课堂实验
模拟实现Linux下Sort -t : -k 2的功能。参考 Sort的实现。
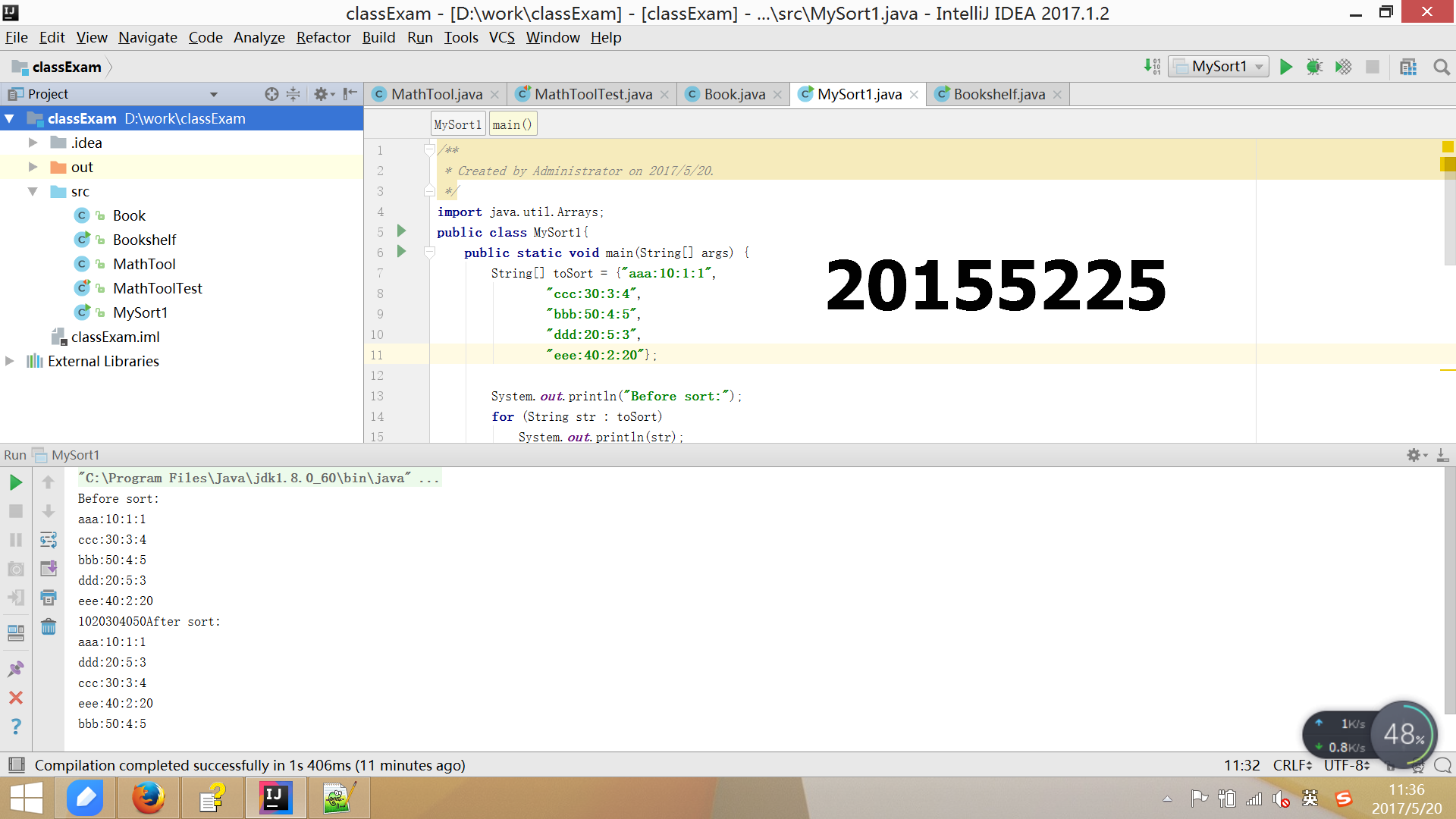
代码如下:
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2017/5/20.
*/
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MySort1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] toSort = {"aaa:10:1:1",
"ccc:30:3:4",
"bbb:50:4:5",
"ddd:20:5:3",
"eee:40:2:20"};
System.out.println("Before sort:");
for (String str : toSort)
System.out.println(str);
int[] tmp=new int [toSort.length];
for(int i=0;i<toSort.length;i++)
{
tmp[i]=Integer.parseInt(toSort[i].split(":")[1]) ;
}
Arrays.sort(tmp);
for (int p : tmp)
System.out.printf("%d",p);
System.out.println("After sort:");
for(int i=0;i<toSort.length;i++)
for(int j=0;j<toSort.length;j++)
if(Integer.parseInt(toSort[j].split(":")[1])==tmp[i])
System.out.println(toSort[j]);
}
}
总结:
tmp[i]=Integer.parseInt(toSort[i].split("😊[1]) ;
排序这句话是核心,依次取字符串数组每个元素,以:分割,取第二行的字符串,再转为int型,再排序。
输出也是一个核心,Integer.parseInt(toSort[j].split("😊[1])==tmp[i];取每个字符串的第二个元素出来与tmp中排好序的元素比对,符合就输出,自然是以temp中排好序的对应顺序输出了!
成果: