pg_stat_statements源代码分析
磨砺技术珠矶,践行数据之道,追求卓越价值
回到上一级页面:PostgreSQL内部结构与源代码研究索引页 回到顶级页面:PostgreSQL索引页
pg_stat_statement的源代码,非常地有示范意义。其中使用了各种hook,同时又定义为extension。
先看初始化是如何发生的:
在postgresql.conf里,如果有 preload_shared_libraries='pg_stat_statements',那么成功启动的时候,会提示:
[root@server ~]# su - postgres [postgres@server ~]$ cd /usr/local/pgsql [postgres@server pgsql]$ ./bin/pg_ctl -D ./data start server starting [postgres@server pgsql]$ LOG: loaded library "pg_stat_statements" LOG: database system was shut down at 2013-08-16 09:24:02 CST LOG: autovacuum launcher started LOG: database system is ready to accept connections
在这个时刻(具体说是loaded library "pg_stat_statements"信息提示之前,会执行 pg_stat_statements的_PG_init函数完成初始化):初始化过程中准备好了各式hook。
/* * Module load callback */ void _PG_init(void) { … /* * Install hooks. */ prev_shmem_startup_hook = shmem_startup_hook; shmem_startup_hook = pgss_shmem_startup; prev_ExecutorStart = ExecutorStart_hook; ExecutorStart_hook = pgss_ExecutorStart; prev_ExecutorRun = ExecutorRun_hook; ExecutorRun_hook = pgss_ExecutorRun; prev_ExecutorFinish = ExecutorFinish_hook; ExecutorFinish_hook = pgss_ExecutorFinish; prev_ExecutorEnd = ExecutorEnd_hook; ExecutorEnd_hook = pgss_ExecutorEnd; prev_ProcessUtility = ProcessUtility_hook; ProcessUtility_hook = pgss_ProcessUtility; }
从整体上来看,画一个图来描述,从执行的角度而言,加挂了hook之后,在postmaster是这样的:
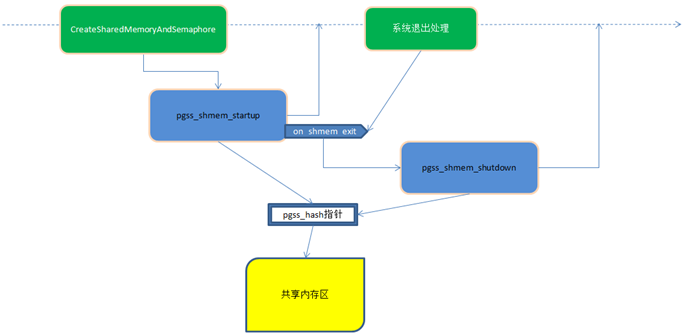
在上图中,Postmaster进程启动之后,当发现有shmem_startup_hook的时候,会去执行此hook函数,这里挂的是
pgss_shmem_startup函数,故此函数被执行,然后返回。
在pgss_shmem_startup中,在shared memory中,建立一个hashtable,由pgss_hash指针来指向。此后,postmaster的各子进程,可以通过此pgss_hash指针,来使用此hashtable存取sql语句执行的信息。
再来看sql问执行时,发生了什么:
对于处理用户请求的,Postmaster的各子进程,加挂了hook后,当用户执行一条SELETE/INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE的SQ文的时候,执行计划确定后,执行过程是这样的:
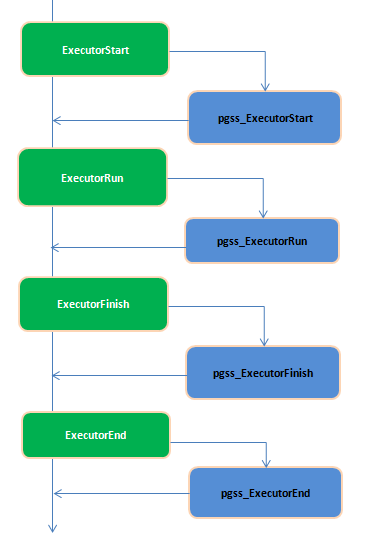
而对于 SELETE/INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE 之外的语句(Utility Command:例:create table),执行过程是这样的:
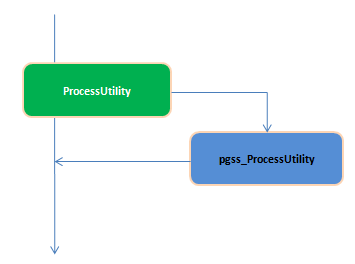
从代码上,可以比较清楚地看到pgss_ProcessUtility是如何发生的:
void ProcessUtility(Node *parsetree, const char *queryString,ParamListInfo params, bool isTopLevel, DestReceiver *dest, char *completionTag) { Assert(queryString != NULL); /* required as of 8.4 */ /* * We provide a function hook variable that lets loadable plugins get * control when ProcessUtility is called. Such a plugin would normally * call standard_ProcessUtility(). */ if (ProcessUtility_hook) (*ProcessUtility_hook) (parsetree, queryString, params, isTopLevel, dest, completionTag); else standard_ProcessUtility(parsetree, queryString, params, isTopLevel, dest, completionTag); }
其余的hook发生过程都与此类似。
那么sql文执行的数据,是如何收集的呢?看如下代码的概要:
执行到pgss_ExecutorEnd的时候,调用了pgss_store来存储sql运行信息到共享内存的hash表里:
/* * ExecutorEnd hook: store results if needed */ static void pgss_ExecutorEnd(QueryDesc *queryDesc) { if (queryDesc->totaltime && pgss_enabled()) { /* * Make sure stats accumulation is done. (Note: it's okay if several * levels of hook all do this.) */ InstrEndLoop(queryDesc->totaltime); pgss_store(queryDesc->sourceText,queryDesc->totaltime->total, queryDesc->estate->es_processed, &queryDesc->totaltime->bufusage); } if (prev_ExecutorEnd) prev_ExecutorEnd(queryDesc); else standard_ExecutorEnd(queryDesc); }
而pgss_store函数的概要,大致如下:
