八数码问题
摘要:近日来,人工智能成为科技领域搜索热词,无论是从人机大战的新闻来看,还是从新提出的深度学习理论来分析,我们可以可以清晰的预见,人工智能即将腾飞。
人工智能,顾名思义,就是模拟人类思考模式的超级算法系统,学习能力和推理能力是其核心内容。举个简单的例子,“机器学习(MachineLearning)”就是人工智能领域里很有前途的课题,其主要内容是利用大数据训练程序,让它们找到一些可遵循的规律,并且让程序本身大胆的预测结果。在这个过程中搜索策略变的尤为关键。本文主要论述计算机科学与技术专业大三下专业课《人工智能》第二个实验算法。
关键字:人工智能,搜索问题,启发式搜索
Eight digital problem
Abstract: in recent days, the artificial intelligence search words become areas of science and technology, whether from the point of man-machine war news, or the depth of the new proposed learning theory to the analysis, we can clearly foresee, artificial intelligence is about to take off.
Artificial intelligence, as the name implies, is to simulate human thinking mode of super algorithm system, learning ability and reasoning ability is the core content. A simple example, the "machine learning (MachineLearning)" is the field of artificial intelligence is a promising subject, its main content is to use big data training program, let them find some follow rules, and make bold prediction to the program itself. In the process of the search strategy is particularly critical. This paper mainly discusses the computer science and technology under the junior in professional course "artificial intelligence".
Keywords: artificial intelligence, search problems, heuristic search
1,问题重述
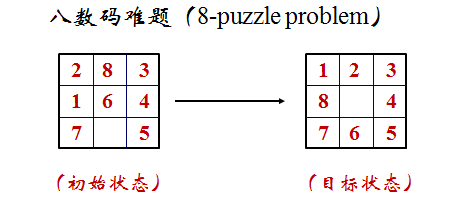
3×3九宫棋盘,放置数码为1 -8的8个棋牌,剩下一个空格,只能通过棋牌向空格的移动来改变棋盘的布局。
要求:根据给定初始布局(即初始状态)和目标布局(即目标状态),如何移动棋牌才能从初始布局到达目标布局,找到合法的走步序列。
2,问题分析
对于八数码问题的解决,首先要考虑是否有答案。每一个状态可认为是一个1×9的矩阵,问题即通过矩阵的变换,是否可以变换为目标状态对应的矩阵?由数学知识可知,可计算这两个有序数列的逆序值,如果两者都是偶数或奇数,则可通过变换到达,否则,这两个状态不可达。这样,就可以在具体解决问题之前判断出问题是否可解,从而可以避免不必要的搜索。
如果初始状态可以到达目标状态,那么采取什么样的方法呢?
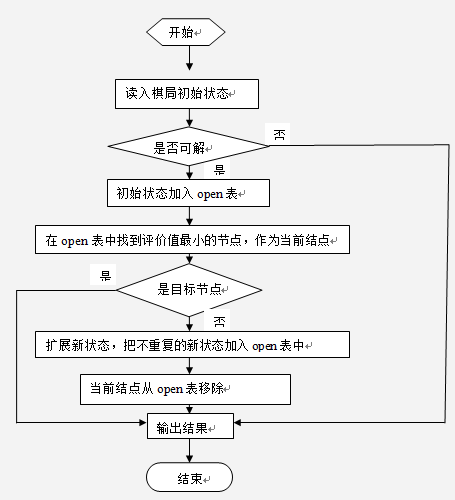
常用的状态空间搜索有深度优先和广度优先。广度优先是从初始状态一层一层向下找,直到找到目标为止。深度优先是按照一定的顺序前查找完一个分支,再查找另一个分支,以至找到目标为止。广度和深度优先搜索有一个很大的缺陷就是他们都是在一个给定的状态空间中穷举。这在状态空间不大的情况下是很合适的算法,可是当状态空间十分大,且不预测的情况下就不可取了。他的效率实在太低,甚至不可完成。由于八数码问题状态空间共有9!个状态,对于八数码问题如果选定了初始状态和目标状态,有9!/2个状态要搜索,考虑到时间和空间的限制,在这里采用A*算法作为搜索策略。在这里就要用到启发式搜索
