翻译:《JavaScript 权威指南(第5版)》第一章(一)
声明:翻译只有一个目的:学习用途。若有版权问题请及时联系本人。
本贴文根据篇幅将第一章的翻译分为两个部分,这是第一部分的内容。
Chapter 1. Introduction to JavaScript
第一章 Javascript 概论
JavaScript is an interpreted programming language with object-oriented (OO) capabilities. Syntactically, the core JavaScript language resembles C, C++, and Java, with programming constructs such as the if statement, the while loop, and the && operator. The similarity ends with this syntactic resemblance, however. JavaScript is a loosely typed language, which means that variables do not need to have a type specified. Objects in JavaScript map property names to arbitrary property values. In this way, they are more like hash tables or associative arrays (in Perl) than they are like structs (in C) or objects (in C++ or Java). The OO inheritance mechanism of JavaScript is prototype-based like that of the little-known language Self. This is quite different from inheritance in C++ and Java. Like Perl, JavaScript is an interpreted language, and it draws inspiration from Perl in a number of areas, such as its regular-expression and array-handling features.
JavaScript 是一门具有面向对象(OO)能力的解释型编程语言。在语法上,JavaScript语言核心与 C、C++ 及 Java 相似,虽然具有诸如 if 语句、while 循环、&& 运算符这样的程序结构,但是也仅限于在语法上与之相似。JavaScript 是一门弱类型的语言,也就是说,变量的类型不必指明。JavaScript 中的对象可映射属性名到随意的属性值。在这点上,它更像散列表或关联数组(在 Perl 中),而不像结构(在 C 中)或对象(在 C++ 或 Java 中)。JavaScript 中面向对象的继承机制是基于原型的,这与 Self 语言有点相似。却与 C++ 和 Java 的继承则大不相同。Java是门解释型语言(与 Perl 一样),而且多处灵感是受 Perl 语言的启发,诸如正则表达式和数组处理的特性。
The core JavaScript language supports numbers, strings, and Boolean values as primitive datatypes. It also includes built-in support for array, date, and regular-expression objects.
JavaScript 语言核心支持数字、字符串、布尔值这些原始数据类型,也包括对数组、日期、正则表达式这些对象的内置支持。
JavaScript is most commonly used in web browsers, and, in that context, the general-purpose core is extended with objects that allow scripts to interact with the user, control the web browser, and alter the document content that appears within the web browser window. This embedded version of JavaScript runs scripts embedded within HTML web pages. It is commonly called client-side JavaScript to emphasize that scripts are run by the client computer rather than the web server.
JavaScript 用得最多的一般是在 Web 浏览器中,在其上下文中,通用渲染核心使允许用户利用脚本来扩展控制浏览器中的对象,更改文档内容的 web 浏览器窗口的外观。JavaScript 的嵌入版运行 HTML 网页嵌入脚本。一般称为客户端 JavaScript来表示脚本是运行在客户计算机上而不是 web 服务器。
The core JavaScript language and its built-in datatypes are the subject of international standards, and compatibility across implementations is very good. Parts of client-side JavaScript are formally standardized, other parts are de facto standards, and other parts are browser-specific extensions. Cross-browser compatibility is often an important concern for client-side JavaScript programmers.
JavaScript 语言核心及其内置数据类型是国际标准化的项目,对兼容实现跨平台是很有意义的。客户端 JavaScript 的部分已被正式标准化了,而特定浏览器扩展的部分已是实际上的标准。跨浏览器兼容是客户端 JavaScript 程序员们常关注的重点之一。
This chapter is a high-level overview of JavaScript; it provides the background information you need before embarking on a study of the language. As motivation and introduction, it includes some simple examples of client-side JavaScript code.
本章是对 JavaScript 的高级概览。它提供了语言学习上手前的背景信息。还有目标和导论,包括一些客户端 JavaScript 示例代码。
1.1. What Is JavaScript?
1.1. 什么是 JavaScript
JavaScript is the subject of a fair bit of misinformation and confusion. Before proceeding any further, it is important to debunk two common and persistent myths about the language.
JavaScript 是相当容易误解和混淆的主题。在对它进行进一步研究之前,有必要澄清两个长期存在的对于该语言的误解。
1.1.1. JavaScript Is Not Java
1.1.1. JavaScript 并非 Java
One of the most common misconceptions about JavaScript is that it is a simplified version of Java, the programming language from Sun Microsystems. Other than an incomplete syntactic resemblance and the fact that both Java and JavaScript can provide executable content in web browsers, the two languages are entirely unrelated. The similarity of names is purely a marketing ploy by Netscape and Sun (the language was originally called LiveScript; its name was changed to JavaScript at the last minute). However, JavaScript can, in fact, script Java (see Chapters 12 and 23).
