排序(三)归并排序
参考文档
https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6194356.html
原理:
归并排序(MERGE-SORT)是利用归并的思想实现的排序方法,该算法采用经典的分治(divide-and-conquer)策略(分治法将问题分(divide)成一些小的问题然后递归求解,而治(conquer)的阶段则将分的阶段得到的各答案"修补"在一起,即分而治之)。即把原始数组分成若干子数组,对每一个子数组进行排序,继续把子数组与子数组合并,合并后仍然有序,直到全部合并完,形成有序的数组

合并相邻字列表
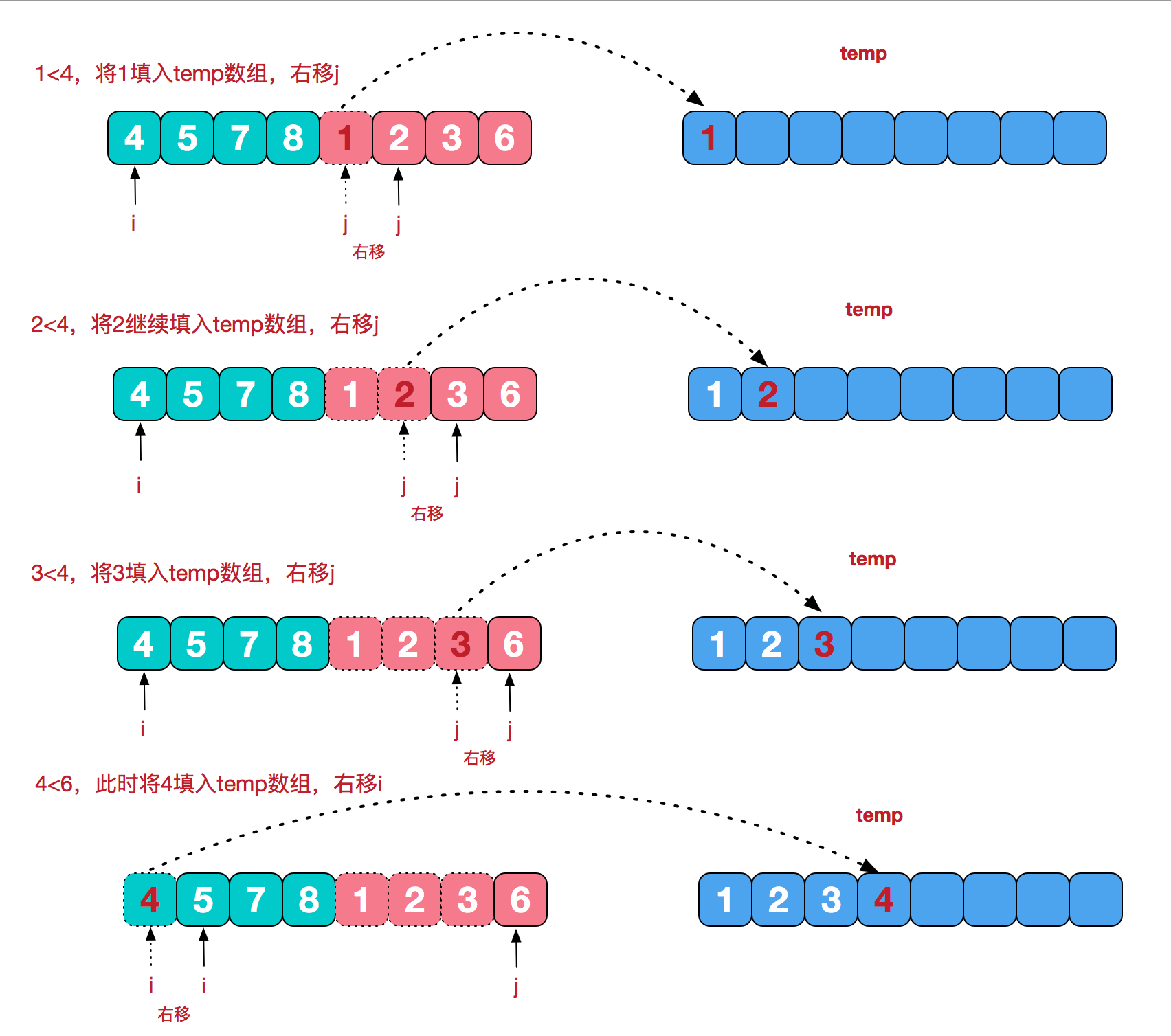
代码实现

public static void mergeSort(int []arr){ int []temp = new int[arr.length];//在排序前,先建好一个长度等于原数组长度的临时数组,避免递归中频繁开辟空间 sort(arr,0,arr.length-1,temp); } private static void sort(int[] arr,int left,int right,int []temp){ if(left<right){ int mid = (left+right)/2; sort(arr,left,mid,temp);//左边归并排序,使得左子序列有序 sort(arr,mid+1,right,temp);//右边归并排序,使得右子序列有序 merge(arr,left,mid,right,temp);//将两个有序子数组合并操作 } } private static void merge(int[] arr,int left,int mid,int right,int[] temp){ int i = left;//左序列指针 int j = mid+1;//右序列指针 int t = 0;//临时数组指针 while (i<=mid && j<=right){ if(arr[i]<=arr[j]){ temp[t++] = arr[i++]; }else { temp[t++] = arr[j++]; } } while(i<=mid){//将左边剩余元素填充进temp中 temp[t++] = arr[i++]; } while(j<=right){//将右序列剩余元素填充进temp中 temp[t++] = arr[j++]; } t = 0; //将temp中的元素全部拷贝到原数组中 while(left <= right){ arr[left++] = temp[t++]; } } }
算法分析
- 时间复杂度 :O(nlogn) 最好最坏均是
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
- 稳定性:稳定
算法优化
应用:
Arrays.sort()采用了一种名为TimSort的排序算法,就是归并排序的优化版本