启发式搜索就是在状态空间中的搜索对每一个搜索的位置进行评估,得到最好的位置,再从这个位置进行搜索直到目标。这样可以省略大量无畏的搜索路径,提到了效率。在启发式搜索中,对位置的估价是十分重要的。采用了不同的估价可以有不同的效果。
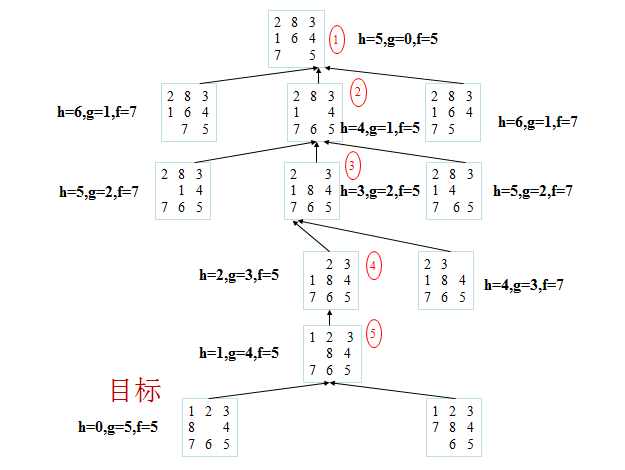
启发中的估价是用估价函数表示的,如:f(n) = g(n) +h(n)其中f(n) 是节点n的估价函数,g(n)是在状态空间中从初始节点到n节点的实际代价,h(n)是从n到目标节点最佳路径的估计代价。 在此八数码问题中,显然g(n)就是从初始状态变换到当前状态所移动的步数,估计函数f(n)我们就可采用当前状态各个数字牌不在目标状态未知的个数,即错位数。
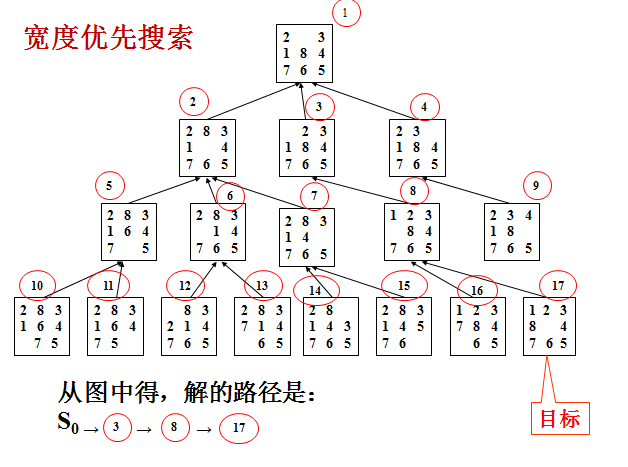
2.1使用宽度优先搜索方法解决该问题
为问题状态的表示建立数据结构:
(1)3×3的一个矩阵,矩阵元素S ij∈{0,1,…,8};其中1≤i,j≤3,
(2)数字0指示空格,
(3)数字1 - 8指示相应棋牌。
(4)制定操作算子集:
直观方法——为每个棋牌制定一套可能的走步:左、上、右、下四种移动。这样就需32个操作算子。
简易方法——仅为空格制定这4种走步,因为只有紧靠空格的棋牌才能移动。
空格移动的唯一约束是不能移出棋盘。
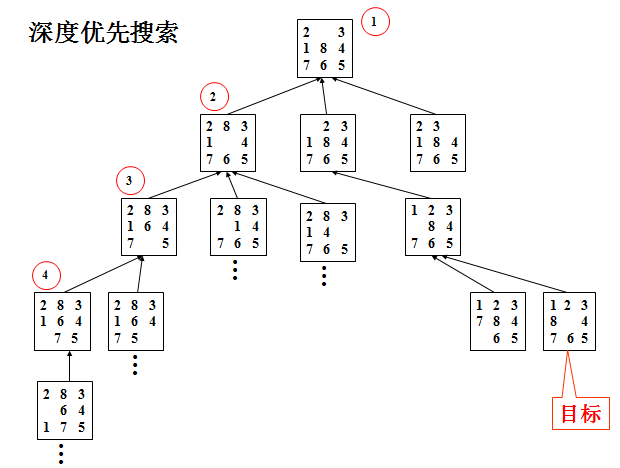
2.2使用深度优先搜索解决该问题
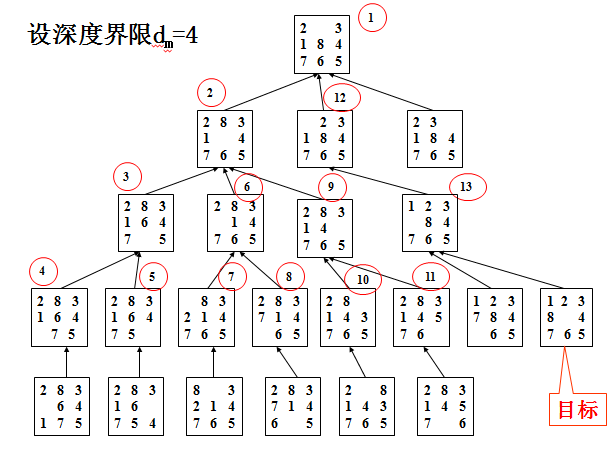
首先扩展最新产生的(即最深的)节点。防止搜索过程沿着无益的路径扩展下去,往往给出一个节点扩展的最大深度——深度界限。与宽度优先搜索算法最根本的不同在于:将扩展的后继节点放在OPEN表的前端。
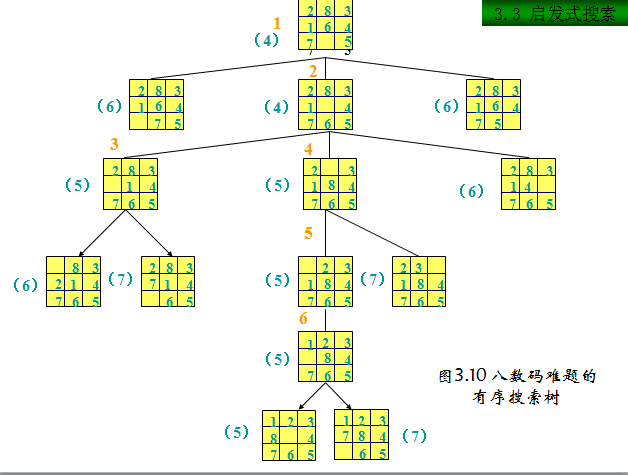
2.3使用启发式搜索
特点:重排OPEN表,选择最有希望的节点加以扩展
用来加速搜索过程的有关问题领域的特征信息。包括:
用于决定要扩展的下一个节点的信息;
在扩展一个节点时,用于决定要生成哪一个或哪几个后继节点的信息;
用于决定某些应该从搜索树中抛弃或修剪的节点的信息;
使用启发式信息指导的搜索过程称为启发式搜索.
