1.help delete

mysql> help delete; Name: 'DELETE' Description: Syntax: DELETE is a DML statement that removes rows from a table. Single-Table Syntax DELETE [LOW_PRIORITY] [QUICK] [IGNORE] FROM tbl_name [PARTITION (partition_name,...)] [WHERE where_condition] [ORDER BY ...] [LIMIT row_count] The DELETE statement deletes rows from tbl_name and returns the number of deleted rows. To check the number of deleted rows, call the ROW_COUNT() function described in http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/information-functions.html. Main Clauses The conditions in the optional WHERE clause identify which rows to delete. With no WHERE clause, all rows are deleted. where_condition is an expression that evaluates to true for each row to be deleted. It is specified as described in http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/select.html. If the ORDER BY clause is specified, the rows are deleted in the order that is specified. The LIMIT clause places a limit on the number of rows that can be deleted. These clauses apply to single-table deletes, but not multi-table deletes. Multiple-Table Syntax DELETE [LOW_PRIORITY] [QUICK] [IGNORE] tbl_name[.*] [, tbl_name[.*]] ... FROM table_references [WHERE where_condition] Or: DELETE [LOW_PRIORITY] [QUICK] [IGNORE] FROM tbl_name[.*] [, tbl_name[.*]] ... USING table_references [WHERE where_condition] Privileges You need the DELETE privilege on a table to delete rows from it. You need only the SELECT privilege for any columns that are only read, such as those named in the WHERE clause. Performance When you do not need to know the number of deleted rows, the TRUNCATE TABLE statement is a faster way to empty a table than a DELETE statement with no WHERE clause. Unlike DELETE, TRUNCATE TABLE cannot be used within a transaction or if you have a lock on the table. See [HELP TRUNCATE TABLE] and [HELP LOCK]. The speed of delete operations may also be affected by factors discussed in http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/delete-speed.html. To ensure that a given DELETE statement does not take too much time, the MySQL-specific LIMIT row_count clause for DELETE specifies the maximum number of rows to be deleted. If the number of rows to delete is larger than the limit, repeat the DELETE statement until the number of affected rows is less than the LIMIT value. Subqueries You cannot delete from a table and select from the same table in a subquery. Partitioned Tables Beginning with MySQL 5.6.2, DELETE supports explicit partition selection using the PARTITION option, which takes a comma-separated list of the names of one or more partitions or subpartitions (or both) from which to select rows to be dropped. Partitions not included in the list are ignored. Given a partitioned table t with a partition named p0, executing the statement DELETE FROM t PARTITION (p0) has the same effect on the table as executing ALTER TABLE t TRUNCATE PARTITION (p0); in both cases, all rows in partition p0 are dropped. PARTITION can be used along with a WHERE condition, in which case the condition is tested only on rows in the listed partitions. For example, DELETE FROM t PARTITION (p0) WHERE c < 5 deletes rows only from partition p0 for which the condition c < 5 is true; rows in any other partitions are not checked and thus not affected by the DELETE. The PARTITION option can also be used in multiple-table DELETE statements. You can use up to one such option per table named in the FROM option. See http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/partitioning-selection.html, for more information and examples. URL: http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/delete.html
2.使用delete语句
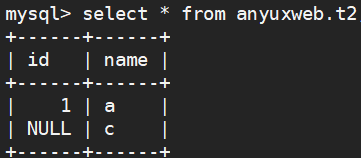
delete from anyuxweb.t2 where id=2;
select * from anyuxweb.t2;
3.delete 语句后面要跟着where子句,否则这个表很危险
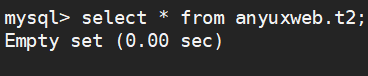
--删除数据不使用where子句,会将表清空 delete from anyuxweb.t2; --查看当前表 select * from anyuxweb.t2;
4. 伪删除
数据表实现伪删除的原理是将数据添加一个状态列(如列名status)。
--添加状态列 alter table anyuxweb.t2 add status int; --更新status状态值 update anyuxweb.t2 set status=1; select * from anyuxweb.t2 where status =1; insert into anyuxweb.t2(id,name) select * from anyuxweb.t1; select * from anyuxweb.t2;
update anyuxweb.t2 set status=1;
select * from anyuxweb.t2;
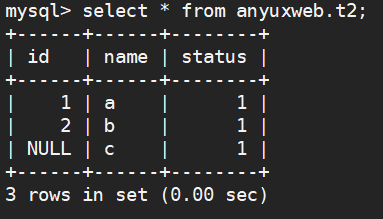
此时使用status状态查询过滤即可