/* * Store some statistics for a statement. */ static void pgss_store(const char *query, double total_time, uint64 rows, const BufferUsage *bufusage) { pgssHashKey key; double usage; pgssEntry *entry; Assert(query != NULL); /* Safety check... */ if (!pgss || !pgss_hash) return; /* Set up key for hashtable search */ key.userid = GetUserId(); key.dbid = MyDatabaseId; key.encoding = GetDatabaseEncoding(); key.query_len = strlen(query); if (key.query_len >= pgss->query_size) key.query_len = pg_encoding_mbcliplen(key.encoding, query, key.query_len, pgss->query_size - 1); key.query_ptr = query; usage = USAGE_EXEC(duration); /* Lookup the hash table entry with shared lock. */ LWLockAcquire(pgss->lock, LW_SHARED); entry = (pgssEntry *) hash_search(pgss_hash, &key, HASH_FIND, NULL); if (!entry) { /* Must acquire exclusive lock to add a new entry. */ LWLockRelease(pgss->lock); LWLockAcquire(pgss->lock, LW_EXCLUSIVE); entry = entry_alloc(&key); } /* Grab the spinlock while updating the counters. */ { volatile pgssEntry *e = (volatile pgssEntry *) entry; SpinLockAcquire(&e->mutex); e->counters.calls += 1; e->counters.total_time += total_time; e->counters.rows += rows; e->counters.shared_blks_hit += bufusage->shared_blks_hit; e->counters.shared_blks_read += bufusage->shared_blks_read; e->counters.shared_blks_written += bufusage->shared_blks_written; e->counters.local_blks_hit += bufusage->local_blks_hit; e->counters.local_blks_read += bufusage->local_blks_read; e->counters.local_blks_written += bufusage->local_blks_written; e->counters.temp_blks_read += bufusage->temp_blks_read; e->counters.temp_blks_written += bufusage->temp_blks_written; e->counters.usage += usage; SpinLockRelease(&e->mutex); } LWLockRelease(pgss->lock); }
如果把上述e->counters的各个组成部分和定义,与下面的pg_stat_statements的文档资料对比,可以发现它们完全一致:
http://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.1/static/pgstatstatements.html
/* * Statistics per statement * * NB: see the file read/write code before changing field order here. */ typedef struct pgssEntry { pgssHashKey key; /* hash key of entry - MUST BE FIRST */ Counters counters; /* the statistics for this query */ slock_t mutex; /* protects the counters only */ char query[1]; /* VARIABLE LENGTH ARRAY - MUST BE LAST */ /* Note: the allocated length of query[] is actually pgss->query_size */ } pgssEntry;
/* * The actual stats counters kept within pgssEntry. */ typedef struct Counters { int64 calls; /* # of times executed */ double total_time; /* total execution time in seconds */ int64 rows; /* total # of retrieved or affected rows */ int64 shared_blks_hit; /* # of shared buffer hits */ int64 shared_blks_read; /* # of shared disk blocks read */ int64 shared_blks_written; /* # of shared disk blocks written */ int64 local_blks_hit; /* # of local buffer hits */ int64 local_blks_read; /* # of local disk blocks read */ int64 local_blks_written; /* # of local disk blocks written */ int64 temp_blks_read; /* # of temp blocks read */ int64 temp_blks_written; /* # of temp blocks written */ double usage; /* usage factor */ } Counters;
