DotNET企业架构应用实践 - 用服务定位器(SL)完成服务的多种实现的统一调用
前面的文章服务定位器(SL)与AgileEAS.NET中的实现介绍了服务定位器的一些概念、应用场景与AgileEAS.NET平台中SL的实现,本文是这骗文件的一个例子与Demo,详细的演示SL在应用开发中的使用。
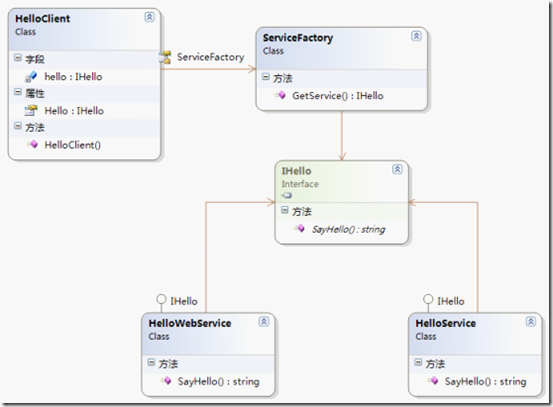
下面我说开始例子,假设有这么一个应用场景,我们需求一个Hello服务,并且需要在XML WebService、.NET Remoting和本地同进程中三种不同环境的应用,也就是说,这个服务可能会有三中实现,具体使用那一个,在应用过程中决定,我先贴个简单的类图:
现在我们来开始干活,一步一步实现这个应用,首先定义服务接口,建一个名称为Hello.Interface的类库项目,定义一个IHello接口:
public interface IHello { string SayHello(string name); }
[WebService(Namespace = "http://tempuri.org/")] [WebServiceBinding(ConformsTo = WsiProfiles.BasicProfile1_1)] [ToolboxItem(false)] public class HelloWebService : System.Web.Services.WebService,Hello.Interface.IHello { [WebMethod] public string SayHello(string name) { return "hello," + name; } }
实现.NET Remoting和LocalComponent,添加一个名称为Hello.Service类库项目,添加一个类Hello:
public string SayHello(string name) { return "hello," + name; }
实现一个简单的.NET Remoting的运行环境,建一个名称为Hello.ServiceConsole的控制台项目:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { TcpChannel channel = new TcpChannel(9001); ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(channel, false); RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownServiceType(typeof(Hello.Service.HelloService), "Hello", WellKnownObjectMode.Singleton); System.Console.ReadLine(); } }
最后完成我们的调用客户端,建一控制台项目Hello.Client,引用Hello.Interface项目和EAS.IOCContainer.dll、EAS.ServiceLocator.dll程序组,定义服务消费者HelloClient:
class HelloClient { IHello hello = null; public HelloClient() { this.hello = ServiceFactory.GetService("HelloService", typeof(IHello)) as IHello; } public IHello Hello { get { return this.hello; } } }
控制台程序入口Program :
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { System.Console.WriteLine(new HelloClient().Hello.SayHello("james")); System.Console.ReadLine(); } }
定义配置文件App.config :
<configuration> <configSections> <section name="EAS.Services" type="EAS.ServiceLocators.ServiceConfigHandler,EAS.ServiceLocator" /> <section name="EAS.Objects" type="EAS.Objects.ConfigHandler,EAS.IOCContainer"/> </configSections> <EAS.Objects> <object name="HelloObject" LifestyleType="Thread" type="Hello.Service.HelloService,Hello.Service" /> </EAS.Objects> <EAS.Services> <Services> <Service name="HelloService" service-type="DotNetRemoting" Singleton=" true" url="tcp://localhost:9001/Hello"/> <!--<Service name="HelloService" service-type="LocalComponent" component="HelloObject" />--> <!--<Service name="HelloService" service-type="WebService" Singleton=" true" url="http://localhost:56824/HelloWebService.asmx"/>--> </Services> </EAS.Services> </configuration>
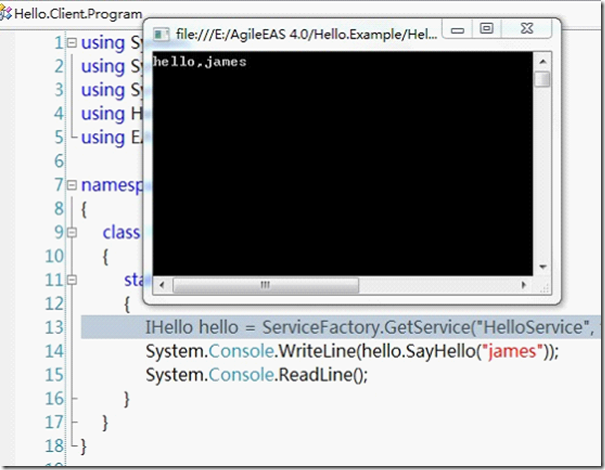
运行客户段,可以看到如下的输入截图:
是不是很简单,在实际应用中,对于这种服务运行环境的未知性,我们可以通过这种简单的方法进行处理,服务消费者只需求知道接口,而无需知道具体的实现,开发人员可以根据客户的不同应用场景而做出不同的实现,上例中的服务定义配置项中,我注释了DotNetRemoting和LocalComponent两种方式的Hello服务,大家可以释放放开其中的一个而注释另外两个用于配置运行。
QQ群:15118502
作者:魏琼东
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/eastjade
关于作者:有13年的软件从业经历,专注于中小软件企业软件开发过程研究,通过在技术与管理帮助中小软件企业实现技术层面开源节流的目的。熟悉需求分析、企业架构、项目管理。现主要从事基于AgileEAS.NET平台的技术咨询工作,主要服务于医疗卫生、铁路、电信、物流、物联网、制造、零售等行业。如有问题或建议,请多多赐教!
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,如有问题,可以通过mail.james@qq.com 联系我,也可以加入QQ群:113723486、199463175、116773358、116773358、212867943、147168308、59827496、193486983、15118502和大家共同讨论,非常感谢。