用来估算节点处于最佳求解路径上的希望程度的函数
f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
n ——搜索图中的某个当前被扩展的节点;
f(n) ——从初始状态节点s, 经由节点n到达目标节点ng,估计的最小路径代价;
g(n) ——从s到n 的实际路径代价;
h(n)——从n到ng,估计的最小路径代价。 估价函数:f(n)=d(n)+w(n)
其中:d(n)为n的深度 w(n)为不在位的棋子数
3,求解过程
不管哪种搜索,都统一用这样的形式表示:搜索的对象是一个图,它面向一个问题,不一定有明确的存储形式,但它里面的一个结点都有可能是一个解(可行解),搜索的目的有两个方面,或者求可行解,或者从可行解集中求最优解。
搜索算法可分为两大类:无信息的搜索算法和有信息的搜索算法。无信息的搜索又称盲目搜索,其特点是只要问题状态可以形式化表示,原则上就可用使用无信息的搜索,无信息搜索有如下常见的几种搜索策略:广度优先搜索、代价一致搜索、深度优先搜索、深度有限搜索、迭代深入优先搜索、双向搜索。我们说DFS和BFS都是蛮力搜索,因为它们在搜索到一个结点时,在展开它的后续结点时,是对它们没有任何‘认识’的,它认为它的孩子们都是一样的‘优秀’,但事实并非如此,后续结点是有好有坏的。好,就是说它离目标结点‘近’,如果优先处理它,就会更快的找到目标结点,从而整体上提高搜索性能。
为了改善上面的算法,我们需要对展开后续结点时对子结点有所了解,这里需要一个估值函数,估值函数就是评价函数,它用来评价子结点的好坏,因为准确评价是不可能的,所以称为估值。这就是我们所谓的有信息搜索。如果估值函数只考虑结点的某种性能上的价值,而不考虑深度,比较有名的就是有序搜索(Ordered-Search),它着重看好能否找出解,而不看解离起始结点的距离(深度)。如果估值函数考虑了深度,或者是带权距离(从起始结点到目标结点的距离加权和),那就是A*如果不考虑深度,就是说不要求最少步数,移动一步就相当于向后多展开一层结点,深度多算一层,如果要求最少步数,那就需要用A*。简单的来说A*就是将估值函数分成两个部分,一个部分是路径价值,另一个部分是一般性启发价值,合在一起算估整个结点的价值,
考虑到八数码问题的特点,在本实验中使用A*算法求解。A*搜索是一种效的搜索算法,它把到达节点的耗散g(n)和从该节点到目标节点的消耗h(n)结合起来对节点进行评价:f(n)=g(n)+h(n)。当h(n)是可采纳时,使用Tree-Search的A*算法将是最优的。
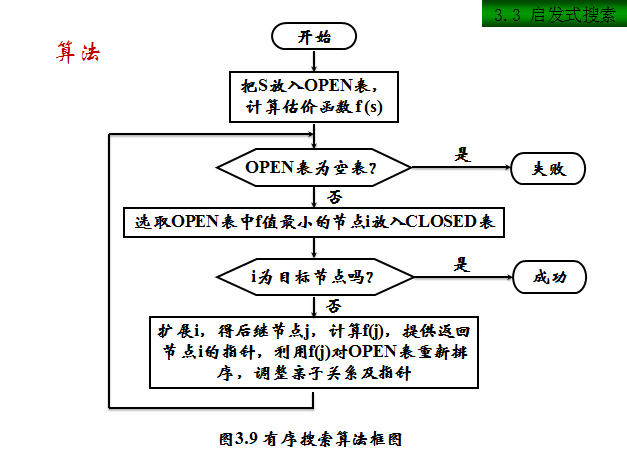
A*算法,1 在GRAPHSEARCH过程中,如果第8步的重排OPEN表是依据f(n)=g(n)+h(n)进行的,则称该过程为A算法。在A算法中,如果对所有的n存在h(n)≤h*(n),则称h(n)为h*(n)的下界,它表示某种偏于保守的估计。采用h*(n)的下界h(n)为启发函数的A算法,称为A*算法。当h=0时,A*算法就变为有序搜索算法。
在A算法中,如果满足条件:
(1) g(n)是对g*(n)的估计,且g(n)>0;
(2) h(n)是h*(n)的下界,即对任意节点n均有0≤h(n)≤h*(n)则A算法称为A*算法
A*算法的可纳性,对任一个图,存在从S到目标的路径,如果一个搜索算法总是结束在一条从S到目标的最佳路径上,则称此算法是可采纳的。算法A*保证只要最短路径存在,就一定能找出这条路径,所以算法A*是可纳的。
估价函数:f(n)=d(n)+w(n)
其中:d(n)为n的深度 w(n)为不在位的棋子数
取h(n)=w(n),则有w(n)≤h*(n),h(n)满足A*算法的限制条件。
在八数码难题中, 令估价函数
f(n)=d(n)+p(n)
启发函数h(n)=p(n),p(n)为不在位的棋子与其目标位置的距离之和,则有p(n)≤h*(n),满足A*算法的限制条件。
w(n)——不在位的棋子数,不够贴切,错误选用节点加以扩展。
更接近于h*(n)的h(n),其值是节点n与目标状态节点相比较,每个错位棋子在假设不受阻拦的情况下,移动到目标状态相应位置所需走步的总和。(n)比w(n)更接近于h*(n),因为p(n)不仅考虑了错位因素,还考虑了错位的距离(移动次数)。
说明h值越大,启发功能越强, 搜索效率越高.特别地
搜索仅沿最佳路径进行, 效率最高.
