Normal synchronous FIFO mode 和 Show-ahead synchronous FIFO mode
FIFO是先进先出,可以用fifo来处理跨时钟域的数据传输问题,用到的地方特别多,一定要搞会。
在学习调用fifo的IP核中发现有normal synchronous FIFO mode 和 Show-ahead synchronous FIFO mode这两种模式,就研究一下。
研究 IP 核最方便的方式就是用 modesim 仿真一下,这样关系就会很明了。
下面的两幅图是我用 Time_Gen 软件自己总结画的,并不是 modesim 的仿真图。
假定存入fifo的第一个数是01,第二个数是02,第三个数是03,以此类推。。。
clk是读时钟,rd是读使能,q是fifo的数据输出端
normal mode,只有在读使能信号有效的时候,才会在读时钟上升沿来的时候输出第一个数01。
Show-ahead 模式的输出要比 normal 模式的输出早一拍,意思是只要FIFO中有数据,他就会把第一个数据输出,
当第一个读使能信号来的时候,则会在读时钟上升沿的时候输出第二个数据02。
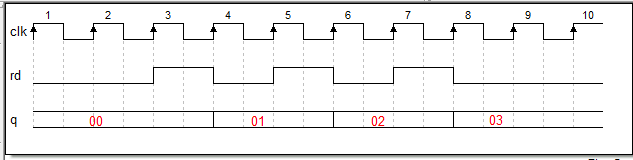

Normal mode Show-ahead mode
既然二者的区别是数据输出相差一拍,因此在设计 fifo 的时候就要根据不同的模式进行设计
下面举个例子,该代码实现了100Mhz 与 80Mhz 不同时钟域的数据传输问题
因为不同时钟域的频率不同,在进行数据传输的时候如果不进行处理必然会有数据丢失
FIFO 可以缓存数据,因此我们可以先把数据放在 fifo 里,再进行传输
当fifo中的数据 resudw>=某个数的时候,就不允许往 fifo 中写入数据,当 FIFO 空的时候也不允许再读数据。
module fifo(
rst_n , clk_in , //100Mhz ,fifo写时钟 data_in , //输入的数据 data_in_vld,//输入数据有效指示信号 clk_out , //80Mhz ,fifo读时钟 data_out , //输出的数据 data_out_vld,//输出数据有效指示信号 b_rdy //当为高,表示可以接收从fifo中读的数据,反之则不行 ); input rst_n ,clk_in,clk_out,b_rdy; input [15:0] data_in ; input data_in_vld ; output[15:0] data_out ; output[15:0] data_out_vld; reg wr_ff0; wire wr_ff1; wire[15:0] q; reg[7:0] data_out; reg data_out_vld; reg rd_ff0; wire rdempty ; wire wrfull ; wire[5:0] wrusedw;
//调用IP核生成位宽为16 位,深度为64的FIFO, Show-ahead模式 my_fifo u1_fifo( .data (data_in), .rdclk(clk_out), .rdreq(rd_ff0), .wrclk(clk_in), .wrreq(wr_ff1), .q (q), .rdempty(rdempty), .wrfull (wrfull ), .wrusedw(wrusedw) ); //---------------------------------------------------------------------- //写满保护 always @(*)begin if(wrusedw>=61) begin wr_ff0<=0; end else wr_ff0<=1; end assign wr_ff1 = (data_in_vld && wr_ff0)?1'b1:1'b0; //rd_ff0 always @(*)begin if(b_rdy==1&&rdempty==0 )begin rd_ff0<=1; end else rd_ff0<=0; end //-------------------------------------------------------------
//如果是Show-ahead 模式入,此时data_out与data_out_vld是对齐的
//如果是normal 模式,则需要将rd_ff0在多打一拍,然后将rd_ff1值给data_out_vld才能对齐
always @(posedge clk_out or negedge rst_n)begin if(rst_n==1'b0)begin data_out<=0; end else begin data_out<=q; end end always @(posedge clk_out or negedge rst_n)begin if(rst_n==1'b0)begin data_out_vld<=0; end else begin data_out_vld<=rd_ff0; end end
endmodule


