spring扩展点之一:BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor
一、BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor的区别
BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor都是spring初始化bean的扩展点。两个接口非常相似。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor可以对bean的定义(配置元数据)进行处理。也就是说,Spring IoC容器允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实际实例化任何其它的bean之前读取配置元数据,并有可能修改它。如果你愿意,你可以配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor。你还能通过设置'order'属性来控制BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行次序。
注册BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实例,需要重载void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
通过beanFactory可以获取bean的示例或定义等。同时可以修改bean的属性,这是和BeanPostProcessor最大的区别。
例如:
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("xxBean");
MutablePropertyValues mpv = bd.getPropertyValues();
if(pv.contains("xxName")) {
pv.addPropertyValue("xxName", "icoder");
}
注册BeanPostProcessor的实例,需要重载
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
和
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
还有一点区别就是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的回调比BeanPostProcessor要早。
二、BeanPostProcessors
1、bean生成过程
首先回顾下bean的生命周期如下图:
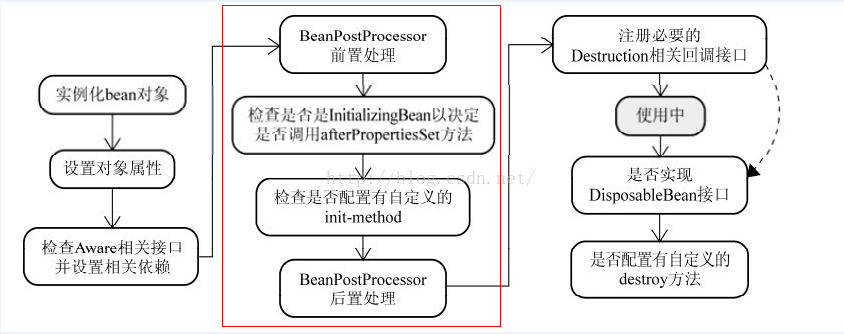
2、BeanPostProcessors接口
public interface BeanPostProcessor { /** * Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean * initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet} * or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values. */ //实例化、依赖注入完毕,在调用显示的初始化之前完成一些定制的初始化任务 Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; /** * Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean * initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet} * or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values. */ //实例化、依赖注入、初始化完毕时执行 Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; }
如果这个接口的某个实现类被注册到某个容器,那么该容器的每个受管Bean在调用初始化方法的前后,都会获得该接口实现类的一个回调。容器调用接口定义的方法时会将该受管Bean的实例和名字通过参数传入方法,进过处理后通过方法的返回值返回给容器。
要使用BeanPostProcessor回调,就必须先在容器中注册实现该接口的类,那么如何注册呢?BeanFactory和ApplicationContext容器的注册方式不大一样:
- 若使用BeanFactory,则必须要显示的调用其addBeanPostProcessor()方法进行注册,参数为BeanPostProcessor实现类的实例;
- 如果是使用ApplicationContext,那么容器会在配置文件在中自动寻找实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的Bean,然后自动注册,我们要做的只是配置一个BeanPostProcessor实现类的Bean就可以了。
假如我们使用了多个的BeanPostProcessor的实现类,那么如何确定处理顺序呢?其实只要实现Ordered接口,设置order属性就可以很轻松的确定不同实现类的处理顺序了。
3、示例
3.1 applicationContext.xml
3.2 自己的业务bean
package com.meituan.hyt.test1; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class User { @Value("老名字") private String name; @Value("50") private Integer id; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", id=" + id + '}'; } }
3.3 postProcessor bean
package com.meituan.hyt.test1; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; public class UserPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException { if(o instanceof User){ User user = (User)o; user.setName("新名字"); user.setId(100); return user; } return o; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException { return o; } }
3.4 测试方法
package com.meituan.hyt.test1; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Main2 { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext cxt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user = (User) cxt.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user.toString()); } }
3.5 执行结果
如果没有<bean id="userPostProcessor" class="com.meituan.hyt.test1.UserPostProcessor"/>
User{name='老名字', id=50}
添加<bean id="userPostProcessor" class="com.meituan.hyt.test1.UserPostProcessor"/>
User{name='新名字', id=100}
4、InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是BeanPostProcessor的子接口

三、与BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的区别
BeanFactoryPostProcessor:允许自定义对ApplicationContext的 bean definitions 进行修饰,扩展功能。
1、实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,会被Application contexts自动发现
2、BeanFactoryPostProcessor 仅仅对 bean definitions 发生关系,不能对bean instances 交互,对bean instances 的交互,由BeanPostProcessor的实现来处理
3、PropertyResourceConfigurer 是一个典型的实现 (PropertyResourceConfigurer是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的一个实现)
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor { /** * Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard * initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans * will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding * properties even to eager-initializing beans. * @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors */ void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; }
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口实现类可以在当前BeanFactory初始化后,bean实例化之前对BeanFactory做一些处理。BeanFactoryPostProcessor是针对于bean容器的,在调用它时,BeanFactory只加载了bean的定义,还没有对它们进行实例化,所以我们可以通过对BeanFactory的处理来达到影响之后实例化bean的效果。跟BeanPostProcessor一样,ApplicationContext也能自动检测和调用容器中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
示例1:
package com.meituan.hyt.test1; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; public class UserBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("BeanFactoryPostProcessor doing"); } }
applicationContext.xml中添加bean配置
<bean id="userBeanFactoryPostProcessor" class="com.meituan.hyt.test1.UserBeanFactoryPostProcessor"/>
BeanFactoryPostProcessor doing
User{name='新名字', id=100}
示例2:
<bean id="user" class="com.gym.UserServiceImpl" > <property name="username" value="${username_}"/> <property name="password" value="${password_}"/> </bean>
spring支持系统对username_进行占位符的配置为properties文件配置,试想如果我们有个配置中心,我们希望spring启动的时候,从远程配置中心取数据,而非本地文件,这里就需要我们自定义一个实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor的PropertyResourceConfigurer 实例。
看下面的例子:
bean.xml配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd" default-autowire="byName"> <bean id="user" class="com.gym.UserServiceImpl" > <property name="username" value="${username_}"/> <property name="password" value="${password_}"/> </bean> <bean id="myFactoryPostProcessor" class="com.gym.MyFilePlaceHolderBeanFactoryPostProcessor"/> </beans>
模拟从远程取文件:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer; import org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertiesLoaderUtils; /** * @author xinchun.wang */ public class MyFilePlaceHolderBeanFactoryPostProcessor extends PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer implements InitializingBean{ public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { List<Properties> list = new ArrayList<Properties>(); Properties p = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties("config.properties"); list.add(p); //这里是关键,这就设置了我们远程取得的List<Properties>列表 setPropertiesArray(list.toArray(new Properties[list.size()])); } }
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService{ private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserServiceImpl.class); public UserServiceImpl(){ logger.info("UserServiceImpl 构造函数 "); } private String username; private String password; public String getUsername() { return username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setUsername(String username) { logger.info("UserServiceImpl setUsername {}",username); this.username = username; } public void setPassword(String password) { logger.info("UserServiceImpl setPassword {}",password); this.password = password; } @Override public String toString() { return "UserServiceImpl [username=" + username + ", password=" + password + "]"; } }
public class TestApplicationContext { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( "classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml"); IUserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(IUserService.class); String password = userService.getPassword(); applicationContext.destroy(); System.out.println(password); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号