(2)h(n)=0
无启发信息, 盲目搜索, 效率低.
(3)h(n)>h*(n)
是一般的A算法,效率高, 但不能保证找到最佳路径. 有时为求解难题取h(n)>h*(n), 以提高效率.
4,程序设计
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdlib> 3 #include<ctime> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class EightPuzzle 7 { 8 private: 9 int num[9]; 10 int malposition; 11 int depth; 12 int evaluation; 13 public: 14 EightPuzzle *parent; 15 EightPuzzle *leaf_last; 16 EightPuzzle *leaf_next; 17 public: 18 EightPuzzle(int *num_input); 19 void init(int *target); 20 void setNum(int num[]); 21 int *getNum(); 22 void getNum(int *num); 23 int getMalposition() 24 { 25 return this->malposition; 26 } 27 int getDepth() 28 { 29 return this->depth; 30 } 31 int getEvaluation() 32 { 33 return this->evaluation; 34 } 35 void print(); 36 bool solvable(int *target); 37 bool find_target(int *target); 38 EightPuzzle& operator=(EightPuzzle& eightPuzzle); 39 EightPuzzle& operator=(int other_num[9]); 40 bool operator==(EightPuzzle& eigthPuzzle); 41 bool operator==(int other_num[9]); 42 }; 43 44 EightPuzzle::EightPuzzle(int *num_input) 45 { 46 int ii; 47 for (ii = 0; ii<9; ii++) 48 { 49 num[ii] = num_input[ii]; 50 } 51 this->leaf_last = NULL; 52 this->leaf_next = NULL; 53 this->parent = NULL; 54 } 55 56 EightPuzzle& EightPuzzle::operator=(EightPuzzle& eightPuzzle) 57 { 58 int ii; 59 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 60 { 61 this->num[ii] = eightPuzzle.getNum()[ii]; 62 } 63 this->malposition = eightPuzzle.getMalposition(); 64 this->depth = eightPuzzle.getDepth() + 1; 65 this->evaluation = this->malposition + this->depth; 66 return *this; 67 } 68 EightPuzzle& EightPuzzle::operator=(int other_num[9]) 69 { 70 int ii; 71 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 72 { 73 num[ii] = other_num[ii]; 74 } 75 return *this; 76 } 77 bool EightPuzzle::operator==(EightPuzzle& eightPuzzle) 78 { 79 int match = 1; 80 int ii; 81 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 82 { 83 if (this->num[ii] != eightPuzzle.getNum()[ii]) 84 { 85 match = 0; 86 break; 87 } 88 } 89 if (match == 0) 90 return false; 91 else 92 return true; 93 } 94 bool EightPuzzle::operator==(int other_num[9]) 95 { 96 int match = 1; 97 int ii; 98 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 99 { 100 if (this->num[ii] != other_num[ii]) 101 { 102 match = 0; 103 break; 104 } 105 } 106 if (match == 0) 107 return false; 108 else 109 return true; 110 } 111 112 void EightPuzzle::init(int *target) 113 { 114 int ii; 115 int temp = 0; 116 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 117 { 118 if (num[ii] != target[ii]) 119 { 120 temp++; 121 } 122 } 123 this->malposition = temp; 124 if (this->parent == NULL) 125 { 126 this->depth = 0; 127 } 128 else 129 { 130 this->depth = this->parent->depth + 1; 131 } 132 this->evaluation = this->malposition + this->depth; 133 } 134 135 void EightPuzzle::setNum(int num[]) 136 { 137 int ii; 138 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 139 { 140 this->num[ii] = num[ii]; 141 } 142 } 143 144 int *EightPuzzle::getNum() 145 { 146 return this->num; 147 } 148 149 void EightPuzzle::getNum(int *num) 150 { 151 int ii; 152 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 153 { 154 num[ii] = this->num[ii]; 155 } 156 } 157 158 bool EightPuzzle::solvable(int *target) 159 { 160 int ii, ij; 161 int count_num=0, count_target=0; 162 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 163 { 164 for (ij = 0; ij < ii; ij++) 165 { 166 if ((this->num[ij] < this->num[ii]) && (this->num[ij] != 0)) 167 { 168 count_num++; 169 } 170 if (target[ij] < target[ii] && target[ij] != 0) 171 { 172 count_target++; 173 } 174 } 175 } 176 if ((count_num + count_target) % 2 == 0) 177 { 178 return true; 179 } 180 else 181 { 182 return false; 183 } 184 } 185 186 bool EightPuzzle::find_target(int *target) 187 { 188 int ii; 189 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 190 { 191 if (this->num[ii] != target[ii]) 192 { 193 break; 194 } 195 } 196 if (ii == 9) 197 { 198 return true; 199 } 200 else 201 { 202 return false; 203 } 204 } 205 206 bool move_up(int *num) 207 { 208 int ii; 209 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 210 { 211 if (num[ii] == 0) 212 { 213 break; 214 } 215 } 216 if (ii < 3) 217 { 218 return false; 219 } 220 else 221 { 222 num[ii] = num[ii - 3]; 223 num[ii - 3] = 0; 224 } 225 return true; 226 } 227 228 bool move_down(int *num) 229 { 230 int ii; 231 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 232 { 233 if (num[ii] == 0) 234 { 235 break; 236 } 237 } 238 if (ii > 5) 239 { 240 return 0; 241 } 242 else 243 { 244 num[ii] = num[ii + 3]; 245 num[ii + 3] = 0; 246 } 247 return true; 248 } 249 250 bool move_left(int *num) 251 { 252 int ii; 253 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 254 { 255 if (num[ii] == 0) 256 { 257 break; 258 } 259 } 260 if (ii == 0 || ii == 3 || ii == 6) 261 { 262 return false; 263 } 264 else 265 { 266 num[ii] = num[ii - 1]; 267 num[ii - 1] = 0; 268 } 269 return true; 270 } 271 272 bool move_right(int *num) 273 { 274 int ii; 275 for (ii = 0; ii < 9; ii++) 276 { 277 if (num[ii] == 0) 278 { 279 break; 280 } 281 } 282 if (ii == 2 || ii == 5 || ii == 8) 283 { 284 return false; 285 } 286 else 287 { 288 num[ii] = num[ii + 1]; 289 num[ii + 1] = 0; 290 } 291 return true; 292 } 293 294 void EightPuzzle::print() 295 { 296 int ii; 297 for (ii = 0; ii<9; ii++) 298 { 299 if ((ii + 1) % 3 != 0) 300 { 301 cout << num[ii] << ","; 302 } 303 else 304 { 305 cout << num[ii] << endl; 306 } 307 } 308 } 309 310 bool existed(int *num, EightPuzzle *start) 311 { 312 EightPuzzle *temp; 313 for (temp = start; temp != NULL; temp = temp->parent) 314 { 315 if (*temp == num) 316 { 317 return true; 318 } 319 } 320 return false; 321 } 322 323 EightPuzzle *best_route(EightPuzzle *start,EightPuzzle *target) 324 { 325 EightPuzzle *temp, *best; 326 temp = best = start; 327 start->init(target->getNum()); 328 int min = start->getEvaluation(); 329 for (temp = start; temp != NULL; temp = temp->leaf_next) 330 { 331 if (min > temp->getEvaluation()) 332 { 333 best = temp; 334 min = temp->getEvaluation(); 335 } 336 } 337 return best; 338 } 339 340 void print_route(EightPuzzle *best,int list_length) 341 { 342 int step = 0; 343 EightPuzzle *temp; 344 for (temp = best->parent; temp != NULL; temp = temp->parent) 345 { 346 cout << endl; 347 temp->print(); 348 step++; 349 } 350 cout << endl << "The total steps is " << step << "." << endl; 351 cout << endl << "The memory cost is " << list_length << "." << endl; 352 return; 353 } 354 355 void proceeding(EightPuzzle &start, EightPuzzle &target) 356 { 357 if (!start.solvable(target.getNum())) 358 { 359 cout <<endl<< "The serious number you input can't be solvable!" << endl; 360 return; 361 } 362 EightPuzzle *best = &start; 363 EightPuzzle *list = &start; 364 EightPuzzle *apply,*temp; 365 int num[9],list_length=0; 366 while (best != NULL) 367 { 368 best = best_route(list,&target); 369 if (best->find_target(target.getNum())) 370 { 371 print_route(best,list_length); 372 return; 373 } 374 temp = best->leaf_last; 375 best->getNum(num); 376 if (move_up(num) && !existed(num, best)) 377 { 378 apply = new EightPuzzle(num); 379 apply->parent = best; 380 apply->init(target.getNum()); 381 apply->leaf_last = temp; 382 if (temp == NULL) 383 { 384 list = apply; 385 } 386 else 387 { 388 temp->leaf_next = apply; 389 } 390 temp = apply; 391 list_length++; 392 } 393 best->getNum(num); 394 if (move_down(num) && !existed(num, best)) 395 { 396 apply = new EightPuzzle(num); 397 apply->parent = best; 398 apply->init(target.getNum()); 399 apply->leaf_last = temp; 400 if (temp == NULL) 401 { 402 list = apply; 403 } 404 else 405 { 406 temp->leaf_next = apply; 407 } 408 temp = apply; 409 list_length++; 410 } 411 best->getNum(num); 412 if (move_left(num) && !existed(num, best)) 413 { 414 apply = new EightPuzzle(num); 415 apply->parent = best; 416 apply->init(target.getNum()); 417 apply->leaf_last = temp; 418 if (temp == NULL) 419 { 420 list = apply; 421 } 422 else 423 { 424 temp->leaf_next = apply; 425 } 426 temp = apply; 427 list_length++; 428 } 429 best->getNum(num); 430 if (move_right(num) && !existed(num, best)) 431 { 432 apply = new EightPuzzle(num); 433 apply->parent = best; 434 apply->init(target.getNum()); 435 apply->leaf_last = temp; 436 if (temp == NULL) 437 { 438 list = apply; 439 } 440 else 441 { 442 temp->leaf_next = apply; 443 } 444 temp = apply; 445 list_length++; 446 } 447 temp->leaf_next = best->leaf_next; 448 if (best->leaf_next != NULL) 449 { 450 best->leaf_next->leaf_last = temp; 451 } 452 best->leaf_next = best->leaf_last = NULL; 453 } 454 } 455 456 void input(int num_init[]) 457 { 458 int ii, ij; 459 cout << "Please input the initial state of the eight puzzle:" << endl; 460 cout << "(0 for the blank)" << endl << endl; 461 for (ii = 0; ii<9; ii++) 462 { 463 cin >> num_init[ii]; 464 if (num_init[ii]<0 || num_init[ii]>8) 465 { 466 cout << "Wrong number! Please input again:(0-8)" << endl; 467 ii--; 468 } 469 for (ij = 0; ij<ii; ij++) 470 { 471 if (num_init[ii] == num_init[ij]) 472 { 473 cout << "The number you inputed is duplicated! Try again:" << endl; 474 ii--; 475 } 476 } 477 } 478 } 479 480 int main(int argc, char **argv) 481 { 482 double time; 483 clock_t START, FINISH; 484 int num_init[9]; 485 input(num_init); 486 EightPuzzle *start = new EightPuzzle(num_init); 487 int num_target[9] = { 1,2,3,8,0,4,7,6,5 }; 488 EightPuzzle *target = new EightPuzzle(num_target); 489 cout << "The initial serial number is:" << endl; 490 start->print(); 491 cout << "The target serial number is:" << endl; 492 target->print(); 493 START = clock(); 494 proceeding(*start, *target); 495 FINISH = clock(); 496 time = (double)(FINISH - START) * 1000 / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 497 cout << endl << "The total time cost to solve the puzzle is: "; 498 cout<< time <<" millisecond."<< endl << endl; 499 system("pause"); 500 return 0; 501 } 502 503 //216408753->18steps