Python基础第三天
一、内容

二、练习
练习1
题目:元素分类
有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key的值中,将小于 66 的值保存至字典的第二个key的值中。
图示:
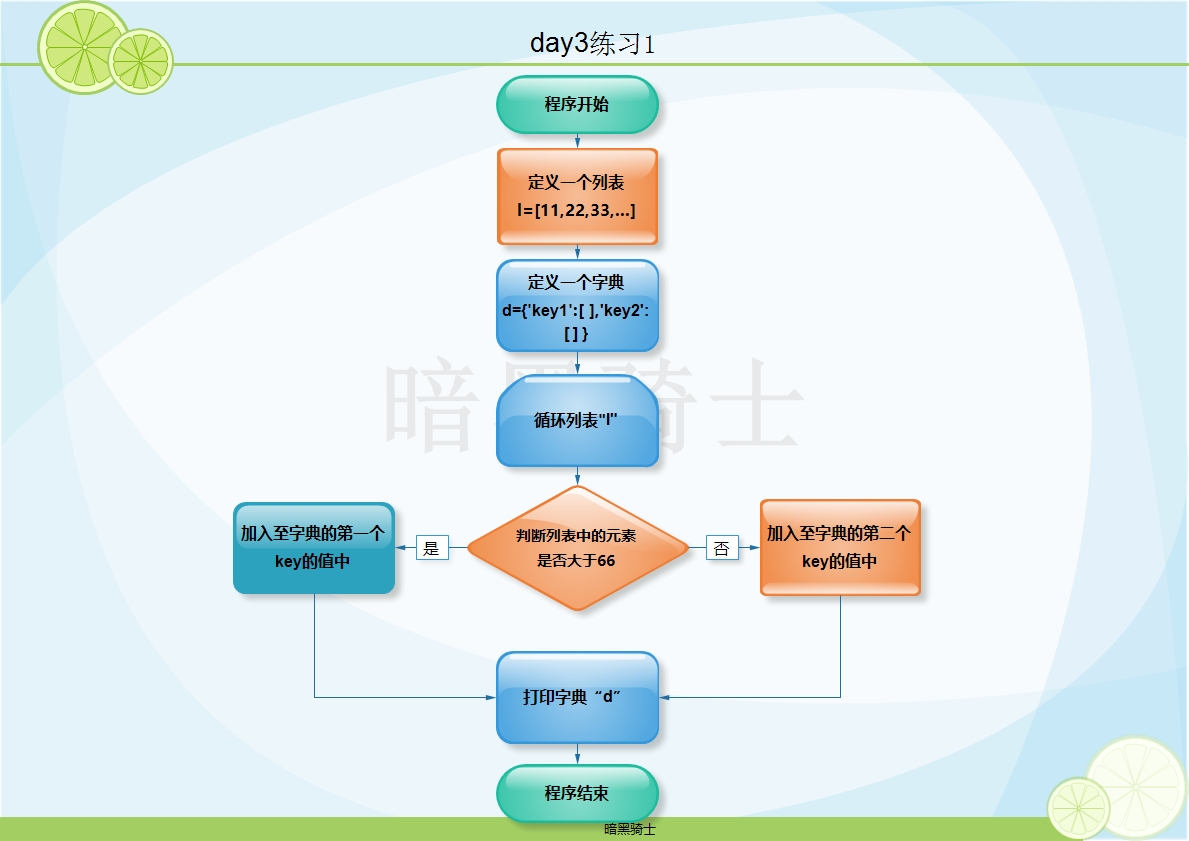
代码:
l = [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]
d = {'key1':[],'key2':[]}
for i in l:
if i > 66:
d['key1'].append(i)
else:
d['key2'].append(i)
print(d)
输出结果:

{'key1': [77, 88, 99, 90], 'key2': [11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66]}
练习2
题目:
查找列表中元素,移除每个元素的空格,并查找以 "k"或"K"开头并且以 "y" 结尾的所有元素。
li = ["kitty", "key", "knight"," Lisa", "sky"]
tu = ("Kitty ", " key", " Knight","Lisa", "xman")
dic = {'k1': " knight", 'k2':' key', "k3": "Knight ", "k4": " Lisa"}
图示:
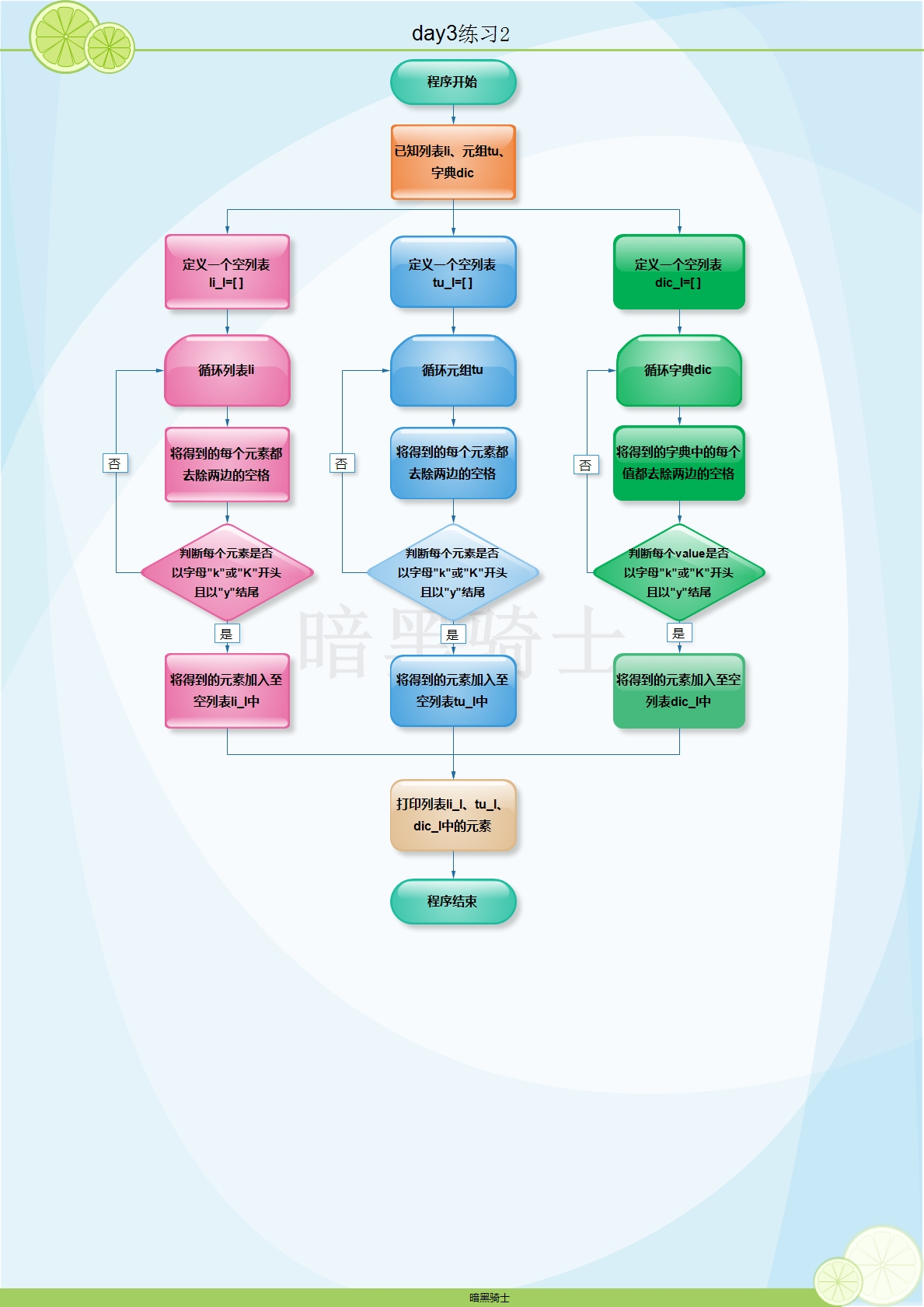
代码:
li = ["kitty", "key", "knight"," Lisa", "sky"]
tu = ("Kitty ", " key", " Knight","Lisa", "xman")
dic = {'k1': " knight", 'k2':' key', "k3": "Knight ", "k4": " Lisa"}
li_l = []
tu_l = []
dic_l = []
for i in li:
i = i.strip()
if i.startswith('k' or 'K') and i.endswith('y'):
li_l.append(i)
for j in tu:
j = j.strip()
