jQuery-1.9.1源码分析系列(十五) 动画处理
首先需要有队列(queue)的基本知识。见上一章。
a.动画入口jQuery.fn.animate函数执行流程详解
先根据参数调用jQuery.speed获取动画相关参数,得到一个类似如下的对象;并且生成动画执行函数doAnimation
optall = { complete: fnction(){...},//动画执行完成的回调 duration: 400,//动画执行时长 easing: "swing",//动画效果 queue: "fx",//动画队列 old: false/fnction(){...}, }
var empty = jQuery.isEmptyObject( prop ), optall = jQuery.speed( speed, easing, callback ), doAnimation = function() { //在特征的副本上操作,保证每个特征效果不会被丢失 var anim = Animation( this, jQuery.extend( {}, prop ), optall ); doAnimation.finish = function() { anim.stop( true ); }; //空动画或完成需要立马解决 if ( empty || jQuery._data( this, "finish" ) ) { anim.stop( true ); } }; doAnimation.finish = doAnimation;
没有动画正在执行则马上执行动画,否则将动画压入动画队列等待执行
//没有动画在执行则马上执行动画,否则将动画压入动画队列等待执行 return empty || optall.queue === false ? this.each( doAnimation ) : this.queue( optall.queue, doAnimation );
可以看出,真正执行动画的地方是Animation( this, jQuery.extend( {}, prop ), optall )函数
b. jQuery内部函数Animation详解
Animation ( elem, properties, options ). properties是要进行动画的css特征,options是动画相关选项{complete: function () {…},duration: 400,easing: undefined,old: false,queue: "fx"}。
首先,初始化一个延时对象,这个延时对象用来处理动画队列。
deferred = jQuery.Deferred().always( function() { // don't match elem in the :animated selector delete tick.elem; }),
然后,生成一个每一个时间点(相邻两个时间点的事件间隔默认为13毫秒)上都会执行的函数tick,这个tick函数会保存在jQuery.timers中,然后每次执行jQuery.fx.tick的时候会取出来执行。
tick = function() { if ( stopped ) { return false; } var currentTime = fxNow || createFxNow(), remaining = Math.max( 0, animation.startTime + animation.duration - currentTime ), // archaic crash bug won't allow us to use 1 - ( 0.5 || 0 ) (#12497) temp = remaining / animation.duration || 0, percent = 1 - temp, index = 0, length = animation.tweens.length; //执行动画效果 for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) { animation.tweens[ index ].run( percent ); } //生成进度报告 deferred.notifyWith( elem, [ animation, percent, remaining ]); if ( percent < 1 && length ) { return remaining; } else { //动画执行完毕,执行所有延时队列中的函数(包括清除动画相关的数据) deferred.resolveWith( elem, [ animation ] ); return false; } }
我们看到jQuery对动画进度的处理:
remaining = Math.max( 0, animation.startTime + animation.duration - currentTime )
temp = remaining / animation.duration || 0,
percent = 1 - temp,
进度百分比 = 1 - 剩余时间百分比。
平常我们是这么处理:假设时间13毫秒执行一次动画,当前是第n此执行,总的动画时长为T。那么
进度百分比 = (n*13)/T
实际上这种算法得到的时间n*13是不准确的,因为cpu不只是你一个程序在执行,时间片分给你的时候往往都比n*13大。而且是一个很不准确的值,导致动画感觉时快时慢,不连贯。而jQuery这种方式保证当前的事件点上动画执行结果的准确性,毕竟事件是最新计算结果。
第三,生成动画用的所有特征组成的对象animation(这个对象结构如源码所示),animation.props中保存的是用户传入的特征(动画最终目标)。
animation = deferred.promise({ elem: elem, props: jQuery.extend( {}, properties ), opts: jQuery.extend( true, { specialEasing: {} }, options ), originalProperties: properties, originalOptions: options, startTime: fxNow || createFxNow(), duration: options.duration, tweens: [], createTween: function( prop, end ) { var tween = jQuery.Tween( elem, animation.opts, prop, end, animation.opts.specialEasing[ prop ] || animation.opts.easing ); animation.tweens.push( tween ); return tween; }, stop: function( gotoEnd ) { var index = 0, // if we are going to the end, we want to run all the tweens // otherwise we skip this part length = gotoEnd ? animation.tweens.length : 0; if ( stopped ) { return this; } stopped = true; for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) { animation.tweens[ index ].run( 1 ); } // resolve when we played the last frame // otherwise, reject if ( gotoEnd ) { deferred.resolveWith( elem, [ animation, gotoEnd ] ); } else { deferred.rejectWith( elem, [ animation, gotoEnd ] ); } return this; } })
第四,调用propFilter修正css特征名称以便能被浏览器识别,其中需要注意的是borderWidth/padding/margin指的不是一个css特征,而是四个(上下左右)。
//经过propFilter,animation.opts.specialEasing添加了相应的特征 propFilter( props, animation.opts.specialEasing );
举例说明propFilter修正成果。
例1,css特征{ height: 200 }的修正后结果为:
props = { height: 200 }
animation.opts.specialEasing = {height: undefined}
例2:,css特征{margin:200}的修正结果为:
props = { marginBottom: 200,marginLeft: 200,marginRight: 200,marginTop: 200 }
animation.opts.specialEasing = { marginBottom: undefined,marginLeft: undefined,marginRight: undefined,marginTop: undefined }
第五,调用defaultPrefilter做适配处理:比如对height/width的动画要求display和overflow为特定的值才能有效果;比如对show/hide动画需要对一大堆css特征值进行动画,并且在函数里就调用createTweens生成缓动动画。
// animationPrefilters[0] = defaultPrefilter for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) { result = animationPrefilters[ index ].call( animation, elem, props, animation.opts ); if ( result ) { return result; } }
其中animationPrefilters[ index ]值得函数就是defaultPrefilter,defaultPrefilter函数处理有几个比较重要的地方
defaultPrefilter重点1:内联元素中height/width相关动画需要设置display特征值为inline-block
// height/width overflow pass if ( elem.nodeType === 1 && ( "height" in props || "width" in props ) ) { //确保没有什么偷偷出来 //记录3个overflow相关特征,因为IE不能改变overflow特征值, //当overflowX和overflowY设置了相同的值 opts.overflow = [ style.overflow, style.overflowX, style.overflowY ]; // 内联元素中height/width相关动画需要设置display特征值为inline-block if ( jQuery.css( elem, "display" ) === "inline" && jQuery.css( elem, "float" ) === "none" ) { // 内联元素接受inline-block; // 块级元素必须内嵌在布局上 if ( !jQuery.support.inlineBlockNeedsLayout || css_defaultDisplay( elem.nodeName ) === "inline" ) { style.display = "inline-block"; } else { style.zoom = 1; } } }
defaultPrefilter重点2:对于height/width动画overflow都要设置为"hidden",动画完成后恢复。这个有利于提高渲染速度。
//对于height/width动画overflow都要设置为"hidden",动画完成后恢复 if ( opts.overflow ) { style.overflow = "hidden"; //收缩包装块 if ( !jQuery.support.shrinkWrapBlocks ) { anim.always(function() { style.overflow = opts.overflow[ 0 ]; style.overflowX = opts.overflow[ 1 ]; style.overflowY = opts.overflow[ 2 ]; }); } }
defaultPrefilter重点3:show/hide动画的特殊处理:show/hide动画调用genFx得到形如
props = { height: "hide" marginBottom: "hide" marginLeft: "hide" marginRight: "hide" marginTop: "hide" opacity: "hide" paddingBottom: "hide" paddingLeft: "hide" paddingRight: "hide" paddingTop: "hide" width: "hide" }