对 JavaScript 最常见的误解是认为它是Sun 微系统的 Java 编程语言的精简版。但是除了语法上有些不完全相似和都提供了 Web 浏览器可执行内容之外,两者则完全不相干。相似的名称只是市场营销的手段罢了(该语言最初被称为 LiveScript,只是到最后那次被改称 JavaScript)。但实际上有 script Java(请见第12章和第23章)。
1.1.2. JavaScript Is Not Simple
1.1.2. JavaScript 并不简单
Because JavaScript is interpreted instead of compiled, it is often considered a scripting language instead of a true programming language. The implication is that scripting languages are simpler and that they are programming languages for nonprogrammers. The fact that JavaScript is loosely typed does make it somewhat more forgiving for unsophisticated programmers. And many web designers have been able to use JavaScript for limited, cookbook-style programming tasks.
因为 JavaScript 是解释型而非编译型,所以一般被作为脚本语言而非真正的编程语言来考虑。脚本语言总被看成很简单,是非程序员的编程语言。但事实上 JavaScript 的松散类型容许非科班出身的程序员编写得灵活而不规范。许多 Web设计人员可用 JavaScript 来执行有限的、照葫芦画瓢的编程任务。
Beneath its thin veneer of simplicity, however, JavaScript is a full-featured programming language, as complex as any and more complex than some. Programmers who attempt to use JavaScript for nontrivial tasks often find the process frustrating if they do not have a solid understanding of the language. This book documents JavaScript comprehensively so that you can develop a sophisticated understanding. If you are used to cookbook-style JavaScript tutorials, you may be surprised at the depth and detail of the chapters ahead.
而 JavaScript 却不是那么简单,它是门具有完全特性的编程语言,有多复杂就有多复杂。程序员如果对 JavaScript 语言的用法没有扎实的理解,他在执行较复杂的任务时,就会发现进展困难重重。本书对JavaScript 无所不包,可使你能全面的理解。如果你是用菜谱式 JavaScript 教程,会对本章的深度和详细感兴趣。
1.2. Versions of JavaScript
1.2. JavaScript 版本
Like any new technology, JavaScript evolved quickly when it was new. Previous editions of this book documented this evolution version by version, explaining exactly which language features were introduced in which version of the language. At the time of this writing, however, the language has stabilized and has been standardized by the European Computer Manufacturer's Association, or ECMA.[*] Implementations of this standard include the JavaScript 1.5 interpreter from Netscape and the Mozilla Foundation, and the JScript 5.5 interpreter from Microsoft. Any web browser newer than Netscape 4.5 or Internet Explorer 4 supports the latest version of the language. As a practical matter, you are unlikely to encounter a noncompliant interpreter.
如同任何新技术一样,JavaScript 更新速度发展很快。本书的前几版历经了版本的迭代,该语言每个版本的特性都有详细的介绍。在著作本书时,该语言趋于稳定,并且由欧洲计算机行业协会(或简称 ECMA)[注1]进行了标准化。该标准的实现方案包括了 Netscape 和 Mozilla 基金 的 JavaScript 1.5 解释器、Microsoft 的 Jscript 5.5 解释器。所有比 Netscape 4.5 或 IE 4 更新的 web 浏览器都支持该语言的更新版本。实际上你也不愿遇到非标准的解释器。
[*] The standard is ECMA-262, version 3 (available at http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/files/ecma-st/ECMA-262.pdf).
注1:ECMA-262 v3 标准见 http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/files/ecma-st/ECMA-262.pdf
Note that the official name of the language, according to the ECMA-262 standard, is ECMAScript. But this awkward name is normally used only when making explicit reference to the standard. Technically, the name "JavaScript" refers only to language implementations from Netscape and the Mozilla Foundation. In practice, however, everyone calls the language JavaScript.
该语言的官方名称按 ECMA-262 标准称为 ECMAScript。但是这个蹩脚的名字一般只在想要详查参考标准时才用。技术上,“JavaScript”只是指在 Netscape 和 Mozilla 基金的语言实现。而在实践中,人们都称该语言为 JavaScript。
After a long period of stability for JavaScript, there are now some signs of change. The Firefox 1.5 web browser from the Mozilla Foundation includes a new JavaScript interpreter with the version number 1.6. This version includes new (nonstandard) array manipulation methods described in Section 7.7.10, as well as support for E4X, which is described next.
JavaScript 版本稳定后现在又有了一些变动。Mozilla 基金的 Firefox 1.5 web 浏览器包含 1.6版的 JavaScript 解释器。此版包括了新的数组处理方法(见 7.7.10 章节)、并同时支持下一代的 E4X。
In addition to the ECMA-262 specification that standardizes the core JavaScript language, ECMA has released another JavaScript-related standard. ECMA-357 standardizes an extension to JavaScript known as E4X, or ECMAScript for XML. This extension adds an XML datatype to the language along with operators and statements for manipulating XML values. At the time of this writing, E4X is implemented only by JavaScript 1.6 and Firefox 1.5. E4X is not documented formally in this book, but Chapter 21 includes an extended introduction in tutorial form.
除了 JavaScript 语言核心标准化的 ECMA-262 规范外,还有另一个与 JavaScript 有关的 ECMA-357 标准。它将 E4X(ECMAScript for XML) 标准化。它将 XML 数据类型(datatype) 添加到语言里结合操作语句和声明语言来操作 XML 值。在著作本书时,E4X 只在 JavaScript 1.6 和 Firefox 1.5 中被实现。E4X 的内容在本书中的第21章有教程来介绍它。
Proposals for a fourth edition of the ECMA-262 specification, to standardize JavaScript 2.0, have been on the table for a number of years. These proposals describe a complete overhaul of the language, including strong typing and true class-based inheritance. To date, there has been little progress toward standardization of JavaScript 2.0. Nevertheless, implementations based on draft proposals include Microsoft's JScript.NET language and the ActionScript 2.0 and ActionScript 3.0 languages used in the Adobe (formerly Macromedia) Flash player. At the time of this writing, there are signs that work on JavaScript 2.0 is resuming, and the release of JavaScript 1.6 can be seen as a preliminary step in this direction. Any new version of the language is expected to be backward-compatible with the version documented here, of course. And even once JavaScript 2.0 is standardized, it will take a few years before it is universally deployed in web browsers.
ECMA 规范的第4版是讨论了多年的 JavaScript 2.0 标准化的提议。这些提议描述了一个完整并改头换面的语言,包含了强类型和真正基于类的继承机制。迄今为止,JavaScript 2.0 的标准化已向前迈出了一小步。Microsoft 的 Jscript.NET 语言和用在 Adobe(以前的 Macromedia) Flash 播放器的 ActionScript 2.0 和 3.0 语言是基于草稿提议实现了。在著作本书时,JavaScript 2.0 还在继续讨论,JavaScript 1.6 的发布给了个方向。该语言的每次新版都必须向后兼容,甚至是 JavaScript 2.0 标准,这几年里 JavaScript 1.6 会在 web 浏览器中普遍部署。
1.3. Client-Side JavaScript
客户端 JavaScript
When a JavaScript interpreter is embedded in a web browser, the result is client-side JavaScript. This is by far the most common variant of JavaScript; when most people refer to JavaScript, they usually mean client-side JavaScript. This book documents client-side JavaScript, along with the core JavaScript language that client-side JavaScript incorporates.
当 JavaScript 解释器嵌入 Web 浏览器时,就是客户端 JavaScript 了。这是迄今为止最普通的 JavaScript 变体。当人们提到 JavaScript 时,通常所指的是客户端 JavaScript。本书中的客户端 JavaScript,它与 JavaScript 语言核心是混为一谈的。
Client-side JavaScript combines the scripting ability of a JavaScript interpreter with the Document Object Model (DOM) defined by a web browser. Documents may contain JavaScript scripts, and those scripts can use the DOM to modify the document or control the web browser that displays the document. Put another way, we can say that client-side JavaScript adds behavior to otherwise static web content. Client-side JavaScript is at the heart of web development techniques such as DHTML (see Chapter 16) and architectures such as Ajax (see Chapter 20). The introduction to Chapter 13 includes an overview of the many capabilities of client-side JavaScript.
客户端 JavaScript 将 JavaScript 脚本编程的能力与 Web 浏览器中定义的 DOM 合二为一。文档可含 JavaScript 脚本,而这些脚本可利用 DOM 修改文档或控制 web 浏览器显示文档。也就是说,客户端 JavaScript 给静态 web 内容层外加了一层额外的行为层。它是 web 开发技术的关键点(如 DHTML(见第16章))和框架结构(如 Ajax(见第20章))。在第13章节中概述了客户端 JavaScript 的各个方面。
Just as the ECMA-262 specification defines a standard version of the core JavaScript language, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) has published a DOM specification that standardizes the features a browser must support in its DOM. (You'll learn much more about this standard in Chapters 15, 16, and 17.) The core portions of the W3C DOM standard are well supported in all major web browsers. One notable exception is Microsoft Internet Explorer, which does not support the W3C standard for event handling.
正如 ECMA-262 规范定义了 JavaScript 语言核心的标准化版本一样,W3C也发布了DOM 规范,将浏览器必须其 DOM 所支持的特性进行了标准化。我们会在第15、16、17章节中了解更多的有关内容。虽然 W3C DOM 标准的核心部分得到了所有主流 web 浏览器的支持,但是有点要注意的是,微软的 IE不支持 W3C 标准的事件处理。
1.3.1. Client-Side JavaScript Examples
1.3.1. 客户端 JavaScript 举例
When a web browser is augmented with a JavaScript interpreter, it allows executable content to be distributed over the Internet in the form of JavaScript scripts. Example 1-1 shows what this looks like: it is a simple JavaScript program, or script, embedded in an HTML file.
