一、收集nginx日志
1.部署nginx
[root@linux-host6 ~]# yum install gcc gcc-c++ automake pcre pcre-devel zlip zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel [root@linux-host6 ~]# cd /usr/local/src/ [root@linux-host6 src]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.10.3.tar.gz [root@linux-host6 src]# tar xvf nginx-1.10.3.tar.gz [root@linux-host6 src]# cd nginx-1.10.3 [root@linux-host6 nginx-1.10.3]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx-1.10.3 [root@linux-host6 nginx-1.10.3]# make && make install [root@linux-host6 nginx-1.10.3]# ln -sv /usr/local/nginx-1.10.3 /usr/local/nginx ‘/usr/local/nginx’ -> ‘/usr/local/nginx-1.10.3’
2.编辑配置文件并准备web页面:
[root@linux-host6 nginx-1.10.3]# cd /usr/local/nginx
[root@linux-host6 nginx]# vim conf/nginx.conf
location /web {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
[root@linux-host6 nginx]# mkdir /usr/local/nginx/html/web
[root@linux-host6 nginx]# echo " Nginx WebPage! " > /usr/local/nginx/html/web/index.html
3.测试nginx配置:
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t #测试配置文件语法 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #启动服务 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload #重读配置文件
4.启动nginx并验证:
[root@linux-host6 nginx]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx-1.10.3/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx-1.10.3/conf/nginx.conf test is successful [root@linux-host6 nginx]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx [root@linux-host6 nginx]# lsof -i:80 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME nginx 17719 root 6u IPv4 90721 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN) nginx 17720 nobody 6u IPv4 90721 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
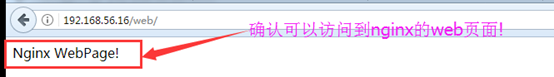
访问nginx页面:
5.将nginx日志转换为json格式:
[root@linux-host6 nginx]# vim conf/nginx.conf
log_format access_json '{"@timestamp":"$time_iso8601",'
'"host":"$server_addr",'
'"clientip":"$remote_addr",'
'"size":$body_bytes_sent,'
'"responsetime":$request_time,'
'"upstreamtime":"$upstream_response_time",'
'"upstreamhost":"$upstream_addr",'
'"http_host":"$host",'
'"url":"$uri",'
'"domain":"$host",'
'"xff":"$http_x_forwarded_for",'
'"referer":"$http_referer",'
'"status":"$status"}';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log access_json;
[root@linux-host6 nginx]# mkdir /var/log/nginx
[root@linux-host6 nginx]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx-1.10.3/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx-1.10.3/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
6.确认日志格式为json:
[root@linux-host6 nginx]# tail /var/log/nginx/access.log # 博主整理了一下,不然太长了
{
"@timestamp":"2017-04-21T17:03:09+08:00",
"host":"192.168.56.16",
"clientip":"192.168.56.1",
"size":0,
"responsetime":0.000,
"upstreamtime":"-",
"upstreamhost":"-",
"http_host":"192.168.56.16",
"url":"/web/index.html",
"domain":"192.168.56.16",
"xff":"-",
"referer":"-",
"status":"304"
}
7.配置logstash收集nginx访问日志:
[root@linux-host6 conf.d]# vim nginx.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/nginx/access.log"
start_position => "end"
type => "nginx-accesslog"
codec => json
}
}
output {
if [type] == "nginx-accesslog" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "logstash-nginx-accesslog-5616-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}}
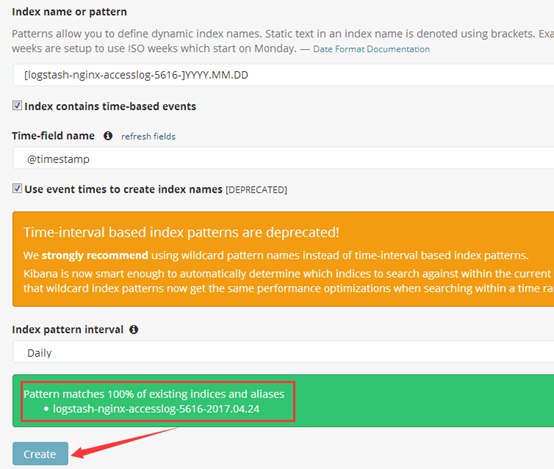
8.kibana界面添加索引:
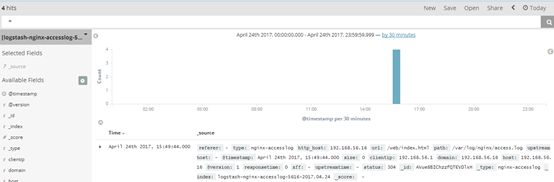
9.kibana界面验证数据:
二、收集TCP/UDP日志
通过logstash的tcp/udp插件收集日志,通常用于在向elasticsearch日志补录丢失的部分日志,可以将丢失的日志通过一个TCP端口直接写入到elasticsearch服务器。
1.logstash配置文件,先进行收集测试:
[root@linux-host6 ~]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/tcp.conf
input {
tcp {
port => 9889
type => "tcplog"
mode => "server"
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
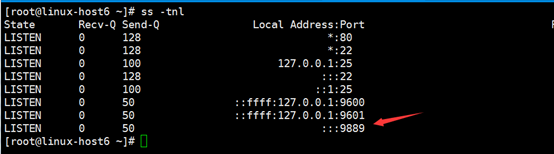
2.验证端口启动成功:
[root@linux-host6 src]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/tcp.conf
在其他服务器安装nc命令:
NetCat简称nc,在网络工具中有“瑞士军刀”美誉,其功能实用,是一个简单、可靠的网络工具,可通过TCP或UDP协议传输读写数据,另外还具有很多其他功能。
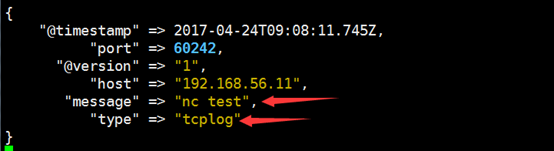
[root@linux-host1 ~]# yum instll nc –y [root@linux-host1 ~]# echo "nc test" | nc 192.168.56.16 9889
3.验证logstash是否接收到数据:
4.通过nc命令发送一个文件:
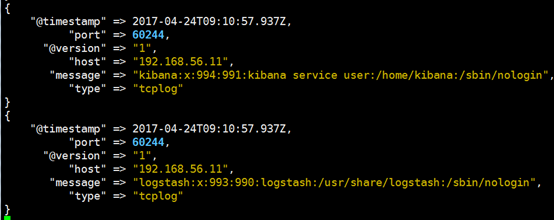
[root@linux-host1 ~]# nc 192.168.56.16 9889 < /etc/passwd
5.logstash验证数据:
6.通过伪设备的方式发送消息:
在类Unix操作系统中,设备节点并不一定要对应物理设备。没有这种对应关系的设备是伪设备。操作系统运用了它们提供的多种功能,tcp只是dev下面众多伪设备当中的一种设备。
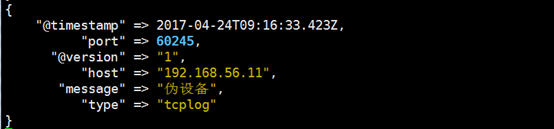
[root@linux-host1 ~]# echo "伪设备" > /dev/tcp/192.168.56.16/9889
7.logstash验证数据:
8.将输出改为elasticsearch:
[root@linux-host6 conf.d]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/tcp.conf
input {
tcp {
port => 9889
type => "tcplog"
mode => "server"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "logstash-tcplog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
[root@linux-host6 conf.d]# systemctl restart logstash
9.通过nc命令或伪设备输入日志:
[root@linux-host1 ~]# echo "伪设备1" > /dev/tcp/192.168.56.16/9889 [root@linux-host1 ~]# echo "伪设备2" > /dev/tcp/192.168.56.16/9889
10.在kibana界面添加索引:
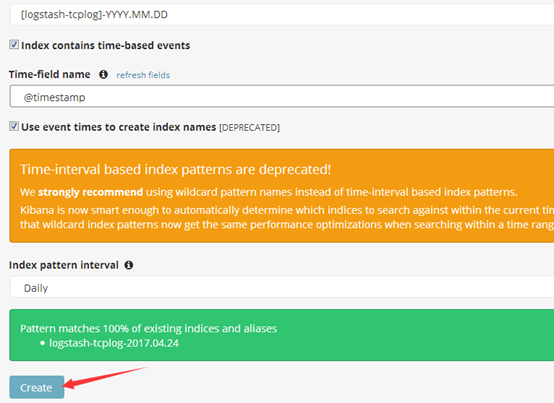
11.验证数据:
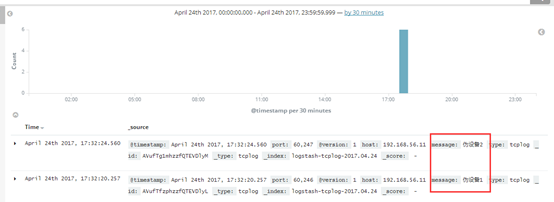
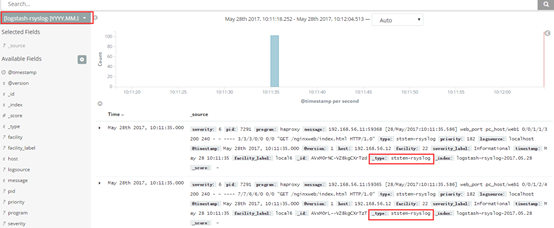
三、通过rsyslog收集haproxy日志。
在centos 6及之前的版本叫做syslog,centos 7开始叫做rsyslog,根据官方的介绍,rsyslog(2013年版本)可以达到每秒转发百万条日志的级别,官方网址:http://www.rsyslog.com/,确认系统安装的版本命令如下:
[root@linux-host1 ~]# yum list syslog Installed Packages rsyslog.x86_64 7.4.7-12.el7
1.编译安装配置haproxy:
[root@linux-host2 ~]# cd /usr/local/src/
[root@linux-host2 src]# wget http://www.haproxy.org/download/1.7/src/haproxy-1.7.5.tar.gz
[root@linux-host2 src]# tar xvf haproxy-1.7.5.tar.gz
[root@linux-host2 src]# cd haproxy-1.7.5
[root@linux-host2 src]# yum install gcc pcre pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel -y [root@linux-host2 haproxy-1.7.5]#make TARGET=linux2628 USE_PCRE=1 USE_OPENSSL=1 USE_ZLIB=1 PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxy
[root@linux-host2 haproxy-1.7.5]# make install PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxy
[root@linux-host2 haproxy-1.7.5]# /usr/local/haproxy/sbin/haproxy -v #确认版本
HA-Proxy version 1.7.5 2017/04/03
Copyright 2000-2017 Willy Tarreau <willy@haproxy.org
准备启动脚步:
[root@linux-host2 haproxy-1.7.5]# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/haproxy.service
[Unit]
Description=HAProxy Load Balancer
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
EnvironmentFile=/etc/sysconfig/haproxy
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/haproxy-systemd-wrapper -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg -p /run/haproxy.pid $OPTIONS
ExecReload=/bin/kill -USR2 $MAINPID
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[root@linux-host2 haproxy-1.7.5]# cp /usr/local/src/haproxy-1.7.5/haproxy-systemd-wrapper /usr/sbin/
[root@linux-host2 haproxy-1.7.5]# cp /usr/local/src/haproxy-1.7.5/haproxy /usr/sbin/
