敏捷软件开发(1)--- STATE 模式
如果状态在运行过程中,不停的切换和改变,我们怎么办?
状态的迁移是我们生活和工程中非常普遍的一个概念。于是在数学上有一种理论来分析和解决这个问题。
有限状态机理论是一个非常成熟的理论,所有动作和流程的迁移可以归结为状态的迁移。
这个理论的前提是:
状态的数目是确定的,或者说是有限的。
状态的迁移方向是固定的,也就是有向的。
状态存储关于过去的信息,就是说:它反映从系统开始到现在时刻的输入变化。转移指示状态变更,并且用必须满足来确使转移发生的条件来描述它。动作是在给定时刻要进行的活动的描述。有多种类型的动作:
进入动作(entry action):在进入状态时进行
退出动作:在退出状态时进行
输入动作:依赖于当前状态和输入条件进行
转移动作:在进行特定转移时进行
下面我们将按照一个地铁轧机的操作来讲解有线状态机理论。
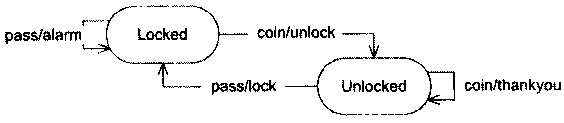
地铁轧机的整体状态图如上。基本就是开和关2种行为。
关于FSM,可以有3种实现方式。
1.switch case方式
package com.joyfulmath.state.switchcase; /** * @author deman.lu * @version on 2016-05-18 09:43 */ public class Turnstile { //status public static final int LOCKED = 0; public static final int UNLOCKED = 1; //events public static final int COIN = 0; public static final int PASS = 1; int state = LOCKED; private TurnstileController turnstileController; public Turnstile(TurnstileController turnstileController) { this.turnstileController = turnstileController; } public void enent(int event) { switch (state) { case LOCKED: switch (event) { case COIN: state = UNLOCKED; turnstileController.unlock(); break; case PASS: turnstileController.alarm(); break; } break; case UNLOCKED: switch (event) { case COIN: turnstileController.thankYou(); break; case PASS: state = LOCKED; turnstileController.lock(); break; } break; } } }
/** * @author deman.lu * @version on 2016-05-18 09:47 */ public interface TurnstileController { void lock(); void unlock(); void alarm(); void thankYou(); }
状态的迁移在switch-case语句里面进行。当前是2种状态 & 2种触发条件。
switch-case 就是2*2 的结果。可以相见,如果情况复杂化,switch-case将呈现爆炸式增长。
2.解释迁移表
该方法在很早以前的C语言中很常见,我个人也经历过这样的代码,并且维护过一段时间。
说句实话,这个东西有点C语言实现面向对象的思想。当然和Java语言没法比较。
package com.joyfulmath.state.switchcase; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author deman.lu * @version on 2016-05-18 10:05 */ public class TurnStyle { int state = Turnstile.LOCKED; TurnstileController turnstileController; List<Transition> mTransitions = new ArrayList<>(); public TurnStyle(final TurnstileController turnstileController) { this.turnstileController = turnstileController; addTransition(Turnstile.LOCKED, Turnstile.COIN, Turnstile.UNLOCKED, new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { turnstileController.unlock(); } }); } private void addTransition(int state, int event, int nextstate, Runnable runnable) { Transition transition = new Transition(); transition.currentState = state; transition.event = event; transition.nextState = nextstate; transition.runnable = runnable; mTransitions.add(transition); } public void event(int event) { for(Transition transition:mTransitions) { if(transition.currentState == state && event == transition.event) { state = transition.nextState; transition.runnable.run(); } } } }
迁移表的维护,有些困难。一点大量状态 & 事件存在,该表将非常复杂。
3.state 模式
好在软件开发中,还有设计模式这个礼物。使用state模式,是目前实现FSM来说,非常适合的一种方式。
package com.joyfulmath.state.statemode; /** * @author deman.lu * @version on 2016-05-18 10:43 */ public interface ITurnstitleState { void coin(TurnsStatus t); void pass(TurnsStatus t); }
这是event事件。
状态的实现:
package com.joyfulmath.state.statemode; /** * @author deman.lu * @version on 2016-05-18 10:52 */ public class LockedStatus implements ITurnstitleState { @Override public void coin(TurnsStatus t) { t.setUnLock(); t.unlock(); } @Override public void pass(TurnsStatus t) { t.alarm(); } }
package com.joyfulmath.state.statemode; /** * @author deman.lu * @version on 2016-05-18 10:53 */ public class UnLockedStatus implements ITurnstitleState { @Override public void coin(TurnsStatus t) { t.thankyou(); } @Override public void pass(TurnsStatus t) { t.setLock(); t.lock(); } }
TurnsStatus是驱动状态迁移的关键。在有些介绍状态模式的书里面,这个类一般定义为context
package com.joyfulmath.state.statemode; import com.joyfulmath.state.switchcase.TurnstileController; /** * @author deman.lu * @version on 2016-05-18 10:52 */ public class TurnsStatus { private static ITurnstitleState lockedStatus = new LockedStatus(); private static ITurnstitleState unlockedStatus = new UnLockedStatus(); private TurnstileController controller; private ITurnstitleState state = lockedStatus; public TurnsStatus(TurnstileController controller) { this.controller = controller; } public void coin() { state.coin(this); } public void pass() { state.pass(this); } public void setLock() { state = lockedStatus; } public void setUnLock() { state = unlockedStatus; } void thankyou() { controller.thankYou(); } void alarm() { controller.alarm(); } void lock() { controller.lock(); } void unlock() { controller.unlock(); } }
其中coin & pass 方法是供外部类进行调用的,而
void unlock() { controller.unlock(); }
这些方法是给state做处理的。
状态模式彻底的分离了状态机的逻辑和动作。
动作在Context类中实现,而逻辑在各个state中实现。
从个人经验来讲,状态模式适合状态会反复切换的场景。
参考:
《敏捷软件开发》 BOb大叔著。
posted on 2016-05-18 11:11 Joyfulmath 阅读(1070) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号