04-String——课后动手动脑
1.请运行以下示例代码StringPool.java,查看输出结果。如何解释这样的输出结果?从中你能总结出什么?
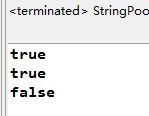
1 public class StringPool { 2 3 public static void main(String args[]) 4 { 5 6 String s0="Hello"; 7 8 String s1="Hello"; 9 10 String s2="He"+"llo"; 11 12 System.out.println(s0==s1);//true 13 14 System.out.println(s0==s2);//true 15 16 System.out.println(new String("Hello")==new String("Hello"));//false 17 18 } 19 20 }
程序运行结果:
结论:
1、在Java中,内容相同的字符常量只保存一份以节省内存,所以s0,s1,s2实际上引用的是同一个对象。
2、编译器在编译s2一句时,会去掉“+”号,直接把两个字串连接起来得一个字串。这种优化工作由Java编译器自动完成。
3、当直接使用new关键字创建字符串对象时,虽然值一致,但仍然是两个独立的对象。
再看……
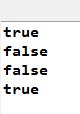
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = "a"; 6 7 String s2 = s1; 8 9 System.out.println(s1 == s2); 10 11 s1 += "b"; 12 13 System.out.println(s1 == s2); 14 15 System.out.println(s1 == "ab"); 16 17 System.out.println(s1.equals("ab")); 18 19 } 20 21 }
程序运行结果:
为什么会有上述的输出结果?从中你又能总结出什么?
1、给字串变量赋值意味着:两个变量(s1,s2)现在引用同一个字符串对象。
2、String对象的内容是只读的,使用“+”修改s1变量的值,实际上是得到了一个新的字符串对象,其内容为“ab”,它与原先s1所引用的对象“a”
无关,所以s1==s2返回false;
3、代码中的“ab”字符串是一个常量,它所引用的字符串与s1所引用的“ab”对象无关。
4、String.equals()方法可以比较两个字符串的内容。
2、请查看String.equals()方法的实现代码,注意学习其实现方法。
String.equals()源代码:
1 public boolean equals(Object anObject) { 2 if (this == anObject) { 3 return true; 4 } 5 if (anObject instanceof String) { 6 String anotherString = (String)anObject; 7 int n = count; 8 if (n == anotherString.count) { 9 char v1[] = value; 10 char v2[] = anotherString.value; 11 int i = offset; 12 int j = anotherString.offset; 13 while (n-- != 0) { 14 if (v1[i++] != v2[j++]) 15 return false; 16 } 17 return true; 18 } 19 } 20 return false; 21 }
由代码可知,这个函数首先判断这两个对象是否引用同一个字符串对象,如果是直接比较是否相同,如果不是,则比较两个对象中的字符是否相等。而且比较的方式是比较单个字符。
3、整理String类的length()、charAt()、 getChars()、replace()、 toUpperCase()、 toLowerCase()、trim()、toCharArray()使用说明。
(1)、int length():返回字符串的长度。
例:
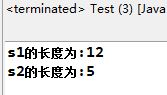
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 String s2 = new String("hello"); 8 9 System.out.println("s1的长度为:"+s1.length()); 10 11 System.out.println("s2的长度为:"+s2.length()); 12 13 } 14 15 }
执行结果:
(2)、 char charAt(int index):取字符串中的某一个字符,其中的参数index值得是字符串中序数。字符串的序数从0开始到length()-1。
例:
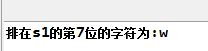
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 System.out.println("排在s1的第7位的字符为:"+s1.charAt(6)); 8 9 } 10 11 }
执行结果:
(3)、void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin):将字符从字符串复制到目标字符数组。
-
srcBegin -- 字符串中要复制的第一个字符的索引。
-
srcEnd -- 字符串中要复制的最后一个字符之后的索引。
-
dst -- 目标数组。
-
dstBegin -- 目标数组中的起始偏移量。
- 无返回值,但会抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常
例:
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 char s2[] = new char[10]; 8 9 s1.getChars(6, 12, s2, 0); 10 11 System.out.println(s2); 12 13 } 14 15 }
执行结果:

(4)、String replace(char oldChar,char newChar):将字符串中的所有oldChar替换成newChar
例:
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 String s2 = s1.replace('o','a'); 8 9 System.out.println("修改之后的字符串为:"+s2); 10 11 } 12 13 }
执行结果:

(5)、String toUpperCase():全部字符变为大写,返回新字符串。
例:
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 System.out.println("修改之后的字符串为:"+s1.toUpperCase()); 8 9 } 10 11 }
执行结果:

(6)、String toLowerCase():全部字符变为小写,返回新字符串。
例:
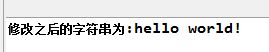
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("HELLO WORLD!"); 6 7 System.out.println("修改之后的字符串为:"+s1.toLowerCase()); 8 9 } 10 11 }
执行结果:
(7)、String trim():去掉字符串首尾的空格。
例:
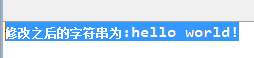
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String(" hello world! "); 6 7 System.out.println("修改之后的字符串为:"+s1.trim()); 8 9 } 10 11 }
执行结果:
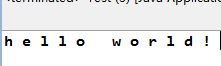
(8)、char [] toCharArray():将该String对象转换成char数组。
例:
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 char s2[] = new char[12]; 8 9 s2 = s1.toCharArray(); 10 11 for(int i = 0 ; i < 12 ; i ++){ 12 13 System.out.print(s2[i]+" "); 14 15 } 16 17 } 18 19 }
执行结果: