Spark核心作业调度和任务调度之DAGScheduler源码
前言:本文是我学习Spark 源码与内部原理用,同时也希望能给新手一些帮助,入道不深,如有遗漏或错误的,请在原文评论或者发送至我的邮箱 tongzhenguotongzhenguo@gmail.com
摘要:
1.作业调度核心——DAGScheduler
2.DAGScheduler类说明
2.1DAGScheduler
2.2ActiveJob
2.3Stage
2.4Task
3.工作流程
3.1划分Stage
3.2生成Job,提交Stage
3.3任务集的提交
3.4任务作业完成状态的监控
3.5任务结果的获取
内容:
1.作业调度核心——DAGScheduler
用户代码都是基于RDD的一系列计算操作,实际运行时,这些计算操作是Lazy执行的,并不是所有的RDD操作都会触发Spark往Cluster上提交实际作业,基本上只有一些需要返回数据或者向外部输出的操作才会触发实际计算工作(Action算子),其它的变换操作基本上只是生成对应的RDD记录依赖关系(Transformation算子)。
在这些RDD.Action操作中(如count,collect)会自动触发runJob提交作业,不需要用户显式的提交作业(这一部分可以看下Spark DAGSheduler生成Stage过程分析实验)
作业调度的两个主要入口是submitJob 和 runJob,两者的区别在于前者返回一个Jobwaiter对象,可以用在异步调用中,用来判断作业完成或者取消作业,runJob在内部调用submitJob,阻塞等待直到作业完成(或失败),以下是源码部分:
submitJob
/**
* Submit an action job to the scheduler.
*
* @param rdd target RDD to run tasks on
* @param func a function to run on each partition of the RDD
* @param partitions set of partitions to run on; some jobs may not want to compute on all
* partitions of the target RDD, e.g. for operations like first()
* @param callSite where in the user program this job was called
* @param resultHandler callback to pass each result to
* @param properties scheduler properties to attach to this job, e.g. fair scheduler pool name
*
* @return a JobWaiter object that can be used to block until the job finishes executing
* or can be used to cancel the job.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException when partitions ids are illegal
*/
def submitJob[T, U](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit,
properties: Properties): JobWaiter[U] = {
// Check to make sure we are not launching a task on a partition that does not exist.
val maxPartitions = rdd.partitions.length
partitions.find(p => p >= maxPartitions || p < 0).foreach { p =>
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Attempting to access a non-existent partition: " + p + ". " +
"Total number of partitions: " + maxPartitions)
}
val jobId = nextJobId.getAndIncrement()
if (partitions.size == 0) {
// Return immediately if the job is running 0 tasks
return new JobWaiter[U](this, jobId, 0, resultHandler)
}
assert(partitions.size > 0)
val func2 = func.asInstanceOf[(TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _]
val waiter = new JobWaiter(this, jobId, partitions.size, resultHandler)
eventProcessLoop.post(JobSubmitted(
jobId, rdd, func2, partitions.toArray, callSite, waiter,
SerializationUtils.clone(properties)))
waiter
}
runJob
/**
* Run an action job on the given RDD and pass all the results to the resultHandler function as
* they arrive.
*
* @param rdd target RDD to run tasks on
* @param func a function to run on each partition of the RDD
* @param partitions set of partitions to run on; some jobs may not want to compute on all
* partitions of the target RDD, e.g. for operations like first()
* @param callSite where in the user program this job was called
* @param resultHandler callback to pass each result to
* @param properties scheduler properties to attach to this job, e.g. fair scheduler pool name
*
* @throws Exception when the job fails
*/
def runJob[T, U](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit,
properties: Properties): Unit = {
val start = System.nanoTime
val waiter = submitJob(rdd, func, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, properties)
val awaitPermission = null.asInstanceOf[scala.concurrent.CanAwait]
waiter.completionFuture.ready(Duration.Inf)(awaitPermission)
waiter.completionFuture.value.get match {
case scala.util.Success(_) =>
logInfo("Job %d finished: %s, took %f s".format
(waiter.jobId, callSite.shortForm, (System.nanoTime - start) / 1e9))
case scala.util.Failure(exception) =>
logInfo("Job %d failed: %s, took %f s".format
(waiter.jobId, callSite.shortForm, (System.nanoTime - start) / 1e9))
// SPARK-8644: Include user stack trace in exceptions coming from DAGScheduler.
val callerStackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace.tail
exception.setStackTrace(exception.getStackTrace ++ callerStackTrace)
throw exception
}
}
DAGScheduler最重要的任务之一即制定基于Stage的逻辑调度。先构建Stage之间的DAG图,然后将Stage提交给TaskScheduler
/** * The high-level scheduling layer that implements stage-oriented scheduling. It computes a DAG of * stages for each job, keeps track of which RDDs and stage outputs are materialized, and finds a * minimal schedule to run the job. It then submits stages as TaskSets to an underlying * TaskScheduler implementation that runs them on the cluster.
2.DAGScheduler类说明
问:DAGScheduler是什么时候生成的?
答:DAGScheduler在SparkContext初始化过程中实例化,一个SparkContext对应一个DAGScheduler
下面提到一些相关的概念:
ActiveJob: Jobs 是以ActiveJob类代表的,ActiveJob 可以根据finalStage区分为两种:a result job(对应ResultStage)或者a map-stage job(对应ShuffleMapStage,主要用在查询计划上)。以下是ActiveJob类:
/*
* Jobs 是以ActiveJob类代表的,ActiveJob 可以根据finalStage区分为两种:
* a result job(对应ResultStage)或者a map-stage job(对应ShuffleMapStage,主要用在查询计划上)。
*/
private[spark] class ActiveJob(
val jobId: Int,
val finalStage: Stage,
val callSite: CallSite,
val listener: JobListener,
val properties: Properties) {
/**
* Number of partitions we need to compute for this job. Note that result stages may not need
* to compute all partitions in their target RDD, for actions like first() and lookup().
*/
val numPartitions = finalStage match {
case r: ResultStage => r.partitions.length
case m: ShuffleMapStage => m.rdd.partitions.length
}
/** Which partitions of the stage have finished */
val finished = Array.fill[Boolean](numPartitions)(false)
var numFinished = 0
}
Stage:一个Stage就是一组并行的task,各个stage之间以Shuffle为边界进行划分;Stage 也相应划分为两种:a shuffle map stage和 a result stage,以下是Stage类:
/*
* 一个Stage就是一组并行的task,各个stage之间以Shuffle为边界进行划分;
* Stage 也相应划分为两种:
* a shuffle map stage
* a result stage
*/
private[scheduler] abstract class Stage(
val id: Int,
val rdd: RDD[_],
val numTasks: Int,
val parents: List[Stage],
val firstJobId: Int,
val callSite: CallSite)
extends Logging {
val numPartitions = rdd.partitions.length
/** Set of jobs that this stage belongs to. */
val jobIds = new HashSet[Int]
val pendingPartitions = new HashSet[Int]
/** The ID to use for the next new attempt for this stage. */
private var nextAttemptId: Int = 0
val name: String = callSite.shortForm
val details: String = callSite.longForm
/**
* Pointer to the [StageInfo] object for the most recent attempt. This needs to be initialized
* here, before any attempts have actually been created, because the DAGScheduler uses this
* StageInfo to tell SparkListeners when a job starts (which happens before any stage attempts
* have been created).
*/
private var _latestInfo: StageInfo = StageInfo.fromStage(this, nextAttemptId)
/**
* Set of stage attempt IDs that have failed with a FetchFailure. We keep track of these
* failures in order to avoid endless retries if a stage keeps failing with a FetchFailure.
* We keep track of each attempt ID that has failed to avoid recording duplicate failures if
* multiple tasks from the same stage attempt fail (SPARK-5945).
*/
private val fetchFailedAttemptIds = new HashSet[Int]
private[scheduler] def clearFailures() : Unit = {
fetchFailedAttemptIds.clear()
}
/**
* Check whether we should abort the failedStage due to multiple consecutive fetch failures.
*
* This method updates the running set of failed stage attempts and returns
* true if the number of failures exceeds the allowable number of failures.
*/
private[scheduler] def failedOnFetchAndShouldAbort(stageAttemptId: Int): Boolean = {
fetchFailedAttemptIds.add(stageAttemptId)
fetchFailedAttemptIds.size >= Stage.MAX_CONSECUTIVE_FETCH_FAILURES
}
/** Creates a new attempt for this stage by creating a new StageInfo with a new attempt ID. */
def makeNewStageAttempt(
numPartitionsToCompute: Int,
taskLocalityPreferences: Seq[Seq[TaskLocation]] = Seq.empty): Unit = {
val metrics = new TaskMetrics
metrics.register(rdd.sparkContext)
_latestInfo = StageInfo.fromStage(
this, nextAttemptId, Some(numPartitionsToCompute), metrics, taskLocalityPreferences)
nextAttemptId += 1
}
/** Returns the StageInfo for the most recent attempt for this stage. */
def latestInfo: StageInfo = _latestInfo
override final def hashCode(): Int = id
override final def equals(other: Any): Boolean = other match {
case stage: Stage => stage != null && stage.id == id
case _ => false
}
/** Returns the sequence of partition ids that are missing (i.e. needs to be computed). */
def findMissingPartitions(): Seq[Int]
}
private[scheduler] object Stage {
// The number of consecutive failures allowed before a stage is aborted
val MAX_CONSECUTIVE_FETCH_FAILURES = 4
}
Task:也相应对应两个类:ShuffleMapTask和ResultTask, 其中前者执行任务并将输出写入分区;后者执行任务将输出发送到驱动程序中(Driver Application)(以后有时间分析任务执行的时候再分析源码吧)
其他相关说明:
* * - Cache tracking: the DAGScheduler figures out which RDDs are cached to avoid recomputing them * and likewise remembers which shuffle map stages have already produced output files to avoid * redoing the map side of a shuffle. *
* - Preferred locations: the DAGScheduler also computes where to run each task in a stage based * on the preferred locations of its underlying RDDs, or the location of cached or shuffle data. * * - Cleanup: all data structures are cleared when the running jobs that depend on them finish, * to prevent memory leaks in a long-running application.
*
DAGScheduler内部维护了各种task / stage / job之间的映射关系表,值得一提的是这里根据执行情况,stages的几种划分,有助于之后阅读submitStages方法。
private[scheduler] val nextJobId = new AtomicInteger(0) private[scheduler] def numTotalJobs: Int = nextJobId.get() private val nextStageId = new AtomicInteger(0) private[scheduler] val jobIdToStageIds = new HashMap[Int, HashSet[Int]] private[scheduler] val stageIdToStage = new HashMap[Int, Stage] private[scheduler] val shuffleToMapStage = new HashMap[Int, ShuffleMapStage] private[scheduler] val jobIdToActiveJob = new HashMap[Int, ActiveJob] // Stages we need to run whose parents aren't done private[scheduler] val waitingStages = new HashSet[Stage] // Stages we are running right now private[scheduler] val runningStages = new HashSet[Stage] // Stages that must be resubmitted due to fetch failures private[scheduler] val failedStages = new HashSet[Stage] private[scheduler] val activeJobs = new HashSet[ActiveJob]
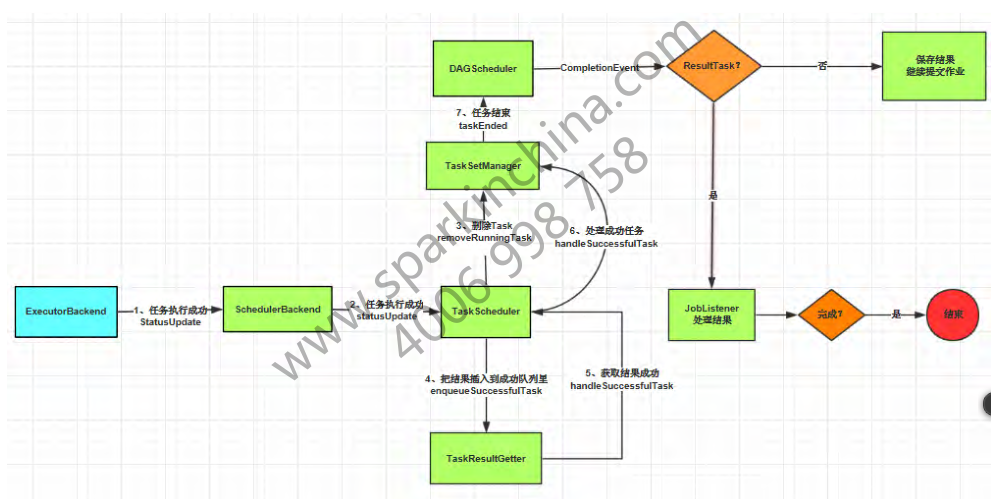
3.工作流程
工作流程图:
3.1 划分Stage
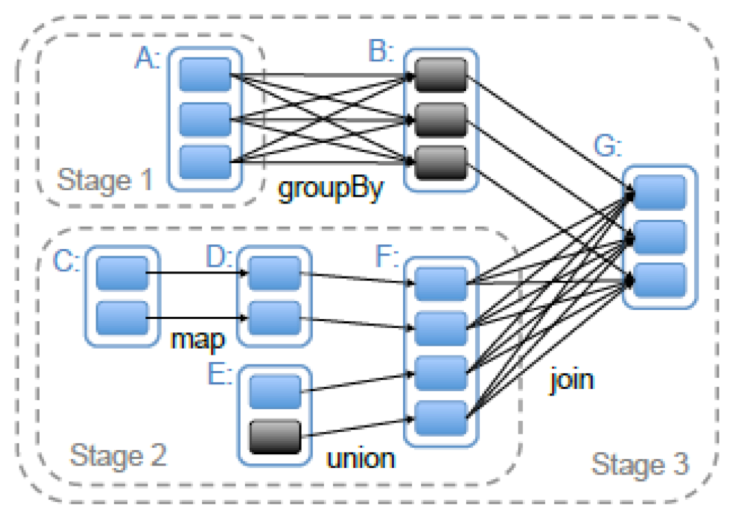
Spark的stages 是以shuffle为边界切分RDD图来创建的。具有窄依赖(例:map(),filter())的操作会在对应Stage的一系列任务中管道式的运行,但是具有宽依赖的操作则需要多个Stage.最后所有的Stage之间将只有shuffle依赖关系。
实际上这些操作发生在RDD.compute(),在各个RDD的实现上,比如MappedRDD,FilteredRDD等
当某个操作触发计算,向DAGScheduler提交作业时,DAGScheduler需要从RDD依赖链最末端的RDD出发,遍历整个RDD依赖链,划分Stage任务阶段,并决定各个Stage之间的依赖关系。Stage的划分是以ShuffleDependency为依据的,也就是说当某个RDD的运算需要将数据进行Shuffle时,这个包含了Shuffle依赖关系的RDD将被用来作为输入信息,构建一个新的Stage,由此为依据划分Stage,可以确保有依赖关系的数据能够按照正确的顺序得到处理和运算。这部分做了一个简单的实验:Spark DAGSheduler生成Stage过程分析实验
以GroupByKey操作为例,该操作返回的结果实际上是一个ShuffleRDD,当DAGScheduler遍历到这个ShuffleRDD的时候,因为其Dependency是一个ShuffleDependency,于是这个ShuffleRDD的父RDD以及shuffleDependency等对象就被用来构建一个新的Stage,这个Stage的输出结果的分区方式,则由ShuffleDependency中的Partitioner对象来决定。
可以看到,尽管划分和构建Stage的依据是ShuffleDependency,对应的RDD也就是这里的ShuffleRDD,但是这个Stage所处理的数据是从这个shuffleRDD的父RDD开始计算的,只是最终的输出结果的位置信息参考了ShuffleRDD返回的ShuffleDependency里所包含的内容。而shuffleRDD本身的运算操作(其实就是一个获取shuffle结果的过程),是在下一个Stage里进行的。
贴一张图:
3.2 生成Job,提交Stage
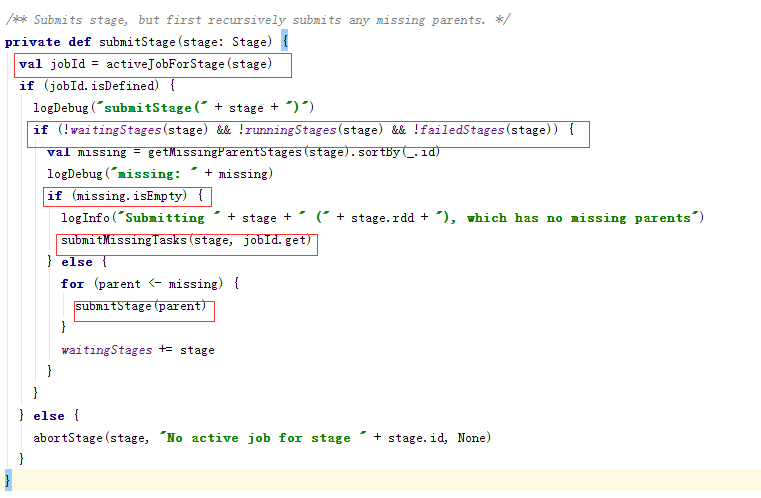
上一个步骤得到一个或多个有依赖关系的Stage,其中直接触发Job的RDD所关联的Stage作为FinalStage生成一个Job实例,这两者的关系进一步存储在resultStageToJob映射表中,用于在该Stage全部完成时做一些后续处理,如报告状态,清理Job相关数据等。具体提交一个Stage时,首先判断该Stage所依赖的父Stage的结果是否可用,如果所有父Stage的结果都可用,则提交该Stage,如果有任何一个父Stage的结果不可用,则迭代尝试提交父Stage。 所有迭代过程中由于所依赖Stage的结果不可用而没有提交成功的Stage都被放到waitingStages列表中等待将来被提交
什么时候waitingStages中的Stage会被重新提交呢?当一个属于中间过程Stage的任务(这种类型的任务所对应的类为ShuffleMapTask)完成以后,DAGScheduler会检查对应的Stage的所有任务是否都完成了,如果是都完成了,则DAGScheduler将重新扫描一次waitingStages中的所有Stage,检查他们是否还有任何依赖的Stage没有完成,如果没有就可以提交该Stage。
此外每当完成一次DAGScheduler的事件循环以后,也会触发一次从等待(waitingStages)和失败列表(failedStages)中扫描并提交就绪Stage的调用过程
下面是submitStage的代码:
3.3 任务集的提交
每个Stage的提交,最终是转换成一个TaskSet任务集的提交,DAGScheduler通过TaskScheduler接口提交TaskSet,这个TaskSet最终会触发TaskScheduler构建一个TaskSetManager的实例来管理这个TaskSet的生命周期,对于DAGScheduler来说提交Stage的工作到此就完成了。而TaskScheduler的具体实现则会在得到计算资源的时候,进一步通过TaskSetManager调度具体的Task到对应的Executor节点上进行运算
3.4 任务作业完成状态的监控
要保证相互依赖的job/stage能够得到顺利的调度执行,DAGScheduler就必然需要监控当前Job / Stage乃至Task的完成情况。这是通过对外(主要是对TaskScheduler)暴露一系列的回调函数来实现的,对于TaskScheduler来说,这些回调函数主要包括任务的开始结束失败,任务集的失败,DAGScheduler根据这些Task的生命周期信息进一步维护Job和Stage的状态信息。
private val messageScheduler =
ThreadUtils.newDaemonSingleThreadScheduledExecutor("dag-scheduler-message")
private[scheduler] val eventProcessLoop = new DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop(this)
taskScheduler.setDAGScheduler(this)
/**
* Called by the TaskSetManager to report task's starting.
*/
def taskStarted(task: Task[_], taskInfo: TaskInfo) {
eventProcessLoop.post(BeginEvent(task, taskInfo))
}
问:DAGScheduler内部是如何运行的?如何循环的?
答:DAGScheduler的事件循环逻辑基于Akka Actor的消息传递机制来构建,在DAGScheduler的taskStarted函数中创建了一个eventProcessLoop用来处理各种DAGSchedulerEvent,这些事件包括作业的提交,任务状态的变化,监控等等
这里跟读一下DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop,来看下这个类是如何处理消息事件(DAGSchedulerEvent)的
private[scheduler] class DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop(dagScheduler: DAGScheduler)
extends EventLoop[DAGSchedulerEvent]("dag-scheduler-event-loop") with Logging {
private[this] val timer = dagScheduler.metricsSource.messageProcessingTimer
/**
* The main event loop of the DAG scheduler.
*/
override def onReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = {
val timerContext = timer.time()
try {
doOnReceive(event)
} finally {
timerContext.stop()
}
}
private def doOnReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = event match {
case JobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties) =>
dagScheduler.handleJobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties)
case MapStageSubmitted(jobId, dependency, callSite, listener, properties) =>
dagScheduler.handleMapStageSubmitted(jobId, dependency, callSite, listener, properties)
case StageCancelled(stageId) =>
dagScheduler.handleStageCancellation(stageId)
case JobCancelled(jobId) =>
dagScheduler.handleJobCancellation(jobId)
case JobGroupCancelled(groupId) =>
dagScheduler.handleJobGroupCancelled(groupId)
case AllJobsCancelled =>
dagScheduler.doCancelAllJobs()
case ExecutorAdded(execId, host) =>
dagScheduler.handleExecutorAdded(execId, host)
case ExecutorLost(execId) =>
dagScheduler.handleExecutorLost(execId, fetchFailed = false)
case BeginEvent(task, taskInfo) =>
dagScheduler.handleBeginEvent(task, taskInfo)
case GettingResultEvent(taskInfo) =>
dagScheduler.handleGetTaskResult(taskInfo)
case completion: CompletionEvent =>
dagScheduler.handleTaskCompletion(completion)
case TaskSetFailed(taskSet, reason, exception) =>
dagScheduler.handleTaskSetFailed(taskSet, reason, exception)
case ResubmitFailedStages =>
dagScheduler.resubmitFailedStages()
}
override def onError(e: Throwable): Unit = {
logError("DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop failed; shutting down SparkContext", e)
try {
dagScheduler.doCancelAllJobs()
} catch {
case t: Throwable => logError("DAGScheduler failed to cancel all jobs.", t)
}
dagScheduler.sc.stop()
}
override def onStop(): Unit = {
// Cancel any active jobs in postStop hook
dagScheduler.cleanUpAfterSchedulerStop()
}
}
此外TaskScheduler还可以通过回调函数通知DAGScheduler具体的Executor的生命状态,如果某一个Executor崩溃了,或者由于任何原因与Driver失去联系了,则对应的Stage的shuffleMapTask的输出结果也将被标志为不可用,这也将导致对应Stage状态的变更,进而影响相关Job的状态,再进一步可能触发对应Stage的重新提交来重新计算获取相关的数据。
3.5 任务结果的获取
一个具体的任务在Executor中执行完毕以后,其结果需要以某种形式返回给DAGScheduler,根据任务类型的不同,任务的结果的返回方式也不同
对于FinalStage所对应的任务(对应的类为ResultTask)返回给DAGScheduler的是运算结果本身,而对于ShuffleMapTask,返回给DAGScheduler的是一个MapStatus对象,MapStatus对象管理了ShuffleMapTask的运算输出结果在BlockManager里的相关存储信息,而非结果本身,这些存储位置信息将作为下一个Stage的任务的获取输入数据的依据
而根据任务结果的大小的不同,ResultTask返回的结果又分为两类,如果结果足够小,则直接放在DirectTaskResult对象内,如果超过特定尺寸(默认约10MB)则在Executor端会将DirectTaskResult先序列化,再把序列化的结果作为一个Block存放在BlockManager里,而后将BlockManager返回的BlockID放在IndirectTaskResult对象中返回给TaskScheduler,TaskScheduler进而调用TaskResultGetter将IndirectTaskResult中的BlockID取出并通过BlockManager最终取得对应的DirectTaskResult。当然从DAGScheduler的角度来说,这些过程对它来说是透明的,它所获得的都是任务的实际运算结果。
// This is a var so that we can reset it for testing purposes. private[spark] var taskResultGetter = new TaskResultGetter(sc.env, this)
ResultSetGetter 的enqueueSuccessfulTask 方法:
def enqueueSuccessfulTask(
taskSetManager: TaskSetManager,
tid: Long,
serializedData: ByteBuffer): Unit = {
getTaskResultExecutor.execute(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = Utils.logUncaughtExceptions {
try {
val (result, size) = serializer.get().deserialize[TaskResult[_]](serializedData) match {
/*
* 根据任务结果的大小的不同,ResultTask返回的结果又分为两类:DirectTaskResult,IndirectTaskResult
* 1.如果结果足够小,则直接放在DirectTaskResult对象内
*/
case directResult: DirectTaskResult[_] =>
if (!taskSetManager.canFetchMoreResults(serializedData.limit())) {
return
}
// deserialize "value" without holding any lock so that it won't block other threads.
// We should call it here, so that when it's called again in
// "TaskSetManager.handleSuccessfulTask", it does not need to deserialize the value.
directResult.value()
(directResult, serializedData.limit())
/**
* 如果超过特定尺寸(默认约10MB)则在Executor端会将DirectTaskResult先序列化,
* 再把序列化的结果作为一个Block存放在BlockManager里,
* 而后将BlockManager返回的BlockID放在IndirectTaskResult对象中返回给TaskScheduler,
* TaskScheduler进而调用TaskResultGetter将IndirectTaskResult中的BlockID取出并通过BlockManager最终取得对应的DirectTaskResult。
*
*/
case IndirectTaskResult(blockId, size) =>
if (!taskSetManager.canFetchMoreResults(size)) {
// dropped by executor if size is larger than maxResultSize
sparkEnv.blockManager.master.removeBlock(blockId)
return
}
logDebug("Fetching indirect task result for TID %s".format(tid))
scheduler.handleTaskGettingResult(taskSetManager, tid)
val serializedTaskResult = sparkEnv.blockManager.getRemoteBytes(blockId)
if (!serializedTaskResult.isDefined) {
/* We won't be able to get the task result if the machine that ran the task failed
* between when the task ended and when we tried to fetch the result, or if the
* block manager had to flush the result. */
scheduler.handleFailedTask(
taskSetManager, tid, TaskState.FINISHED, TaskResultLost)
return
}
val deserializedResult = serializer.get().deserialize[DirectTaskResult[_]](
serializedTaskResult.get.toByteBuffer)
sparkEnv.blockManager.master.removeBlock(blockId)
(deserializedResult, size)
}
// Set the task result size in the accumulator updates received from the executors.
// We need to do this here on the driver because if we did this on the executors then
// we would have to serialize the result again after updating the size.
result.accumUpdates = result.accumUpdates.map { a =>
if (a.name == Some(InternalAccumulator.RESULT_SIZE)) {
val acc = a.asInstanceOf[LongAccumulator]
assert(acc.sum == 0L, "task result size should not have been set on the executors")
acc.setValue(size.toLong)
acc
} else {
a
}
}
scheduler.handleSuccessfulTask(taskSetManager, tid, result)
} catch {
case cnf: ClassNotFoundException =>
val loader = Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader
taskSetManager.abort("ClassNotFound with classloader: " + loader)
// Matching NonFatal so we don't catch the ControlThrowable from the "return" above.
case NonFatal(ex) =>
logError("Exception while getting task result", ex)
taskSetManager.abort("Exception while getting task result: %s".format(ex))
}
}
})
}


