Java有关多态类的小程序
1.使用instanceof运算符判断一个对象是否可以转换为指定的类型:
代码:
public class TestInstanceof { public static void main(String[] args) { //声明hello时使用Object类,则hello的编译类型是Object,Object是所有类的父类 //但hello变量的实际类型是String Object hello = "Hello"; //String是Object类的子类,所以返回true。 System.out.println("字符串是否是Object类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Object)); //返回true。 System.out.println("字符串是否是String类的实例:" + (hello instanceof String)); //返回false。 System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Math)); //String实现了Comparable接口,所以返回true。 System.out.println("字符串是否是Comparable接口的实例:" + (hello instanceof Comparable)); String a = "Hello"; //String类既不是Math类,也不是Math类的父类,所以下面代码编译无法通过 //System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (a instanceof Math)); } }
运行结果:

2.关于类型转换:
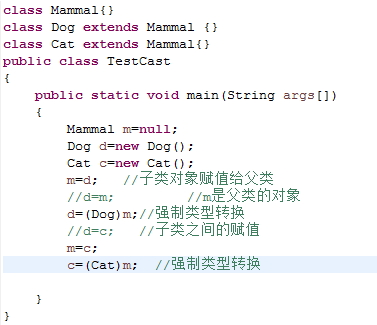
下列语句哪一个将引起编译错误?为什么?哪一个会引起运行时错误?为什么? m=d; d=m; d=(Dog)m; d=c; c=(Cat)m;进行判断并运行结果证明:
d=m;d=c;有错误
程序运行及解释如下图:
3.子类和父类定义同样的函数,运行结果会怎样?
代码示例:
public class ParentChildTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); //父类 parent.printValue(); Child child=new Child(); //子类 child.printValue(); parent=child; parent.printValue(); //调用子类方法 parent.myValue++; //父类变量改变,但已经调用子类方法,仍引用子类变量数据 parent.printValue(); //父类变量的改变不影响输出结果 ((Child)parent).myValue++; //强制类型转换,改变子类变量 parent.printValue(); } }
//子类和父类定义一模一样的字段和方法 class Parent{ public int myValue=100; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } } class Child extends Parent{ public int myValue=200; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } }
输出结果为(原因如程序注释):
Parent.printValue(),myValue=100
Child.printValue(),myValue=200
Child.printValue(),myValue=200
Child.printValue(),myValue=200
Child.printValue(),myValue=201
由此可得Java的一些语法特性(多态):
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
如果子类与父类有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。 如果子类被当作父类使用,则通过子类访问的字段是父类的。
因此,我们进行程序设计时应避免子类与父类同名的字段!
4.多态代码即:当多个类实现同一接口(或派生自同一抽象类)时,针对这些类所创建的对象调用接口所定义的方法时,会分别调用相应的类的具体实现代码。
编译器在编译多态diamante时采用滞后绑定的方法。
使用javap查看编译器为TestPolymorphism.java生成的字节码指令。
程序代码:
class Parent { public int value=100; public void Introduce() { System.out.println("I'm father"); } } class Son extends Parent { public int value=101; public void Introduce() { System.out.println("I'm son"); } } class Daughter extends Parent { public int value=102; public void Introduce() { System.out.println("I'm daughter"); } } public class TestPolymorphism { public static void main(String args[]) { Parent p=new Parent(); p.Introduce(); System.out.println(p.value); p=new Son(); p.Introduce(); System.out.println(p.value); //调用方法改变,对象不变 p=new Daughter(); p.Introduce(); System.out.println(p.value); } }

程序运行结果:

5.在编程中应用多态,可以使我们的代码具有更强的适用性。当需求变化时,多态特性可以帮助我们将需要改动的地方减少到最低限度。 多态编程有两种主要形式:继承多态和接口多态。
使用多态最大的好处是: 当你要修改程序并扩充系统时,你需要修改的地方较少,对其它部分代码的影响较小!千万不要小看这两个“较”字!程序规模越大,其优势就越突出。
6.使用接口代替抽象类(接口多态):
import java.util.Vector; public class Zoo { public static void main(String args[]) { Feeder f = new Feeder("小李"); Vector<Animal> ans = new Vector<Animal>(); ans.add(new Lion()); //饲养员小李喂养一只狮子 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { //饲养员小李喂养十只猴子 ans.add(new Monkey()); } for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { //饲养员小李喂养5只鸽子 ans.add(new Pigeon()); } f.feedAnimals(ans); } } class Feeder { public String name; Feeder(String name) { this.name = name; } public void feedAnimals(Vector<Animal> ans) { for (Animal an : ans) { an.eat(); } } } interface Animal { //用接口代替抽象类 public abstract void eat(); } class Lion implements Animal { //用调用接口代替继承抽象基类 public void eat() { System.out.println("我不吃肉谁敢吃肉!"); } } class Monkey implements Animal { public void eat() { System.out.println("我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。"); } } class Pigeon implements Animal { public void eat() { System.out.println("我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。"); } }
7.用多态的方法模拟ATM机。
多态编程有两种主要形式: (1)继承多态(2)接口多态
(程序仍有错误)
代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Accountduotai extends Account2{ public void input(Account2 account){ int a; String b; int choose; System.out.println("请选择语言:1.汉语;2.英语"+'\n'+"(Please select :1.Chinese;2.English)"); Scanner in =new Scanner(System.in); a=in.nextInt(); //语言 if(a==1) //汉语 { Scanner in1 =new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入密码:"); Scanner in2=new Scanner(System.in); //密码 b=in2.nextLine(); while(b.equals(account.password)){ System.out.println("请选择操作:1.取款;2.存款;3.转账;4.查询余额;5:退卡"); choose=in1.nextInt(); //操作 if(b.equals(account.password)) { if(choose==1)//取款 { System.out.println("请选择:1.100;2.500;3.1500;4.2000;4.5000;5.其他;6.退卡;7.返回"); account.qukuan(account); continue; } else if(choose==2) //存款 { System.out.println("请输入存款金额:"); account.cunkuan(account); } else if(choose==3) //转账 { account.zhuanzhang(account); } /* else if(choose==4) //修改密码 { account.xiugai(null); }*/ else if(choose==4) //查询余额 { //account.chaxun(null); System.out.println("您的余额为:"+account.yue); } else if(choose==5) { System.out.println("请取出您的卡!"); break; } else System.out.println("无此功能"); } } if(!b.equals(account.password)) System.out.println("该卡已被锁定,无法操作!"); } else //英语 { Scanner in1 =new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Please input the password:"); Scanner in2=new Scanner(System.in); //密码 b=in2.nextLine(); while(b.equals(account.password)){ System.out.println("Please select:1.qukuan;2:cunkuan;3.zhuanzhang;4.chauxunyue;5.break"); choose=in1.nextInt(); //操作 if(b.equals(account.password)) { if(choose==1)//取款 { System.out.println("Please select:1.100;2.500;3.1500;4.2000;4.5000;5.else;6:exit;7.return"); account.qukuan(account); } else if(choose==2) //存款 { System.out.println("Please input the save money:"); account.cunkuan(account); } else if(choose==3) //转账 { account.zhuanzhang(account); } /*else if(choose==4) //修改密码 { account.xiugai(null); }*/ else if(choose==4) //查询余额 { //account.chaxun(null); System.out.println("The rest is:"+account.yue); } else if(choose==5) { System.out.println("Take the card away!"); break; } else System.out.println("Without this function"); } } if(!b.equals(account.password)) System.out.println("Wrong!"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Accountduotai A=new Accountduotai(); Account2 account=new Account2(); account.setAccount1("12345678901","20161115","000000",5000); A.input(account); } } abstract class Atm{ public void qukuan() {}; public void cunkuan(){}; public void zhuanzhang(){}; public void chaxun(){}; } class Account2 extends Atm{ String name; String data; String password; int caozuo; double yue; public void setName(String n){name=n;} String getNmae(){return name;} public void setData(String d){data=d;} String getData(){return data;} public void setPassword (String p){password=p;} String getPassword(){return password;} public void setCaozuo (int i){caozuo=i;} int getCaozuo(){return caozuo;} public void setYue(double y){yue=y;} double getYue(){return yue;} public void setAccount1(String string, String string2, String string3, int j) { name=string; data=string2; // caozuo=i; password=string3; yue=j; } /*public void xiugai(Account2 account){ System.out.println("请输入原密码:"); Scanner in7=new Scanner(System.in); String m=in7.nextLine(); if(m.equals(account.password)) { System.out.println("请输入新密码:"); Scanner in8=new Scanner(System.in); String n=in8.nextLine(); account.password=n; System.out.println("修改成功"); } else System.out.println("密码输入错误!"); }*/ /*public void chaxun(Account2 account) { System.out.println("您的余额为:"+account.yue); }*/ public void zhuanzhang(Account2 account) { //Account2 account=new Account2("12345678901","20161115",1,"000000",5000); System.out.println("请输入本人卡号:"); Scanner in6=new Scanner(System.in); String hang=in6.nextLine(); if(hang.equals(account.name)) { System.out.println("转账卡号:"); Scanner in4=new Scanner(System.in); double money=in4.nextDouble(); System.out.println("请输入转账金额:"); Scanner in5=new Scanner(System.in); double zhuan=in5.nextDouble(); account.yue=account.yue-zhuan; System.out.println("转账成功!本身余额为:"+account.yue); } } public void cunkuan(Account2 account) { //Account2 account=new Account2("12345678901","20161115",1,"000000",5000); //System.out.println("请输入存款金额:"); Scanner in3 =new Scanner(System.in); double cun=in3.nextInt(); account.yue=account.yue+cun; System.out.println("本身余额为:"+account.yue); } public void qukuan(Account2 account){ //Account2 account=new Account2("12345678901","20161115",1,"000000",5000); while(true){ //System.out.println("请选择:1.100;2.500;3.1500;4.2000;4.5000;5.其他;6.退卡;7.返回"); int b; Scanner in1=new Scanner(System.in); b=in1.nextInt(); if(b==1) { account.yue=account.yue-100; System.out.println("本身余额为:"+account.yue); } if(b==2) { account.yue=account.yue-500; System.out.println("本身余额为:"+account.yue); } if(b==3) { account.yue=account.yue-1500; System.out.println("本身余额为:"+account.yue); } if(b==4) { account.yue=account.yue-2000; System.out.println("本身余额为:"+account.yue); } else if(b==5) //其他金额 { int c; Scanner in2=new Scanner(System.in); c=in2.nextInt(); account.yue=account.yue-c; System.out.println("本身余额为:"+account.yue); } else if(b==6){ //退卡 System.out.println("请取走您的卡!"); break; } else if(b==7){ //返回 break; } } } }
运行结果:




