AutoMapper(六)
返回总目录
List和数组
AutoMapper只要求元素类型的配置而不要求可能会用到的任何数组或者list类型。比如,我们有一个简单的源和目标类型:
public class Source { public int Value { get; set; } }public class Destination
{
public int Value { get; set; }
}
支持所有的基本泛型集合,代码如下:
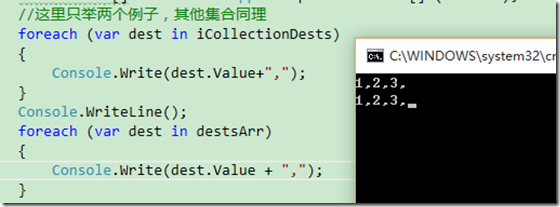
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Mapper.CreateMap<Source, Destination>(); var sources = new[] { new Source() {Value = 1}, new Source() {Value = 2}, new Source() {Value = 3}, }; IEnumerable<Destination> iEnumerableDests= Mapper.Map<IEnumerable<Destination>>(sources); ICollection<Destination> iCollectionDests= Mapper.Map<ICollection<Destination>>(sources); IList<Destination> iListDests= Mapper.Map<IList<Destination>>(sources); List<Destination> listDests= Mapper.Map<List<Destination>>(sources); Destination[] destsArr= Mapper.Map<Destination[]>(sources); //这里只举两个例子,其他集合同理 foreach (var dest in iCollectionDests) { Console.Write(dest.Value+","); } Console.WriteLine(); foreach (var dest in destsArr) { Console.Write(dest.Value + ","); }Console.Read(); }}
以上代码是集合和集合之间的映射,但是映射的配置CreateMap方法中只是配置的是类型之间的映射,而没有设计任何集合类型。
测试结果如下,可见集合之间映射成功:
具体来说,支持的源集合类型包括:
- IEnumerable
- IEnumerable<T>
- ICollection
- ICollection<T>
- IList
- IList<T>
- List<T>
- Arrays
集合中的多态元素类型
很多时候,在我们的源和目标类型中可能有一个类型层次关系。AutoMapper支持多态数组和集合,因此如果发现派生的源或者目标类型,就会使用它们。
public class ParentSource { public int Value1 { get; set; } }public class ChildSource : ParentSource
{
public int Value2 { get; set; }
}public class ParentDestination
{
public int Value1 { get; set; }
}public class ChildDestination : ParentDestination
{
public int Value2 { get; set; }
}
AutoMapper仍然要求显示配置孩子映射,因为它不能“猜出”具体使用哪一个孩子目标映射。
在Main方法中添加如下代码:
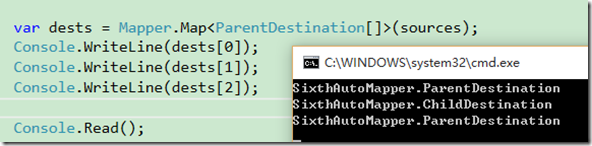
Mapper.Initialize(c => { c.CreateMap<ParentSource, ParentDestination>() .Include<ChildSource, ChildDestination>(); c.CreateMap<ChildSource, ChildDestination>(); }); var sources = new[] { new ParentSource(){Value1 = 11}, new ChildSource(){Value2 = 22}, new ParentSource(), };var dests = Mapper.Map<ParentDestination[]>(sources);
Console.WriteLine(dests[0]);
Console.WriteLine(dests[1]);
Console.WriteLine(dests[2]);
测试结果如下:
上面我们创建了一个源的数组,其中包含两个ParentSource和一个ChildSource,所以两个ParentSource成功地映射到了ParentDestination,而CreateMap配置中,ParentSource到ParentDestination的映射配置包含了ChildSource到ChildDestination的配置,所以执行Mapper.Map<ParentDestination[]>(sources)的时候,也可以将ChildSource映射到ChildDestination。
映射继承
在派生类中标明继承
上面的代码,是在基类中配置继承的,除此之外,也可以在派生类中配置继承:
//在基类中配置继承 Mapper.Initialize(c => { c.CreateMap<ParentSource, ParentDestination>() .Include<ChildSource, ChildDestination>(); c.CreateMap<ChildSource, ChildDestination>(); }); //在派生类中配置继承 Mapper.Initialize(c => { c.CreateMap<ParentSource, ParentDestination>(); c.CreateMap<ChildSource, ChildDestination>() .IncludeBase<ParentSource, ParentDestination>(); });
继承映射属性
这里介绍一下额外的复杂性,因为一个属性映射时可以有多种方式。下面是这些源的优先级:
- 显式映射 (使用.MapFrom())
- 继承的显式映射
- 惯例映射 (通过惯例匹配的属性)
- 忽略的属性映射
下面来演示一下:
这里还是用上面定义的四个类:Order,OrderDto,PCOrder,MobileOrder:
//领域对象 public class Order { } //电脑端订单 public class PCOrder : Order { public string Referrer { get; set; } } //手机订单 public class MobileOrder : Order { }//Dtos
public class OrderDto
{
public string Referrer { get; set; }
}
配置映射的方法使用的是在父类中配置继承映射
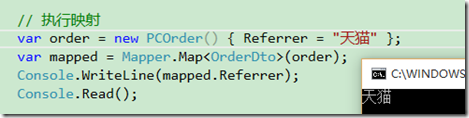
//在父类中配置继承映射 Mapper.CreateMap<Order, OrderDto>() .Include<PCOrder,OrderDto>() .Include<MobileOrder,OrderDto>() .ForMember(o => o.Referrer, m => m.Ignore());//这里配置了忽略目标属性Referrer的映射 Mapper.CreateMap<PCOrder,OrderDto>(); Mapper.CreateMap<MobileOrder, OrderDto>();
// 执行映射 var order = new PCOrder() { Referrer = "天猫" }; var mapped = Mapper.Map<OrderDto>(order); Console.WriteLine(mapped.Referrer);
执行结果如下:
注意在我们的映射配置中,我们已经忽略了Referrer(因为Order基类中不存在这个属性),但是在基类的映射中,惯例比忽略的属性有更高的优先级,因而属性仍然得到了映射。
已将所有赞助者统一放到单独页面!签名处只保留最近10条赞助记录!查看赞助者列表
| 衷心感谢打赏者的厚爱与支持!也感谢点赞和评论的园友的支持! | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 打赏者 | 打赏金额 | 打赏日期 | |
| 微信:匿名 | 10.00 | 2017-08-03 | |
| 微信:匿名 | 10.00 | 2017-08-04 | |
| 微信:匿名 | 5.00 | 2017-06-15 | |
| 支付宝:一个名字499***@qq.com | 5.00 | 2017-06-14 | |
| 微信:匿名 | 16.00 | 2017-04-08 | |
| 支付宝:向京刘 | 10.00 | 2017-04-13 | |
| 微信:匿名 | 10.00 | 2017-003-08 | |
| 微信:匿名 | 5.00 | 2017-03-08 | |
| 支付宝:lll20001155 | 5.00 | 2017-03-03 | |
| 支付宝:她是一个弱女子 | 5.00 | 2017-03-02 | |