一个基于JRTPLIB的轻量级RTSP客户端(myRTSPClient)——解码篇:(一)用ffmpeg解码视频
2016-02-23 11:30 Ansersion 阅读(4256) 评论(2) 编辑 收藏 举报一、概述
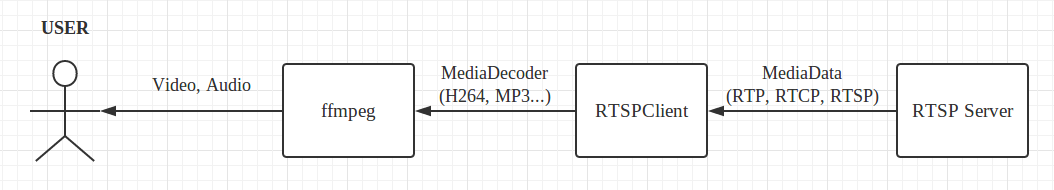
myRTSPClient(RTSPClient)获取音视频数据之后,接下来的工作便是将音视频数据交给解码器去解码(ffmpeg),ffmpeg解码之后于是便有了呈现在终端用户(USER)面前的视频(Video)和音频(Audio),具体过程如下图所示。
关于myRTSPClient从RTSP Server那里接收多媒体数据的过程,在《收流篇》中已经做了基本介绍了。接下来,我们来讨论当RTSPClient获取到多媒体数据之后,是怎么将数据交给解码器的。首先介绍视频部分。
二、代码示例(源码见‘附录’)
整体的代码结构如下:
1 'RTSP Client' send PLAY command to 'RTSP Server'; 2 Register callback function for ffmpeg; 3 Initialize ffmpeg and SDL; 4 while(get frame) { 5 ffmpeg loop; 6 } 7 free ffmpeg; 8 'RTSP Client' send TEARDOWN command to 'RTSP Server'
其中第1、2、8部分是以下要讨论的重点,其他部分均为ffmpeg的解码内容,这里有一片不错的博客,以供参考。
第一部分:'RTSP Client' send PLAY command to 'RTSP Server';
首先,我们需要向RTSP Server发送PLAY命令,让RTSP Server给RTSPClient发送多媒体数据。
1 rtspClientRequest(&Client, argv[1]);
该函数接受2个参数,第1个参数为myRtspClient的对象,第2个为一个RTSP URI。该函数的具体内容如下:
1 int rtspClientRequest(RtspClient * Client, string url) 2 { 3 if(!Client) return -1; 4 5 // cout << "Start play " << url << endl; 6 string RtspUri(url); 7 // string RtspUri("rtsp://192.168.81.145/ansersion"); 8 9 /* Set up rtsp server resource URI */ 10 Client->SetURI(RtspUri); 11 12 /* Send DESCRIBE command to server */ 13 Client->DoDESCRIBE(); 14 15 /* Parse SDP message after sending DESCRIBE command */ 16 Client->ParseSDP(); 17 18 /* Send SETUP command to set up all 'audio' and 'video' 19 * sessions which SDP refers. */ 20 Client->DoSETUP(); 21 22 /* Send PLAY command to play only 'video' sessions.*/ 23 Client->DoPLAY("video"); 24 25 return 0; 26 }
该函数首先给RTSP Client设置好RTSP URI,然后让Client按照RTSP的播放流程,分别给RTSP Server发送一系列命令,然后播放"video“。该函数被调用之后,RTSP Server就开始不停的向RTSP Client发送多媒体数据了。
第二部分:Register callback function for ffmpeg;
现在,客户端已经可以接收到服务端发送过来的多媒体数据了,接下来的工作就是将多媒体数据交给解码器。网上有很多关于ffmpeg的解码示例,不过都是直接读取音视频文件的。但是我们现在的音视频数据并不是什么具体的文件,而是写在内存里的。要让ffmpeg直接从内存而不是从某个文件里获取多媒体数据,我们需要对ffmpeg做一些设置。
1 pFormatCtx = NULL; 2 pFormatCtx = avformat_alloc_context(); 3 unsigned char * iobuffer = (unsigned char *)av_malloc(32768); 4 AVIOContext * avio = avio_alloc_context(iobuffer, 32768, 0, &Client, fill_iobuffer, NULL, NULL); 5 pFormatCtx->pb = avio;
在我们的代码示例中,用ffmpeg解码部分的代码基本是照搬ffmpeg教程中的示例,唯独以上5行代码是新添加的内容。其中的关键是pFormatCtx->pb这个数据结构。这个数据结构指定了frame的buffer,处理frame的回调函数等一系列解码细节。所以我们需要修改这个结构体让ffmpeg从RTSP Client获取多媒体数据,从而完成多媒体数据从RTSP Client交接到ffmpeg的过程。
