CSharpGL(6)在OpenGL中绘制UI元素
CSharpGL(6)在OpenGL中绘制UI元素
2016-08-13
由于CSharpGL一直在更新,现在这个教程已经不适用最新的代码了。CSharpGL源码中包含10多个独立的Demo,更适合入门参考。
为了尽可能提升渲染效率,CSharpGL是面向Shader的,因此稍有难度。
主要内容
学习使用IUILayout接口及其机制,以实现在OpenGL中绘制UI元素。
以SimpleUIAxis为例演示如何使用IUILayout。
下载
您可以在(https://github.com/bitzhuwei/CSharpGL)找到最新的源码。欢迎感兴趣的同学fork之。
什么是OpenGL中的UI元素
您可以在源码中找到SimpleUIAxis这一示例。
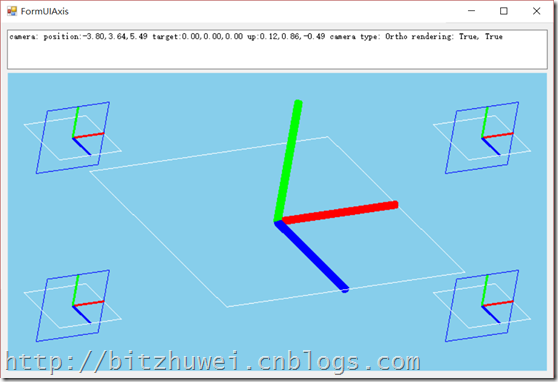
如上图所示,有5个坐标轴,中间那个是一个普通的三维模型(元素),作为对照。
四个角上各有一个坐标轴,这四个坐标轴的位置是绑定到窗口对应的边的,即会随着窗口的缩放自动调整位置,就想Winform里的Control一样。这样的元素就称为OpenGL里的UI元素。
上面那个UI元素是立体的,一般我们在Winform里常见的UI都是二维的,像下面这个色标条一样。当然了,如果我们能实现上图中的三维的UI元素,自然就能实现二维的UI元素了。
IUILayout机制
接口
为实现UI元素,我的思路是:设计一个接口IUILayout,让那些应当作为UI元素布局的元素实现此接口,之后就可以通过简单地调用IUILayout的扩展方法来实现UI布局。
1 /// <summary>
2 /// 实现在OpenGL窗口中的UI布局
3 /// </summary>
4 public interface IUILayout
5 {
6 IUILayoutParam Param { get; set; }
7 }
一个UI元素,需要哪些参数呢?它需要知道它应绑定到窗口的上下左右哪边;需要知道其长度是固定的还是随窗口变化的;需要知道它是否应显示在所有元素的最前方(即不被其他元素覆盖)。
1 public struct IUILayoutParam
2 {
3
4 /// <summary>
5 /// the edges of the <see cref="GLCanvas"/> to which a UI’s rect is bound and determines how it is resized with its parent.
6 /// <para>something like AnchorStyles.Left | AnchorStyles.Bottom.</para>
7 /// </summary>
8 public System.Windows.Forms.AnchorStyles Anchor;
9
10 /// <summary>
11 /// Gets or sets the space between viewport and SimpleRect.
12 /// </summary>
13 public System.Windows.Forms.Padding Margin;
14
15 /// <summary>
16 /// Stores width when <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.Left & <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.Right is <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.None.
