什么是欧拉回路?
一句话概括就是在一个双向图中,如果从一个节点开始经历整个图的所有边有且仅有一次,然后回到了起点,这个就是欧拉回路。如果图存在欧拉回路,那么这条从起点出发回到起点的路径称为欧拉路径。
例如
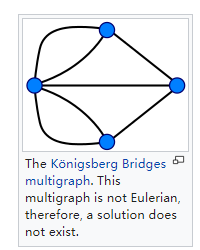
这个不是欧拉回路
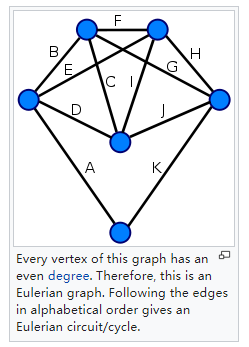
这个是欧拉回路
怎么样才会生成欧拉回路?
只有三种情况
①节点的度数全部为偶数。
②存在一个奇数节点。
③存在两个奇数节点
④如果存在三个或三个以上的奇数节点,那么肯定无法构成欧拉回路
欧拉回路的起点如何选择?
①对于全部偶数度数的图来说,起始节点是任意的。
②如果存在奇数点,那么一定从奇数点开始。
③如果存在两个奇数点,那么一定从一个奇数点开始一个奇数点结束。
如何实现欧拉回路的算法?
Hierholzer算法
wiki

wiki原文
Hierholzer's 1873 paper provides a different method for finding Euler cycles that is more efficient than Fleury's algorithm:
By using a data structure such as a doubly linked list to maintain the set of unused edges incident to each vertex, to maintain the list of vertices on the current tour that have unused edges, and to maintain the tour itself, the individual operations of the algorithm (finding unused edges exiting each vertex, finding a new starting vertex for a tour, and connecting two tours that share a vertex) may be performed in constant time each, so the overall algorithm takes linear time, {\displaystyle O(|E|)} O(|E|).[8]
代码模板
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//二位数组G用来存图,du是保存每个节点的度数,jl是保存欧拉路径的数组
int G[1500][1500],du[1500],jl[1500];
//mi是最小值,因为节点不一定是从1开始,maxn保存最大的节点,start是开始的节点,p是数组计数器
int mi=INT_MAX,maxn,start=1,p;
void dfs(int num)//核心算法
{
for(int i=mi;i<=maxn;i++)//对每一个节点进行枚举,如果存在连通的情况,那么边数--,继续搜索下一个连通的节点
if(G[num][i])
{
G[num][i]--;
G[i][num]--;
dfs(i);
}
jl[p++]=num;//路径存入数组
}
int main()
{
int m;
cin>>m;
while(m--)
{
int t1,t2;
cin>>t1>>t2;
G[t1][t2]++;
G[t2][t1]++;
du[t1]++;du[t2]++;
maxn=max(max(maxn,t1),max(maxn,t2));//找最大值和最小值
mi=min(min(mi,t1),min(mi,t2));
}
for(int i=mi;i<=maxn;i++)
if(du[i]%2)//寻找最小的奇点
{
start=i;
break;
}
dfs(start);
for(int i=p-1;i>=0;i--)//根据递归返回的性质,应该倒叙输出
cout<<jl[i]<<endl;
}