/* * Hashtable key that defines the identity of a hashtable entry. The * hash comparators do not assume that the query string is null-terminated; * this lets us search for an mbcliplen'd string without copying it first. * * Presently, the query encoding is fully determined by the source database * and so we don't really need it to be in the key. But that might not always * be true. Anyway it's notationally convenient to pass it as part of the key. */ typedef struct pgssHashKey { Oid userid; /* user OID */ Oid dbid; /* database OID */ int encoding; /* query encoding */ int query_len; /* # of valid bytes in query string */ const char *query_ptr; /* query string proper */ } pgssHashKey;
再:看看建立extension时使用的脚本,也是一致的:
CREATE FUNCTION pg_stat_statements( OUT userid oid, OUT dbid oid, OUT query text, OUT calls int8, OUT total_time float8, OUT rows int8, OUT shared_blks_hit int8, OUT shared_blks_read int8, OUT shared_blks_written int8, OUT local_blks_hit int8, OUT local_blks_read int8, OUT local_blks_written int8, OUT temp_blks_read int8, OUT temp_blks_written int8 ) RETURNS SETOF record AS 'MODULE_PATHNAME' LANGUAGE C;
那么,在pg_stat_statements的hook函数中,保存在hash表里的sql文执行信息,是如何通过
类似于 select * from pg_stat_statemens的语句取得的呢?这是因为 此extension的定义和实现:
Datum pg_stat_statements_reset(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS);
Datum pg_stat_statements(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS);
PG_FUNCTION_INFO_V1(pg_stat_statements_reset);
PG_FUNCTION_INFO_V1(pg_stat_statements);
在pg_stat_statements函数中,从hash表中取出了所有数据:
/* * Retrieve statement statistics. */ Datum pg_stat_statements(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS) { ... MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldcontext); LWLockAcquire(pgss->lock, LW_SHARED); hash_seq_init(&hash_seq, pgss_hash); while ( (entry = hash_seq_search(&hash_seq)) != NULL ) { Datum values[PG_STAT_STATEMENTS_COLS]; bool nulls[PG_STAT_STATEMENTS_COLS]; int i = 0; Counters tmp; memset(values, 0, sizeof(values)); memset(nulls, 0, sizeof(nulls)); values[i++] = ObjectIdGetDatum(entry->key.userid); values[i++] = ObjectIdGetDatum(entry->key.dbid); if (is_superuser || entry->key.userid == userid) { char *qstr; qstr = (char *) pg_do_encoding_conversion((unsigned char *) entry->query, entry->key.query_len, entry->key.encoding, GetDatabaseEncoding()); values[i++] = CStringGetTextDatum(qstr); if (qstr != entry->query) pfree(qstr); } else values[i++] = CStringGetTextDatum("<insufficient privilege>"); /* copy counters to a local variable to keep locking time short */ { volatile pgssEntry *e = (volatile pgssEntry *) entry; SpinLockAcquire(&e->mutex); tmp = e->counters; SpinLockRelease(&e->mutex); } values[i++] = Int64GetDatumFast(tmp.calls); values[i++] = Float8GetDatumFast(tmp.total_time); values[i++] = Int64GetDatumFast(tmp.rows); values[i++] = Int64GetDatumFast(tmp.shared_blks_hit); values[i++] = Int64GetDatumFast(tmp.shared_blks_read); values[i++] = Int64GetDatumFast(tmp.shared_blks_written); values[i++] = Int64GetDatumFast(tmp.local_blks_hit); values[i++] = Int64GetDatumFast(tmp.local_blks_read); values[i++] = Int64GetDatumFast(tmp.local_blks_written); values[i++] = Int64GetDatumFast(tmp.temp_blks_read); values[i++] = Int64GetDatumFast(tmp.temp_blks_written); Assert(i == PG_STAT_STATEMENTS_COLS); tuplestore_putvalues(tupstore, tupdesc, values, nulls); } LWLockRelease(pgss->lock); /* clean up and return the tuplestore */ tuplestore_donestoring(tupstore); return (Datum) 0; }
分析到此结束!
回到上一级页面:PostgreSQL内部结构与源代码研究索引页 回到顶级页面:PostgreSQL索引页
磨砺技术珠矶,践行数据之道,追求卓越价值