需要进行动画处理的特征压入handled列表,并将相应的特征删除,后面会生成相应的缓动动画。
for ( index in props ) { value = props[ index ];
//rfxtypes = /^(?:toggle|show|hide)$/。可以看到最终只有和show/hide的动画才会被饶茹handled中 if ( rfxtypes.exec( value ) ) { delete props[ index ]; toggle = toggle || value === "toggle"; //如果当前节点的状态和指定的状态相同则不需要处理直接进行下一个状态判断 if ( value === ( hidden ? "hide" : "show" ) ) { continue; } handled.push( index ); } } //有需要执行的动画处理则进入分支,里面会对各个特征动画生成缓动动画 length = handled.length; if ( length ) { dataShow = jQuery._data( elem, "fxshow" ) || jQuery._data( elem, "fxshow", {} ); if ( "hidden" in dataShow ) { hidden = dataShow.hidden; } // toggle需要保存状态 - enables .stop().toggle() to "reverse" if ( toggle ) { dataShow.hidden = !hidden; } if ( hidden ) { jQuery( elem ).show(); } else { anim.done(function() { jQuery( elem ).hide(); }); } anim.done(function() { var prop; jQuery._removeData( elem, "fxshow" ); for ( prop in orig ) { jQuery.style( elem, prop, orig[ prop ] ); } }); for ( index = 0 ; index < length ; index++ ) { prop = handled[ index ]; //生成缓动动画 tween = anim.createTween( prop, hidden ? dataShow[ prop ] : 0 ); orig[ prop ] = dataShow[ prop ] || jQuery.style( elem, prop ); if ( !( prop in dataShow ) ) { dataShow[ prop ] = tween.start; if ( hidden ) { tween.end = tween.start; tween.start = prop === "width" || prop === "height" ? 1 : 0; } } } }
第六,生成缓动动画,show/hide在defaultPrefilter函数里面已经处理(上面的源码)。
createTweens( animation, props );
我们来看一看createTweens中具体做了什么,先看一下createTweens之前的animation对象

然后看一下经过createTweens之后的animation对象的tweens数组变成了
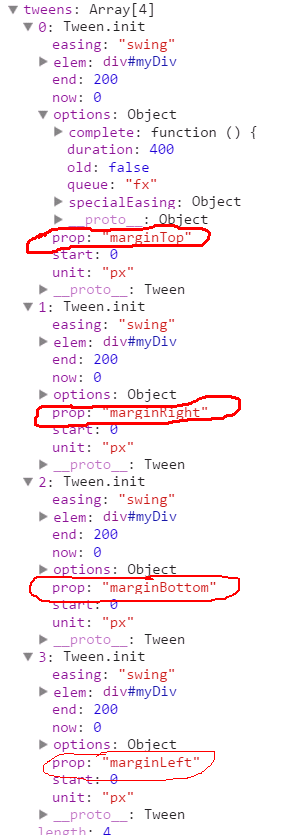
将margin分解成了四个属性(marginTop/Right/Bottom/Left)并且每个属性都有自己的动画特征。
第七,启动动画计时,定时执行tick
//启动动画计时 jQuery.fx.timer( jQuery.extend( tick, { elem: elem, anim: animation, queue: animation.opts.queue }) );
最后,将传入的动画结束回调加入延时队列
//从options中获取回调函数添加到延时队列中 return animation.progress( animation.opts.progress ) .done( animation.opts.done, animation.opts.complete ) .fail( animation.opts.fail ) .always( animation.opts.always );
Animation函数流程到此为止
拓展:
前面提到的genFx函数是专门用在toggle、hide、show时获取相关的需要动画的特征的
最终生成的attrs = { height: "show", marginTop: "show", marginRight: "show",//当includeWidth为false时没有 marginBottom: "show", marginLeft: "show",//当includeWidth为false时没有 opacity: "show", width: "show" }
function genFx( type, includeWidth ) { var which, attrs = { height: type }, i = 0; //如果包括宽度,步长值为1来完成所有cssExpand值, //如果不包括宽度,步长值是2跳过左/右值 //cssExpand = [ "Top", "Right", "Bottom", "Left" ] includeWidth = includeWidth? 1 : 0; for( ; i < 4 ; i += 2 - includeWidth ) { which = cssExpand[ i ]; attrs[ "margin" + which ] = attrs[ "padding" + which ] = type; } if ( includeWidth ) { attrs.opacity = attrs.width = type; } return attrs; }
Animation函数比较复杂,童鞋们可以随便使用例子去跟踪代码。这个是理解jQuery源码的一种比较好的方式。推荐两个例子:
第一个,有hide/show的例子:$("#id").hide(1000);
第二个,其他例子:$("#id").animate({"marginLeft":500},1000);
这一章先到这里,后面一章接着分析。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号