# print(j)
if j.startswith('k' or 'K') and j.endswith('y'):
tu_l.append(j)
for k in dic:
value = (dic[k].strip())
if value.startswith('k' or 'K') and i.endswith('y'):
dic_l.append(value)
li_l.extend(tu_l)
dic_l.extend(li_l)
print(dic_l)
输出结果:
['knight', 'key', 'kitty', 'key', 'key']
练习3
题目:输出商品列表,用户输入序号,显示用户选中的商品
li = ["努比亚手机", "小米笔记本", 'iphone X', '苹果笔记本']
说明:
enumerate()内置函数的作用
是python的内置函数
enumerate在字典上是枚举、列举的意思
对于一个可迭代的(iterable)/可遍历的对象(如列表、字符串),enumerate将其组成一个索引序列,利用它可以同时获得索引和值
enumerate多用于在for循环中得到计数
图示:

代码:
li = ["努比亚手机", "小米笔记本", 'iphone X', '苹果笔记本']
for i,v in enumerate(li,1):
print(i,v)
# 其中变量i遍历得到的是序列号
# 其中变量v遍历得到的是列表的每个元素
while True:
user=input('请输入序号:')
if not user.isdigit() or int(user)>4 or int(user)==0:
# 判断用户输入内容的是否不是数字
# 判断用户输入的数字是否大于4
# 判断用户输入的数字是否为0
# 如果满足以上要求则提示用户重新输入,并退出本次循环继续循环
print('请重新输入数字')
continue
print(li[int(user)-1])
# 将用户输入的序号相对应的商品取出来,并打印
注意:
1、列表的索引是从0开始的,而给用户选商品则必须从数字1开始,在使用enumerate()内置函数时,初始的计数就要给数字”1“。
2、isdigit()方法是判断用户输入的内容是否是数字,不包含负数。例如传入一个”-1“时,因为负数占了两个字符了,它会认为是一个”-“和”1“,所以得到的是False
例:
x = input('>>:')
if x.isdigit():
print('OK')
else:
print('not ok')
输出结果:
>>:-1
not ok
3、在打印阶段必须减1,是因数初始计数是从数字1开始的,而列表的取值则是从0开始,所以必须减1
练习4
题目:购物车
功能要求:
用户登陆成功后要求用户输入总资产,例如:20000
显示商品列表,让用户根据序号选择商品,加入购物车
购买,如果商品总额大于总资产,提示账户余额不足,否则,购买成功。
附加:可充值、某商品移除购物车
goods = [
{"name": "努比亚手机", "price": 1499},
{"name": "小米笔记本电脑", "price": 4999},
{"name": "Iphone X", "price": 7999},
{"name": "手机壳", "price": 10},
{"name": "笔记本外壳", "price": 99},
{"name": "苹果笔记本电脑", "price": 11000},
]
代码:
goods = [
{"name": "努比亚手机", "price": 1499},
{"name": "小米笔记本电脑", "price": 4999},
{"name": "Iphone X", "price": 7999},
{"name": "手机壳", "price": 10},
{"name": "笔记本外壳", "price": 99},
{"name": "苹果笔记本电脑", "price": 11000},
]
user = 'knight'
pwd = 'dk123'
j = 1 # 将序列从1开始
b = [] # 用于添加序列,用户的购物车
p = {} # 存放序列和价格
n = {} # 存放序列和商品名
tag = True
while tag:
username = input('Please enter the username:').strip()
password = input('Please enter the password:')
if username == user and password == pwd:
print('Login successfully!')
while True:
user_money = input('Please enter your funds:').strip()
if user_money.isdigit():
user_money = int(user_money)
break
else:
print('Please try again.')
print('********Product List********')
for i in goods:
# print(i) # 得到每件商品的字典形式
print(j,i['name'],i['price']) # 打印序列,打印每件商品的商品名,打印每件商品的价格
p[str(j)] = i['price'] # 为字典p添加商品的价格,key为序列,value为商品的价格
n[str(j)] = i['name'] # 为字典n添加商品的名称,key为序列,value为商品名
j += 1
# print(p)
# # 此时打印p字典得到{'1': 1499, '2': 4999, '3': 7999, '4': 10, '5': 99, '6': 11000}
# print(n)
# # 此时打印n字典得到
# # {'1': '努比亚手机', '2': '小米笔记本电脑', '3': 'Iphone X', '4': '手机壳', '5': '笔记本外壳', '6': '苹果笔记本电脑'}
print('Please select the product code added to your shopping cart(One at a time, press "7" to complete the selection)')
while tag:
user_select = input('Please enter the product code:').strip()
if not user_select in ['1','2','3','4','5','6','7']:
print('Please enter the correct product code')
continue
elif int(user_select) >= 0 and int(user_select) <=6:
b.append(user_select)
continue
elif len(b) == 0:
print('The shopping cart is empty')
continue
elif user_select == '7':
while tag:
print('This is your shopping list:')
if b.count('1') != 0:
print('name:%s number:%s price:%s'%(n['1'],b.count('1'),b.count('1')*p['1']))
if b.count('2') != 0:
print('name:%s number:%s price:%s'%(n['2'],b.count('2'),b.count('2')*p['2']))
if b.count('3') != 0:
print('name:%s number:%s price:%s'%(n['3'],b.count('3'),b.count('3')*p['3']))
if b.count('4') != 0:
print('name:%s number:%s price:%s'%(n['4'],b.count('4'),b.count('4')*p['4']))
if b.count('5') != 0:
print('name:%s number:%s price:%s'%(n['5'],b.count('5'),b.count('5')*p['5']))
if b.count('6') != 0:
print('name:%s number:%s price:%s'%(n['6'],b.count('6'),b.count('6')*p['6']))
s = 0
for i in b:
s = s + p[i] # 此时的s为购买商品后的总价格
if s > user_money:
print('Sorry, your balance is not enough,still need ¥%s RMB,please select again.'%(s-int(user_money)))
while tag:
print('Press "a" to increase the money')
print('Press "d" to delete the product')
print('Press "q" to quit')
print('Press "r" to resubmit')
user_select2 = input('Please select:').strip()
if not user_select2 in ['a','d','q','r']:
print('Please enter again.')
continue
# 用户充值功能
if user_select2 == 'a':
while True:
top_up = input('Please top-up:')
if not top_up.isdigit():
print('Try again')
continue
top_up = int(top_up)
break
user_money = user_money + top_up
break
# 删除商品功能
if user_select2 == 'd':
while True:
print('Your shopping list:')
if b.count('1') != 0 :
print('Number:1 Name:%s Quantity:%s Price:%s' % (n['1'], b.count('1'), b.count('1') * p['1']))
if b.count('2') != 0 :
print('Number:1 Name:%s Quantity:%s Price:%s' % (n['2'], b.count('2'), b.count('2') * p['2']))
if b.count('3') != 0 :
print('Number:1 Name:%s Quantity:%s Price:%s' % (n['3'], b.count('3'), b.count('3') * p['3']))
if b.count('4') != 0 :
print('Number:1 Name:%s Quantity:%s Price:%s' % (n['4'], b.count('4'), b.count('4') * p['4']))
if b.count('5') != 0 :
print('Number:1 Name:%s Quantity:%s Price:%s' % (n['5'], b.count('5'), b.count('5') * p['5']))
if b.count('6') != 0 :
print('Number:1 Name:%s Quantity:%s Price:%s' % (n['6'], b.count('6'), b.count('6') * p['6']))
# 用户输入的钱减去购买商品后的钱。
res1 = int(b.count('1') * p['1'])
res2 = int(b.count('2') * p['2'])
res3 = int(b.count('3') * p['3'])
res4 = int(b.count('4') * p['4'])
res5 = int(b.count('5') * p['5'])
res6 = int(b.count('6') * p['6'])
print('Your balance is ¥%s'%(user_money - res1 -res2 -res3 -res4 -res5 -res6))
while True:
goods_del = input('Please enter the code of the product you intend to delete,(Press "7" to end):').strip()
if not goods_del.isdigit():
print('Try again')
continue
goods_del = int(goods_del)
break
if goods_del == '7':
print('End delete operation')
break
elif not goods_del in ['1','2','3','4','5','6','7'] or not user_money in b:
print('Your shopping cart has no corresponding product!')
