[Leetcode] Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.

Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].

The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
For example,
Given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3],
return 10.
最笨的办法,暴力算,果然超时了!
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height) { 4 int minHeight; 5 int maxArea = 0, area; 6 for (int i = 0; i < height.size(); ++i) { 7 minHeight = height[i]; 8 for (int j = i; j < height.size(); ++j) { 9 minHeight = (minHeight < height[j]) ? minHeight : height[j]; 10 area = minHeight * (j - i + 1); 11 maxArea = (maxArea > area) ? maxArea : area; 12 } 13 } 14 return maxArea; 15 } 16 };
下面是重点, 可以通过两个栈来保存之前的信息,以减少比较次数,经典就是经典啊。我们要维护两个栈,要注意的是栈中的节点的高度一定是比当前节点小的,若发现height栈顶元素比当前元素大,则要将其出栈,同时计算面积。还有一点要注意的是处理完所有元素后若栈不为空,那么这些元素肯定是从idx延伸到最后的,还要计算其面积。
Actually, we can decrease the complexity by using stack to keep track of the height and start indexes. Compare the current height with previous one.
Case 1: current > previous (top of height stack)
Push current height and index as candidate rectangle start position.
Case 2: current = previous
Ignore.
Case 3: current < previous
Need keep popping out previous heights, and compute the candidate rectangle with height and width (current index - previous index). Push the height and index to stacks.
(Note: it is better use another different example to walk through the steps, and you will understand it better).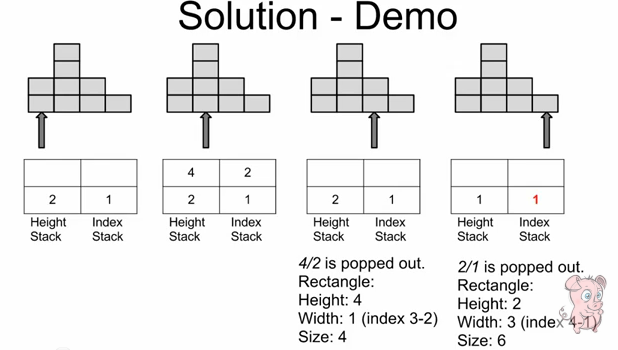
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height) { 4 int n = height.size(); 5 stack<int> stkHeight; 6 stack<int> stkIdx; 7 int maxArea = 0, tmpArea; 8 int tmpHeight, tmpIdx; 9 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 10 if (stkHeight.empty() || height[i] > stkHeight.top()) { 11 stkHeight.push(height[i]); 12 stkIdx.push(i); 13 } 14 else if (height[i] < stkHeight.top()) { 15 //tmpIdx = 0; 16 while (!stkHeight.empty() && height[i] <= stkHeight.top()) { 17 tmpHeight = stkHeight.top(); 18 stkHeight.pop(); 19 tmpIdx = stkIdx.top(); 20 stkIdx.pop(); 21 tmpArea = tmpHeight * (i - tmpIdx); 22 maxArea = (maxArea > tmpArea) ? maxArea : tmpArea; 23 } 24 stkHeight.push(height[i]); 25 stkIdx.push(tmpIdx); 26 } 27 } 28 while (!stkHeight.empty()) { 29 tmpHeight = stkHeight.top(); 30 stkHeight.pop(); 31 tmpIdx = stkIdx.top(); 32 stkIdx.pop(); 33 tmpArea = tmpHeight * (n - tmpIdx); 34 maxArea = (maxArea > tmpArea) ? maxArea : tmpArea; 35 } 36 return maxArea; 37 } 38 };
上面的代码太臃肿了,可以简化如下:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &line) { 4 if (line.size() < 1) return 0; 5 stack<int> S; 6 line.push_back(0); 7 int maxArea = 0, tmpArea; 8 for (int i = 0; i < line.size(); ++i) { 9 if (S.empty() || line[i] > line[S.top()]) { 10 S.push(i); 11 } else { 12 int idx = S.top(); 13 S.pop(); 14 tmpArea = line[idx] * ((S.empty() ? i : i - S.top() - 1)); 15 maxArea = (maxArea > tmpArea) ? maxArea : tmpArea; 16 --i; 17 } 18 } 19 return maxArea; 20 } 21 };