以上代码完成了2个任务,第一个是指定解码缓存的大小(“32768”),第二个是指定了ffmpeg获取多媒体数据的回调函数(fill_iobuffer)以及该回调函数的第一个参数(&Client)。
1 int fill_iobuffer(void * opaque, uint8_t * buf, int bufsize) { 2 size_t size = 0; 3 if(!opaque) return -1; 4 RtspClient * Client = (RtspClient *)opaque; 5 // while(true) { 6 // if(Client->GetMediaData("video", buf, &size, bufsize)) break; 7 // } 8 Client->GetMediaData("video", buf, &size, bufsize); 9 printf("fill_iobuffer size: %u\n", size); 10 return size; 11 }
这个回调函数由ffmpeg指定格式,作用就是将多媒体数据填充进该回调函数的第2个参数指定的缓冲区(buf),第3个参数bufsize指定了该缓冲区的大小,其值就是
AVIOContext * avio = avio_alloc_context(iobuffer, 32768, 0, &Client, fill_iobuffer, NULL, NULL);
指定的"32768",第1个参数opaque就是&Client。在ffmpeg解码的过程中,该回调函数会一直被调用,使参数buf装载音视频数据用于解码。
第三部分:'RTSP Client' send TEARDOWN command to 'RTSP Server'
1 Client.DoTEARDOWN();
向RTSP Server发送TEARDOWN命令,从而结束此次会话。
附录一:
1 extern "C" 2 { 3 #include <libavcodec/avcodec.h> 4 #include <libavformat/avformat.h> 5 #include <libswscale/swscale.h> 6 } 7 8 #include <SDL.h> 9 #include <SDL_thread.h> 10 11 #ifdef __MINGW32__ 12 #undef main /* Prevents SDL from overriding main() */ 13 #endif 14 15 #include <stdio.h> 16 17 // compatibility with newer API 18 #if LIBAVCODEC_VERSION_INT < AV_VERSION_INT(55,28,1) 19 #define av_frame_alloc avcodec_alloc_frame 20 #define av_frame_free avcodec_free_frame 21 #endif 22 23 #include "rtspClient.h" 24 #include <iostream> 25 #include <string> 26 using namespace std; 27 28 // FILE * fp_open; 29 int rtspClientRequest(RtspClient * Client, string url); 30 int fill_iobuffer(void * opaque, uint8_t * buf, int bufsize); 31 32 int fill_iobuffer(void * opaque, uint8_t * buf, int bufsize) { 33 size_t size = 0; 34 if(!opaque) return -1; 35 RtspClient * Client = (RtspClient *)opaque; 36 // while(true) { 37 // if(Client->GetMediaData("video", buf, &size, bufsize)) break; 38 // } 39 Client->GetMediaData("video", buf, &size, bufsize); 40 printf("fill_iobuffer size: %u\n", size); 41 return size; 42 } 43 44 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { 45 AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx = NULL; 46 int i, videoStream; 47 AVCodecContext *pCodecCtxOrig = NULL; 48 AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx = NULL; 49 AVCodec *pCodec = NULL; 50 AVFrame *pFrame = NULL; 51 AVPacket packet; 52 int frameFinished; 53 float aspect_ratio; 54 struct SwsContext *sws_ctx = NULL; 55 56 AVInputFormat *piFmt = NULL; 57 RtspClient Client; 