[root@linux-host2 haproxy-1.7.5]# vim /etc/sysconfig/haproxy #系统级配置文件
# Add extra options to the haproxy daemon here. This can be useful for
# specifying multiple configuration files with multiple -f options.
# See haproxy(1) for a complete list of options.
OPTIONS=""
[root@linux-host2 haproxy-1.7.5]# mkdir /etc/haproxy
[root@linux-host2 haproxy-1.7.5]# cat /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
global
maxconn 100000
chroot /usr/local/haproxy
uid 99
gid 99
daemon
nbproc 1
pidfile /usr/local/haproxy/run/haproxy.pid
log 127.0.0.1 local6 info
defaults
option http-keep-alive
option forwardfor
maxconn 100000
mode http
timeout connect 300000ms
timeout client 300000ms
timeout server 300000ms
listen stats
mode http
bind 0.0.0.0:9999
stats enable
log global
stats uri /haproxy-status
stats auth haadmin:123456
#frontend web_port
frontend web_port
bind 0.0.0.0:80
mode http
option httplog
log global
option forwardfor
###################ACL Setting##########################
acl pc hdr_dom(host) -i www.elk.com
acl mobile hdr_dom(host) -i m.elk.com
###################USE ACL##############################
use_backend pc_host if pc
use_backend mobile_host if mobile
########################################################
backend pc_host
mode http
option httplog
balance source
server web1 192.168.56.11:80 check inter 2000 rise 3 fall 2 weight 1
backend mobile_host
mode http
option httplog
balance source
server web1 192.168.56.11:80 check inter 2000 rise 3 fall 2 weight 1
2.编辑rsyslog服务配置文件
$ModLoad imudp $UDPServerRun 514 $ModLoad imtcp $InputTCPServerRun 514 #去掉15/16/19/20行前面的注释 local6.* @@192.168.56.11:5160 #最后面一行添加,local6对应haproxy配置文件定义的local级别
3.重新启动haproxy和rsyslog服务
[root@linux-host2 ~]# systemctl enable haproxy [root@linux-host2 ~]# systemctl restart haproxy [root@linux-host2 ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog
4.验证haproxy端口及服务
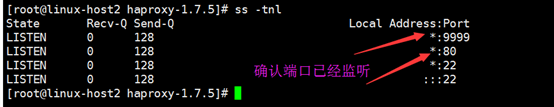
确认服务进程已经存在:
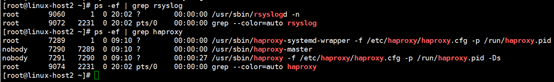
更改本地host文件
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc 192.168.56.12 www.elk.com 192.168.56.12 m.elk.com
测试域名及访问
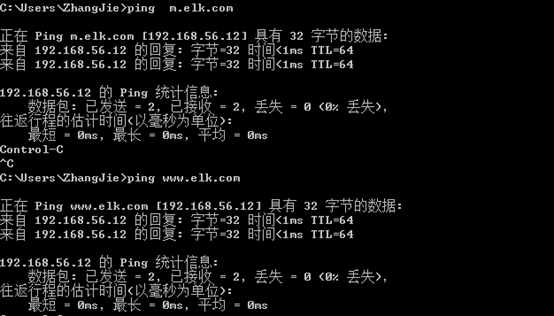
启动后端web服务器的nginx:
[root@linux-host1 ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
确认可以访问到nginx的web界面:
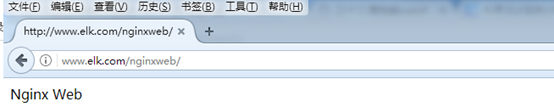
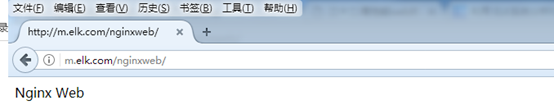
5.编辑logstash配置文件
配置logstash监听一个本地端口作为日志输入源,haproxy服务器的rsyslog输出IP和端口要等同于logstash服务器监听的IP:端口,本次的配置是在Host1上开启logstash,在Host2上收集haproxy的访问日志并转发至Host1服务器的logstash进行处理,logstash的配置文件如下:
[root@linux-host1 conf.d]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/rsyslog.conf
input{
syslog {
type => "system-rsyslog-haproxy5612"
port => "5160" #监听一个本地的端口
}}
output{
stdout{
codec => rubydebug
}}
6.通过-f命令测试logstash
[root@linux-host1 conf.d]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/rsyslog.conf
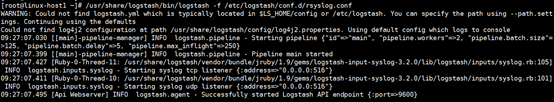
7.web访问haproxy并验证数据
添加本地解析:
[root@linux-host1 ~]# tail –n2 /etc/hosts 192.168.56.12 www.elk.com 192.168.56.12 m.elk.com [root@linux-host1 ~]# curl http://www.elk.com/nginxweb/index.html
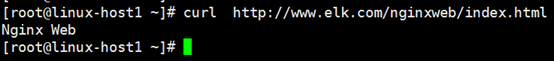
8.访问haproxy管理界面
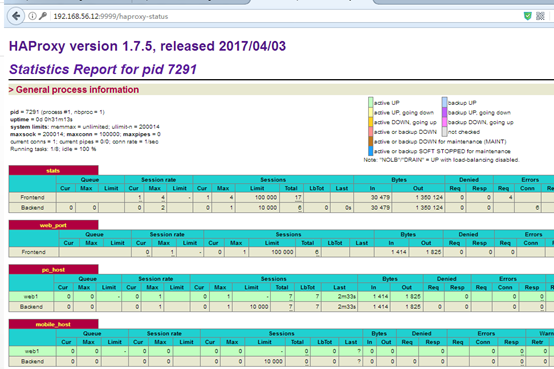
9.haproxy管理界面
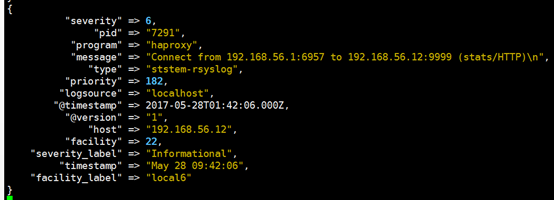
10.验证logstash输出
11.将输出改为elasticsearch
[root@linux-host1 conf.d]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/rsyslog.conf
input{
syslog {
type => "ststem-rsyslog"
port => "516"
}}
output{
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "logstash-rsyslog-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
[root@linux-host6 conf.d]# systemctl restart logstash
12.web访问haproxy以生成新日志
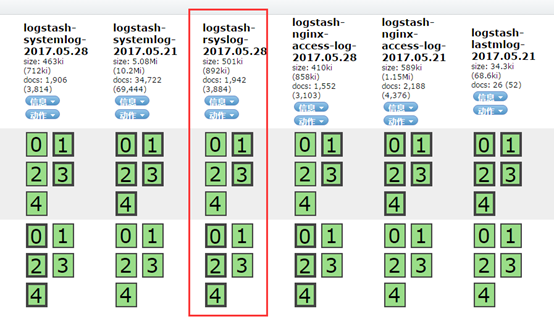
访问head插件以确认生成index:
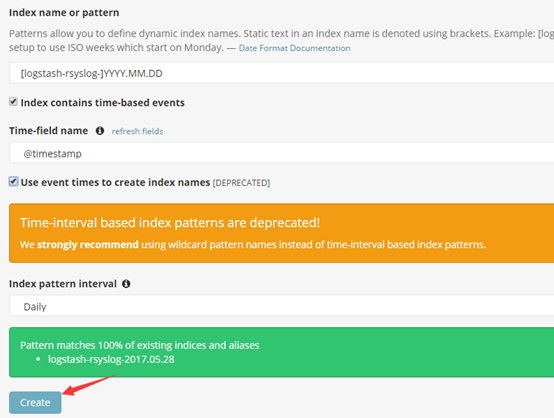
13.kibana界面添加索引
14.kibana验证数据