFRESH_PROGRESS = 1000; private float mProgress = 0; //利用handler实现动画 private Handler mHandler = new Handler() { public void handleMessage(Message msg) { switch (msg.what) { case REFRESH_PROGRESS: if (mProgress <= 100) { mProgress += 1; // 随机100ms以内刷新一次 mHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(REFRESH_PROGRESS, 100); mLoadingView.setProgress(mProgress); } break; default: break; } }; }; private LoadingLeafView mLoadingView; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); findControl(); } private void findControl(){ mLoadingView = (LoadingLeafView) findViewById(R.id.loading_leaf_view);// mLoadingView.setProgressColor(Color.RED);// mLoadingView.setAmplitude(16);// mLoadingView.setAmplitudeDisparity(10); mHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(REFRESH_PROGRESS, 100); } |
(2)layout:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal"> <com.ha.cjy.myproject.view.widget.LoadingLeafView android:id="@+id/loading_leaf_view" android:layout_marginTop="48dp" android:layout_marginLeft="24dp" android:layout_width="302dp" android:layout_height="61dp"/> </LinearLayout> |



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步