17 /// <para> and height when <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.Top & <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.Bottom is <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.None.</para>
18 /// </summary>
19 public System.Drawing.Size Size;
20
21 public int zNear;
22
23 public int zFar;
24
25 public IUILayoutParam(AnchorStyles anchorStyle, Padding padding, System.Drawing.Size size,
26 int zNear = -1000, int zFar = 1000)
27 {
28 // TODO: Complete member initialization
29 this.Anchor = anchorStyle;
30 this.Margin = padding;
31 this.Size = size;
32 this.zNear = zNear;
33 this.zFar = zFar;
34 }
35
36 }
熟悉Winform里控件的同学,一定常用Control.Anchor属性、Padding属性和Control.Size属性,这里我们完全借用了Winform现成的这三个数据结构。我希望这样能方便理解。
实现
实现UI布局的根本问题就是得到一个特殊的变换矩阵,能够让指定元素在窗口的固定位置显示(根据其UIParam值)。这个变换矩阵的计算过程有点长,其思路就是根据viewpoint大小和UI元素的布局设定(UIParam值),计算其应有的宽高及其在ortho()或perspective()中应有的参数。

1 public static class IUILayoutHelper
2 {
3 /// <summary>
4 /// 获取此UI元素的投影矩阵、视图矩阵和模型矩阵
5 /// </summary>
6 /// <param name="uiElement"></param>
7 /// <param name="projectionMatrix"></param>
8 /// <param name="viewMatrix"></param>
9 /// <param name="modelMatrix"></param>
10 /// <param name="camera">如果为null,会以glm.lookAt(new vec3(0, 0, 1), new vec3(0, 0, 0), new vec3(0, 1, 0))计算默认值。</param>
11 /// <param name="maxDepth">UI元素的外接球半径的倍数。</param>
12 public static void GetMatrix(this IUILayout uiElement,
13 out mat4 projectionMatrix, out mat4 viewMatrix, out mat4 modelMatrix,
14 IViewCamera camera = null, float maxDepth = 2.0f)
15 {
16 IUILayoutArgs args = uiElement.GetArgs();
17 float max = (float)Math.Max(args.UIWidth, args.UIHeight);
18
19 {
20 //projectionMatrix = glm.ortho((float)args.left, (float)args.right, (float)args.bottom, (float)args.top,
21 // TODO: / 2后与legacy opengl的UI元素显示就完全一致了。为什么???
22 projectionMatrix = glm.ortho((float)args.left / 2, (float)args.right / 2, (float)args.bottom / 2, (float)args.top / 2,
23 uiElement.Param.zNear, uiElement.Param.zFar);
24 // 下面注释掉的代码是用来测试legacy OpenGL的matrix与GLM库计算的matrix是否相同用的。已经证明了两者完全相同,此处仅作留念+以防万一。
25 //{
26 // float[] matrix = new float[16];
27
28 // GL.MatrixMode(GL.GL_PROJECTION);
29 // GL.PushMatrix();
30 // GL.GetFloat(GetTarget.ProjectionMatrix, matrix);
31
32 // GL.LoadIdentity();
33 // GL.GetFloat(GetTarget.ProjectionMatrix, matrix);
34
35 // GL.Ortho(args.left / 2, args.right / 2, args.bottom / 2, args.top / 2, uiElement.Param.zNear, uiElement.Param.zFar);
36 // GL.GetFloat(GetTarget.ProjectionMatrix, matrix);// this equals projectionMatrix
37
38 // GL.PopMatrix();
39 //}
40 // 把UI元素移到ortho长方体的最靠近camera的地方,这样就可以把UI元素放到OpenGL最前方。
41 projectionMatrix = glm.translate(projectionMatrix, new vec3(0, 0, uiElement.Param.zFar - max / 2 * maxDepth));
42 }
43 {
44 // UI元素不在三维场景中,所以其Camera可以是null。
45 if (camera == null)
46 {
47 //viewMatrix = glm.lookAt(new vec3(0, 0, 1), new vec3(0, 0, 0), new vec3(0, 1, 0));
48 viewMatrix = glm.lookAt(
49 Camera.defaultPosition,
50 Camera.defaultTarget,
51 Camera.defaultUpVector);
52 }
53 else
54 {
55 vec3 position = camera.Position - camera.Target;
56 position.Normalize();
57 viewMatrix = glm.lookAt(position, new vec3(0, 0, 0), camera.UpVector);
58 }
59 // 下面注释掉的代码是用来测试legacy OpenGL的matrix与GLM库计算的matrix是否相同用的。已经证明了两者完全相同,此处仅作留念+以防万一。
60 //{
61 // float[] matrix = new float[16];
62
63 // GL.MatrixMode(GL.GL_MODELVIEW);
64 // GL.PushMatrix();
65 // GL.GetFloat(GetTarget.ModelviewMatix, matrix);
66
67 // GL.LoadIdentity();
68 // GL.GetFloat(GetTarget.ModelviewMatix, matrix);
69
70 // if(camera==null)
71 // {
72 // GL.gluLookAt(0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0);