continue
elif goods_del >= 0 and goods_del <= 6:
b.remove(goods_del)
continue
# 重新提交功能
if user_select2 == 'r':
break
# 退出功能
if user_money == 'q':
tag = False
tag = False
print('Exit the purchase,Your balance is ¥%s'%user_money)
else:
print('The product was successfully added to the shopping cart,Your balance is ¥%s,'%(user_money - s))
while tag:
user_select3 = input('Press "y" to complete the purchase, continue to buy press "n",y/n:').strip()
if not user_select3 in ['y','n']:
print('Try again!')
continue
if user_select3 == 'y':
tag = False
print('End shopping')
if user_select3 == 'n':
break
tag = False
else:
print('Sorry,the username or password you entered is incorrect,please try again!')
练习5
题目:实现用户交互,显示省市县三级联动的选择
dic = {
"江西": {
"萍乡": ["安源", "彭高", "上栗"],
"新余": ["良山", "新钢", "兴安岭"],
},
"北京": {
"大兴区": ["礼贤镇", "魏善庄镇", "北臧村镇"],
"昌平区": ["沙河", "化庄", "白浮泉"],
},
"福建": {
"莆田": ["荔城", "西天尾", "九华山"],
"厦门": ["湖里", "思明", "海仓"],
}
}
图示:
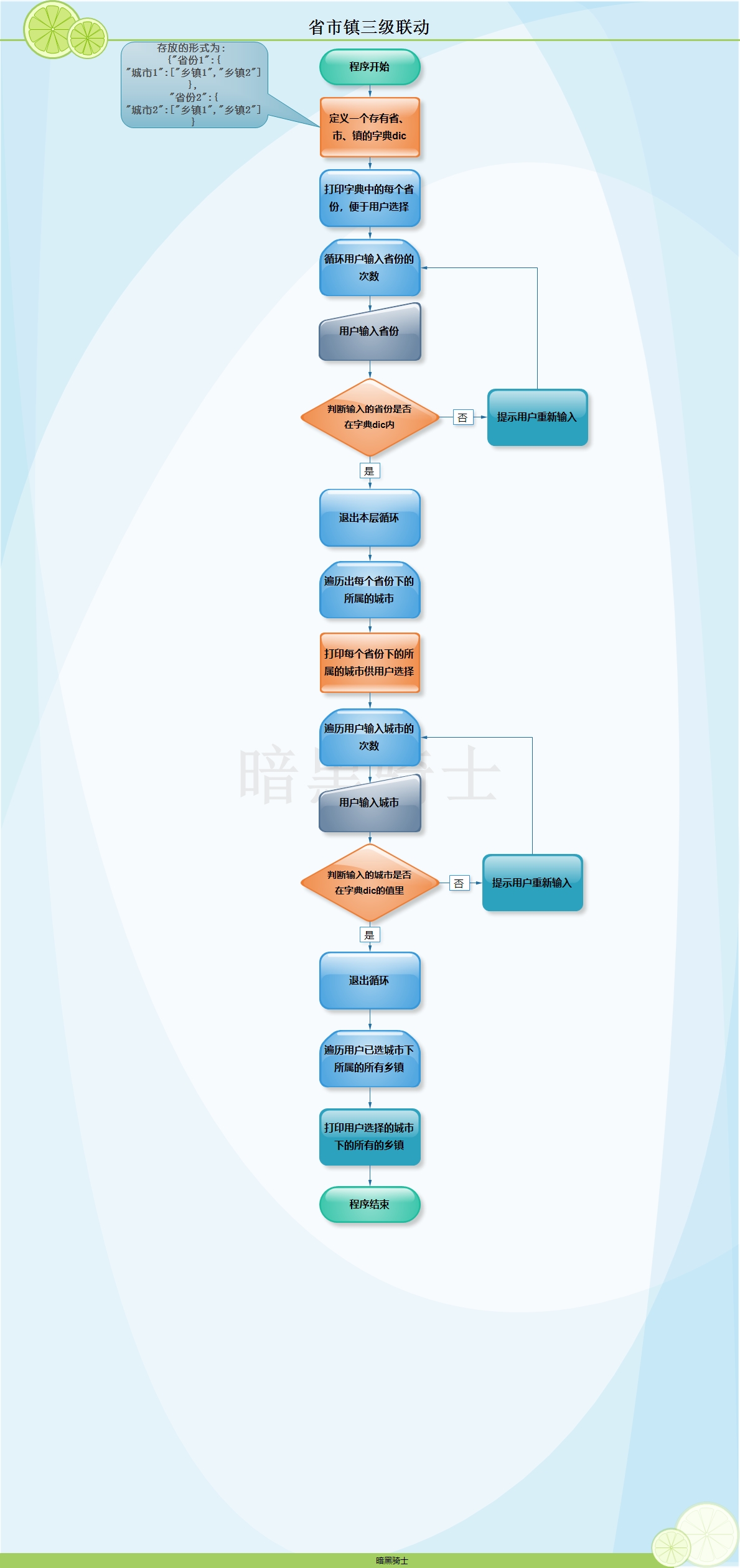
代码:
dic = {
"Jiangxi": {
"Pingxiang": ["Anyuan", "Penggao", "Shangli"],
"Xinyu": ["Liangshan", "Xingang", "Xinganling"],
},
"Peking": {
"Daxing": ["Lixian", "Weishanzhuan", "Beizang"],
"Changping": ["Shahe", "Huazhuang", "Baifuquan"],
},
"Fujian": {
"Putian": ["Zhicheng", "Xitianwei", "Jiuhuashan"],
"Xiamen": ["Huli", "Siming", "Haicang"],
}
}
print('You can check the following cities information:\n*****Jiangxi,Peking,Fujian*****')
# 让用户查询的省份
while True:
province = input('Please select the province:').strip()
if not province in dic:
print('Did not find what you want to search, please re-enter')
continue
break
# 遍历出每个省份中的城市
for i in dic[province]:
print(i,end=' ')
# 让用户查询城市
while True:
city = input('Please select the city:').strip()
if not city in dic[province]:
print('Did not find what you want to search, please re-enter')
continue
break
# 遍历出每个城市中的乡镇
for j in dic[province][city]:
print(j,end=' ')
三、英语
1、str 即string的简写
[strɪŋ] n.字符串
2、int 即integer的简写
['ɪntɪdʒɚ] 整型
3、list
[lɪst] n.列表
4、tuple
[ˈtjʊpəl; ˈtʌpəl] n.元组
5、dict 即dictionaries的简写
['dɪkʃən,ɛriz] n.字典
6、set 即python se的简写t
n.python集合
7、index
['ɪndɛks] n.索引
8、find
[faɪnd] vt.查找
9、append
[ə'pɛnd] vt.附加、添加
10、pop 即popup的简写
v.删除
11、len 即length的简写
n.长度
12、nest
[nɛst] vt.嵌套
13、correct
[kə'rɛkt] adj.正确的
14、disabled
[dɪs'ebld] v.失能
15、incorrect
[,ɪnkə'rɛkt] adj.不正确的