在内嵌 JavaScript 解释器的 web 浏览器中,可允许可执行内容以 JavaScript 脚本的形式分布到 Internet 中。例 1-1 是简单的在 HTML 文件内的 JavaScript 程序(或称脚本)。
<html>
<head><title>Factorials</title></head>
<body>
<h2>Table of Factorials</h2>
<script>
var fact = 1;
for(i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
fact = fact*i;
document.write(i + "! = " + fact + "<br>");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
When loaded into a JavaScript-enabled browser, this script produces the output shown in Figure 1-1.
在启用 JavaScript 的浏览器中载入后,就会产生如图 1-1 所示的输出结果。
Figure 1-1. A web page generated with JavaScript
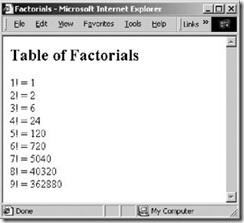
图 1-1 用了 JavaScript 所生成的网页
As you can see in this example, the <script> and </script>tags are used to embed JavaScript code in an HTML file. I'll describe the <script> tag further in Chapter 13. The main feature of JavaScript demonstrated by this example is the use of the document.write() method.[*] This method is used to dynamically output HTML text into an HTML document while it is being loaded into the browser.
在这个例子中可以看到,<script> 与 </script> 标签是将 JavaScript 代码嵌到 HTML 文件内。我们将会在第13章中了解到更多 <script> 标签的内容。这个例子表明了 JavaScript 的一个主要功能: document.write() 方法(注1)的应用。该方法用于动态地将 HTML 文本输出到被载入的浏览器,并显示在 HTML 文档中。
[*] "Method" is the OO term for function or procedure; you'll see it used throughout this book.
注1:方法是面向对象(OO)的术语,指函数或过程。在本书中会常看到它。
JavaScript can control not only the content of HTML documents but also the behavior of those documents. That is, a JavaScript program might respond in some way when you enter a value in an input field or hover the mouse over an image in a document. JavaScript does this by defining event handlers for the document pieces of JavaScript code that are executed when a particular event occurs, such as when the user clicks on a button. Example 1-2 shows a simple HTML fragment that includes an event handler executed in response to a button click.
JavaScript 不仅能控制 HTML 文档的内容,而且也能控制这些文档的行为。也就是说,在输入区域中输入值时,或是在文档中把鼠标移到了图像之上时,JavaScript 程序可做些反应。JavaScript由文档的事件处理来实现,事件处理是指特定的事件发生时有段 JavaScript 代码被执行,如用户点击了按钮。例 1-2 是一段简单的 HTML,响应到按钮点击便执行事件处理。
Example 1-2. An HTML button with a JavaScript event handler defined
例 1-2 带 JavaScript 事件处理定义的HTML按钮
<button onclick="alert('You clicked the button');">
Click here
</button>
Figure 1-2 illustrates the result of clicking the button.
图 1-2 为点击按钮时的效果。
Figure 1-2. The JavaScript response to an event
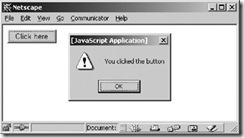
The onclick attribute shown in Example 1-2 holds a string of JavaScript code that's executed when the user clicks the button. In this case, the onclick event handler calls the alert() function. As you can see in Figure 1-2, alert() pops up a dialog box to display the specified message.
上例中的 onclick 属性内是 JavaScript 代码,该代码在用户点击按钮时会被执行。 Onclick 事件处理调用了 alert() 函数。可在图 1-2 中看到,alert() 弹出了一个对话框,其实显示所指定的消息。
Example 1-1 and 1-2 highlight only the simplest features of client-side JavaScript. The real power of JavaScript on the client side is that scripts have access to the content of HTML documents. Example 1-3 contains a complete, nontrivial JavaScript program. The program computes the monthly payment on a home mortgage or other loan, given the amount of the loan, the interest rate, and the repayment period. It reads user input from HTML form fields, performs computations on that input, and then alters the document to display the results of the computation.
例 1-1 和 1-2 只不过用了客户端 JavaScript 最简单的特性。JavaScript 在客户端真正的威力是脚本访问 HTML 文档的内容。例 1-3 是个完整的而不简单的JavaScript程序。它计算了每月在房贷及其它借贷的花销,可算得借贷的总额、利息率、还贷期限。它将用户在HTML表单字段中的输入读取,通过计算,然后将计算结果显示在文档中。