73 // }
74 // else
75 // {
76 // vec3 position = camera.Position - camera.Target;
77 // position.Normalize();
78 // GL.gluLookAt(position.x, position.y, position.z, 0, 0, 0, camera.UpVector.x, camera.UpVector.y, camera.UpVector.z);
79 // }
80 // GL.GetFloat(GetTarget.ModelviewMatix, matrix);// this equals viewMatrix
81
82 // GL.PopMatrix();
83 //}
84 }
85 {
86 modelMatrix = glm.scale(mat4.identity(), new vec3(args.UIWidth / 2, args.UIHeight / 2, max / 2));
87 // 下面注释掉的代码是用来测试legacy OpenGL的matrix与GLM库计算的matrix是否相同用的。已经证明了两者完全相同,此处仅作留念+以防万一。
88 //{
89 // float[] matrix = new float[16];
90
91 // GL.MatrixMode(GL.GL_MODELVIEW);
92 // GL.PushMatrix();
93 // GL.GetFloat(GetTarget.ModelviewMatix, matrix);
94
95 // GL.LoadIdentity();
96 // GL.GetFloat(GetTarget.ModelviewMatix, matrix);
97
98 // GL.Scale(args.UIWidth / 2, args.UIHeight / 2, max / 2);
99 // GL.GetFloat(GetTarget.ModelviewMatix, matrix);// this equals modelMatrix
100
101 // GL.PopMatrix();
102 //}
103 }
104 }
105
106
107 /// <summary>
108 /// leftRightAnchor = (AnchorStyles.Left | AnchorStyles.Right);
109 /// </summary>
110 const AnchorStyles leftRightAnchor = (AnchorStyles.Left | AnchorStyles.Right);
111
112 /// <summary>
113 /// topBottomAnchor = (AnchorStyles.Top | AnchorStyles.Bottom);
114 /// </summary>
115 const AnchorStyles topBottomAnchor = (AnchorStyles.Top | AnchorStyles.Bottom);
116
117 /// <summary>
118 /// 获取为UI元素布局所需的参数对象。
119 /// </summary>
120 /// <param name="uiElement"></param>
121 /// <returns></returns>
122 public static IUILayoutArgs GetArgs(this IUILayout uiElement)
123 {
124 var args = new IUILayoutArgs();
125
126 CalculateViewport(args);
127
128 CalculateCoords(uiElement, args.viewportWidth, args.viewportHeight, args);
129
130 return args;
131 }
132
133 /// <summary>
134 /// 计算opengl画布的大小。
135 /// </summary>
136 /// <param name="args"></param>
137 static void CalculateViewport(IUILayoutArgs args)
138 {
139 int[] viewport = new int[4];
140 GL.GetInteger(GetTarget.Viewport, viewport);
141 args.viewportWidth = viewport[2];
142 args.viewportHeight = viewport[3];
143 }
144
145 /// <summary>
146 /// 根据UI元素的布局设定,计算其应有的宽高及其在ortho()中应有的参数。
147 /// </summary>
148 /// <param name="uiElement"></param>
149 /// <param name="viewportWidth"></param>
150 /// <param name="viewportHeight"></param>
151 /// <param name="args"></param>
152 static void CalculateCoords(IUILayout uiElement, int viewportWidth, int viewportHeight, IUILayoutArgs args)
153 {
154 IUILayoutParam param = uiElement.Param;
155
156 if ((param.Anchor & leftRightAnchor) == leftRightAnchor)
157 {
158 args.UIWidth = viewportWidth - param.Margin.Left - param.Margin.Right;
159 if (args.UIWidth < 0) { args.UIWidth = 0; }
160 }
161 else
162 {
163 args.UIWidth = param.Size.Width;
164 }
165
166 if ((param.Anchor & topBottomAnchor) == topBottomAnchor)
167 {
168 args.UIHeight = viewportHeight - param.Margin.Top - param.Margin.Bottom;
169 if (args.UIHeight < 0) { args.UIHeight = 0; }
170 }
171 else
172 {
173 args.UIHeight = param.Size.Height;
174 }
175
176 if ((param.Anchor & leftRightAnchor) == AnchorStyles.None)
177 {
178 args.left = -(args.UIWidth / 2
179 + (viewportWidth - args.UIWidth)
180 * ((double)param.Margin.Left / (double)(param.Margin.Left + param.Margin.Right)));
181 }
182 else if ((param.Anchor & leftRightAnchor) == AnchorStyles.Left)
183 {
184 args.left = -(args.UIWidth / 2 + param.Margin.Left);
185 }
186 else if ((param.Anchor & leftRightAnchor) == AnchorStyles.Right)
187 {
188 args.left = -(viewportWidth - args.UIWidth / 2 - param.Margin.Right);
189 }
190 else // if ((Anchor & leftRightAnchor) == leftRightAnchor)
191 {
192 args.left = -(args.UIWidth / 2 + param.Margin.Left);
193 }
194
195 if ((param.Anchor & topBottomAnchor) == AnchorStyles.None)
196 {
197 args.bottom = -viewportHeight / 2;
198 args.bottom = -(args.UIHeight / 2
199 + (viewportHeight - args.UIHeight)
200 * ((double)param.Margin.Bottom / (double)(param.Margin.Bottom + param.Margin.Top)));
201 }
202 else if ((param.Anchor & topBottomAnchor) == AnchorStyles.Bottom)
203 {
204 args.bottom = -(args.UIHeight / 2 + param.Margin.Bottom);
205 }
206 else if ((param.Anchor & topBottomAnchor) == AnchorStyles.Top)
207 {
208 args.bottom = -(viewportHeight - args.UIHeight / 2 - param.Margin.Top);
209 }
210 else // if ((Anchor & topBottomAnchor) == topBottomAnchor)
211 {
212 args.bottom = -(args.UIHeight / 2 + param.Margin.Bottom);
213 }
214 }
215 }
如何使用
示例SimpleUIAxis
以本文开头的坐标轴元素为例。这个例子很常用,所以我放到CSharpGL.UIs类库里了,顺便可以作为参考。SimpleUIAxis实现了IUILayout,说明它想要实现UI布局;实现了IMVP,说明它要通过指定mvp矩阵的方式来设置自己的位置。

1 /// <summary>
2 /// 用一个<see cref="AxisElement"/>绘制一个固定在窗口某处的坐标系。
3 /// </summary>
4 public class SimpleUIAxis : SceneElementBase, IUILayout, IMVP, IDisposable
5 {
6 public AxisElement axisElement;
7
8 /// <summary>
9 ///
10 /// </summary>
11 /// <param name="anchor">the edges of the viewport to which a SimpleUIRect is bound and determines how it is resized with its parent.
12 /// <para>something like AnchorStyles.Left | AnchorStyles.Bottom.</para></param>
13 /// <param name="margin">the space between viewport and SimpleRect.</param>
14 /// <param name="size">Stores width when <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.Left & <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.Right is <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.None.
15 /// <para> and height when <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.Top & <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.Bottom is <see cref="OpenGLUIRect.Anchor"/>.None.</para></param>
16 /// <param name="zNear"></param>
17 /// <param name="zFar"></param>
18 /// <param name="rectColor">default color is red.</param>
19 public SimpleUIAxis(IUILayoutParam param, GLColor rectColor = null,
20 float radius = 0.3f, float axisLength = 10, int faceCount = 10)
21 {
22 // 把AxiesElement缩放到恰好放进此UI
23 radius = radius / axisLength / 2;
24 axisLength = 0.5f;
25 this.axisElement = new AxisElement(radius, axisLength, faceCount);
26
27 IUILayout layout = this;
28 layout.Param = param;
29 }
30
31 #region IDisposable Members
32
33 /// <summary>
34 /// Internal variable which checks if Dispose has already been called
35 /// </summary>
36 protected Boolean disposed;
37
38 /// <summary>
39 /// Releases unmanaged and - optionally - managed resources
40 /// </summary>
41 /// <param name="disposing"><c>true</c> to release both managed and unmanaged resources; <c>false</c> to release only unmanaged resources.</param>
42 protected void Dispose(Boolean disposing)
43 {
44 if (disposed)
45 {
46 return;
47 }
48
49 if (disposing)
50 {
51 //Managed cleanup code here, while managed refs still valid
52 this.axisElement.Dispose();
53 }
54 //Unmanaged cleanup code here
55
56 disposed = true;
57 }
58
59 /// <summary>
60 /// Performs application-defined tasks associated with freeing, releasing, or resetting unmanaged resources.
61 /// </summary>
62 public void Dispose()
63 {
64 // Call the private Dispose(bool) helper and indicate
65 // that we are explicitly disposing
66 this.Dispose(true);
67
68 // Tell the garbage collector that the object doesn't require any
69 // cleanup when collected since Dispose was called explicitly.