58 59 if(argc != 2) { 60 cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <URL>" << endl; 61 cout << "For example: " << endl; 62 cout << argv[0] << " rtsp://127.0.0.1/ansersion" << endl; 63 return 1; 64 } 65 rtspClientRequest(&Client, argv[1]); 66 67 SDL_Overlay *bmp; 68 SDL_Surface *screen; 69 SDL_Rect rect; 70 SDL_Event event; 71 72 // if(argc < 2) { 73 // fprintf(stderr, "Usage: test <file>\n"); 74 // exit(1); 75 // } 76 // Register all formats and codecs 77 av_register_all(); 78 79 if(SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO | SDL_INIT_AUDIO | SDL_INIT_TIMER)) { 80 fprintf(stderr, "Could not initialize SDL - %s\n", SDL_GetError()); 81 exit(1); 82 } 83 84 // Open video file 85 // if(avformat_open_input(&pFormatCtx, argv[1], NULL, NULL)!=0) 86 // return -1; // Couldn't open file 87 88 // fp_open = fopen("test_packet_recv.h264", "rb+"); 89 pFormatCtx = NULL; 90 pFormatCtx = avformat_alloc_context(); 91 unsigned char * iobuffer = (unsigned char *)av_malloc(32768); 92 AVIOContext * avio = avio_alloc_context(iobuffer, 32768, 0, &Client, fill_iobuffer, NULL, NULL); 93 pFormatCtx->pb = avio; 94 95 if(!avio) { 96 printf("avio_alloc_context error!!!\n"); 97 return -1; 98 } 99 100 if(av_probe_input_buffer(avio, &piFmt, "", NULL, 0, 0) < 0) { 101 printf("av_probe_input_buffer error!\n"); 102 return -1; 103 } else { 104 printf("probe success\n"); 105 printf("format: %s[%s]\n", piFmt->name, piFmt->long_name); 106 } 107 108 cout << "before avformat_open_input" << endl; 109 int err = avformat_open_input(&pFormatCtx, "nothing", NULL, NULL); 110 if(err) { 111 printf("avformat_open_input error: %d\n", err); 112 return -1; 113 } 114 115 cout << "before avformat_find_stream_info" << endl; 116 // Retrieve stream information 117 if(avformat_find_stream_info(pFormatCtx, NULL)<0) { 118 printf("avformat_find_stream_info error!!!\n"); 119 return -1; // Couldn't find stream information 120 } 121 122 // cout << "before av_dump_format" << endl; 123 // Dump information about file onto standard error 124 av_dump_format(pFormatCtx, 0, "", 0); 125 126 // Find the first video stream 127 videoStream=-1; 128 // cout << "before for(i = 0; i < pFormatCtx->nb_streams; i++)" << endl; 129 for(i=0; i<pFormatCtx->nb_streams; i++) 130 if(pFormatCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type==AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) { 131 videoStream=i; 132 break; 133 } 134 if(videoStream==-1) { 135 printf("videoStream error!!!\n"); 136 return -1; // Didn't find a video stream 137 } 138 139 // Get a pointer to the codec context for the video stream 140 pCodecCtxOrig=pFormatCtx->streams[videoStream]->codec; 141 // Find the decoder for the video stream 142 // cout << "before avcodec_find_decoder" << endl; 143 pCodec=avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecCtxOrig->codec_id); 144 if(pCodec==NULL) { 145 fprintf(stderr, "Unsupported codec!\n"); 146 return -1; // Codec not found 147 } 148 149 // Copy context 150 pCodecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(pCodec); 151 // cout << "before avcodec_copy_context" << endl; 152 if(avcodec_copy_context(pCodecCtx, pCodecCtxOrig) != 0) { 153 fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't copy codec context"); 154 return -1; // Error copying codec context 155 } 156 157 // Open codec 158 cout << "before avcodec_open2" << endl; 159 if(avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec, NULL)<0) { 160 printf("avcodec_open2 error!!!\n"); 161 return -1; // Could not open codec 162 } 163 164 // Allocate video frame 165 pFrame=av_frame_alloc(); 166 167 printf("Everything OK\n"); 168 169 // Make a screen to put our video 170 #ifndef __DARWIN__ 171 screen = SDL_SetVideoMode(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, 0, 0); 172 #else 173 screen = SDL_SetVideoMode(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, 24, 0); 174 #endif 175 if(!screen) { 176 fprintf(stderr, "SDL: could not set video mode - exiting\n"); 177 exit(1); 178 } 179 180 // Allocate a place to put our YUV image on that screen 181 bmp = SDL_CreateYUVOverlay(pCodecCtx->width, 182 pCodecCtx->height, 183 SDL_YV12_OVERLAY, 184 screen); 185 186 // initialize SWS context for software scaling 187 sws_ctx = sws_getContext(pCodecCtx->width, 188 pCodecCtx->height, 189 pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, 190 pCodecCtx->width, 191 pCodecCtx->height, 192 PIX_FMT_YUV420P, 193 SWS_BILINEAR, 194 NULL, 195 NULL, 196 NULL 197 ); 198 199 200 201 // Read frames and save first five frames to disk 202 i=0; 203 while(av_read_frame(pFormatCtx, &packet)>=0) { 204 // Is this a packet from the video stream? 205 if(packet.stream_index==videoStream) { 206 // Decode video frame 207 avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx, pFrame, &frameFinished, &packet); 208 209 // Did we get a video frame? 210 if(frameFinished) { 211 SDL_LockYUVOverlay(bmp); 212 213 AVPicture pict; 214 pict.data[0] = bmp->pixels[0]; 215 pict.data[1] = bmp->pixels[2]; 216 pict.data[2] = bmp->pixels[1]; 217 218 pict.linesize[0] = bmp->pitches[0]; 219 pict.linesize[1] = bmp->pitches[2]; 220 pict.linesize[2] = bmp->pitches[1]; 221 222 // Convert the image into YUV format that SDL uses 223 sws_scale(sws_ctx, (uint8_t const * const *)pFrame->data, 224 pFrame->linesize, 0, pCodecCtx->height, 225 pict.data, pict.linesize); 226 227 SDL_UnlockYUVOverlay(bmp); 228 229 rect.x = 0; 230 rect.y = 0; 231 rect.w = pCodecCtx->width; 232 rect.h = pCodecCtx->height; 233 SDL_DisplayYUVOverlay(bmp, &rect); 234 235 } 236 } 237 238 // Free the packet that was allocated by av_read_frame 239 av_free_packet(&packet); 240 SDL_PollEvent(&event); 241 switch(event.type) { 242 case SDL_QUIT: 243 SDL_Quit(); 244 exit(0); 245 break; 246 default: 247 break; 248 } 249 250 } 251 252 // Free the YUV frame 253 av_frame_free(&pFrame); 254 255 // Close the codec 256 avcodec_close(pCodecCtx); 257 avcodec_close(pCodecCtxOrig); 258 259 // Close the video file 260 avformat_close_input(&pFormatCtx); 261 262 Client.DoTEARDOWN(); 263 return 0; 264 } 265 266 int rtspClientRequest(RtspClient * Client, string url) 267 { 268 if(!Client) return -1; 269 270 // cout << "Start play " << url << endl; 271 string RtspUri(url); 272 // string RtspUri("rtsp://192.168.81.145/ansersion"); 273 274 /* Set up rtsp server resource URI */ 275 Client->SetURI(RtspUri); 276 277 /* Send DESCRIBE command to server */ 278 Client->DoDESCRIBE(); 279 280 /* Parse SDP message after sending DESCRIBE command */ 281 Client->ParseSDP(); 282 283 /* Send SETUP command to set up all 'audio' and 'video' 284 * sessions which SDP refers. */ 285 Client->DoSETUP(); 286 287 /* Send PLAY command to play only 'video' sessions.*/ 288 Client->DoPLAY("video"); 289 290 return 0; 291 }
温馨提示:
1, 兼容myRtspClient-1.2.1及以上版本,且仅支持h264,h265视频;
2, 示例源码编译需要SDL和ffmpeg,具体可参见附录二;
3, 博主编译环境为 x86_64位ubuntu 16.04,以供参考。
附录二:
编译ffmpeg:
./configure --disable-yasm
make
编译myRtspClient:
./genMakefiles linux
make
安装SDL:
sudo apt-get install libsdl1.2-dev
配置Makefile:
将FFMPEG_DIR和MYRTSPCLIENT_DIR配置成刚刚编译好的两个目录
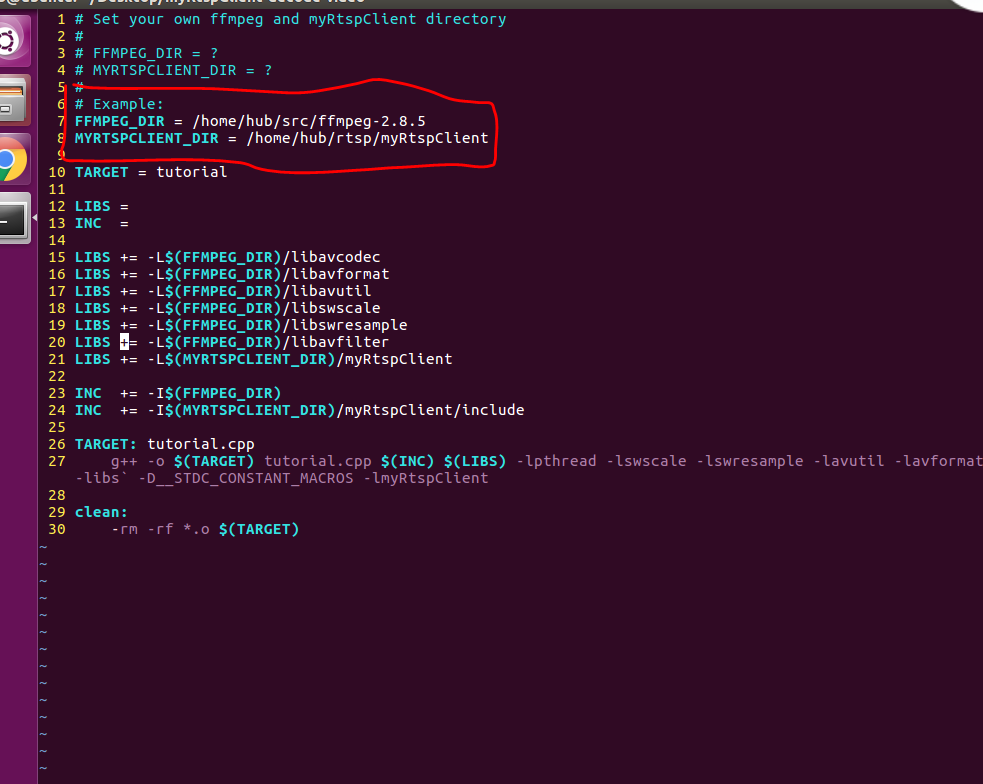
编译示例代码:
make
运行:
./tutorial rtsp://192.168.2.196:8554/ansersion
(192.168.2.196为rtsp服务器)