70 GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
71 }
72
73 #endregion
74
75 #region IUILayout
76
77 public IUILayoutParam Param { get; set; }
78
79 #endregion IUILayout
80
81
82 protected override void DoInitialize()
83 {
84 this.axisElement.Initialize();
85
86 this.BeforeRendering += this.GetSimpleUI_BeforeRendering();
87 this.AfterRendering += this.GetSimpleUI_AfterRendering();
88 }
89
90 protected override void DoRender(RenderEventArgs e)
91 {
92 this.axisElement.Render(e);
93 }
94
95 void IMVP.SetShaderProgram(mat4 mvp)
96 {
97 IMVP element = this.axisElement as IMVP;
98 element.SetShaderProgram(mvp);
99 }
100
101
102 void IMVP.ResetShaderProgram()
103 {
104 IMVP element = this.axisElement as IMVP;
105 element.ResetShaderProgram();
106 }
107
108 ShaderProgram IMVP.GetShaderProgram()
109 {
110 return ((IMVP)this.axisElement).GetShaderProgram();
111 }
112 }
这里我还为BeforeRendering和AfterRendering事件提供了一个默认的事件函数。有了它,连BeforeRendering和AfterRendering事件函数都不用再写了。

1 public static class IUILayoutRenderingHelper
2 {
3 private static readonly object synObj = new object();
4 private static EventHandler<RenderEventArgs> simpleUIAxis_BeforeRendering = null;
5 private static EventHandler<RenderEventArgs> simpleUIAxis_AfterRendering = null;
6
7 /// <summary>
8 /// 对Xxx : SceneElementBase, IUILayout, IMVP有效的After事件。
9 /// <para>此处用泛型方法是为了让编译器检测where约束条件,这样就没有“坑”了。</para>
10 /// </summary>
11 /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
12 /// <param name="element"></param>
13 /// <returns></returns>
14 public static EventHandler<RenderEventArgs> GetSimpleUI_AfterRendering<T>(this T element)
15 where T : SceneElementBase, IUILayout, IMVP
16 {
17 if (simpleUIAxis_AfterRendering == null)
18 {
19 lock (synObj)
20 {
21 if (simpleUIAxis_AfterRendering == null)
22 {
23 simpleUIAxis_AfterRendering = new EventHandler<RenderEventArgs>(SimpleUI_AfterRendering);
24 }
25 }
26 }
27
28 return simpleUIAxis_AfterRendering;
29 }
30
31 /// <summary>
32 /// 对Xxx : SceneElementBase, IUILayout, IMVP有效的Before事件。
33 /// <para>此处用泛型方法是为了让编译器检测where约束条件,这样就没有“坑”了。</para>
34 /// </summary>
35 /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
36 /// <param name="element"></param>
37 /// <returns></returns>
38 public static EventHandler<RenderEventArgs> GetSimpleUI_BeforeRendering<T>(this T element)
39 where T : SceneElementBase, IUILayout, IMVP
40 {
41 if (simpleUIAxis_BeforeRendering == null)
42 {
43 lock (synObj)
44 {
45 if (simpleUIAxis_BeforeRendering == null)
46 {
47 simpleUIAxis_BeforeRendering = new EventHandler<RenderEventArgs>(SimpleUI_BeforeRendering);
48 }
49 }
50 }
51
52 return simpleUIAxis_BeforeRendering;
53 }
54
55 static void SimpleUI_AfterRendering(object sender, RenderEventArgs e)
56 {
57 IMVP element = sender as IMVP;
58 element.ResetShaderProgram();
59 }
60
61 static void SimpleUI_BeforeRendering(object sender, RenderEventArgs e)
62 {
63 mat4 projectionMatrix, viewMatrix, modelMatrix;
64 {
65 IUILayout element = sender as IUILayout;
66 element.GetMatrix(out projectionMatrix, out viewMatrix, out modelMatrix, e.Camera);
67 }
68
69 {
70 IMVP element = sender as IMVP;
71 element.SetShaderProgram(projectionMatrix * viewMatrix * modelMatrix);
72 }
73 }
74 }
总结
元素的UI布局是一个很实用的功能。所以我尽早地为其写了此篇说明。有什么问题请留言。

|
微信扫码,自愿捐赠。天涯同道,共谱新篇。
微信捐赠不显示捐赠者个人信息,如需要,请注明联系方式。 |




 靡不有初,鲜克有终
靡不有初,鲜克有终



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· 一个奇形怪状的面试题:Bean中的CHM要不要加volatile?
· [.NET]调用本地 Deepseek 模型
· 一个费力不讨好的项目,让我损失了近一半的绩效!
· 微软正式发布.NET 10 Preview 1:开启下一代开发框架新篇章
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· PowerShell开发游戏 · 打蜜蜂
· 在鹅厂做java开发是什么体验
· WPF到Web的无缝过渡:英雄联盟客户端的OpenSilver迁移实战