20172324 结对编程项目-四则运算 第二周 阶段总结
20172324 结对编程项目-四则运算 第二周 阶段总结
结对对象
- 学号 20172321
- 姓名 吴恒佚
- 伙伴第二周博客:
- 对结对伙伴的评价:感谢小吴同学对我的不离不弃,我这周因为啦啦操耽误了好多,小吴还一直帮助我,感动🙆
项目中自己负责的部分
基本上都是一起讨论完成的,比如比较难的中缀转后缀,我负责的差不多就是随机生成两种类型的题目。
个人贡献度划分
五五开
小组结对编程的照片
相关过程的截图
-
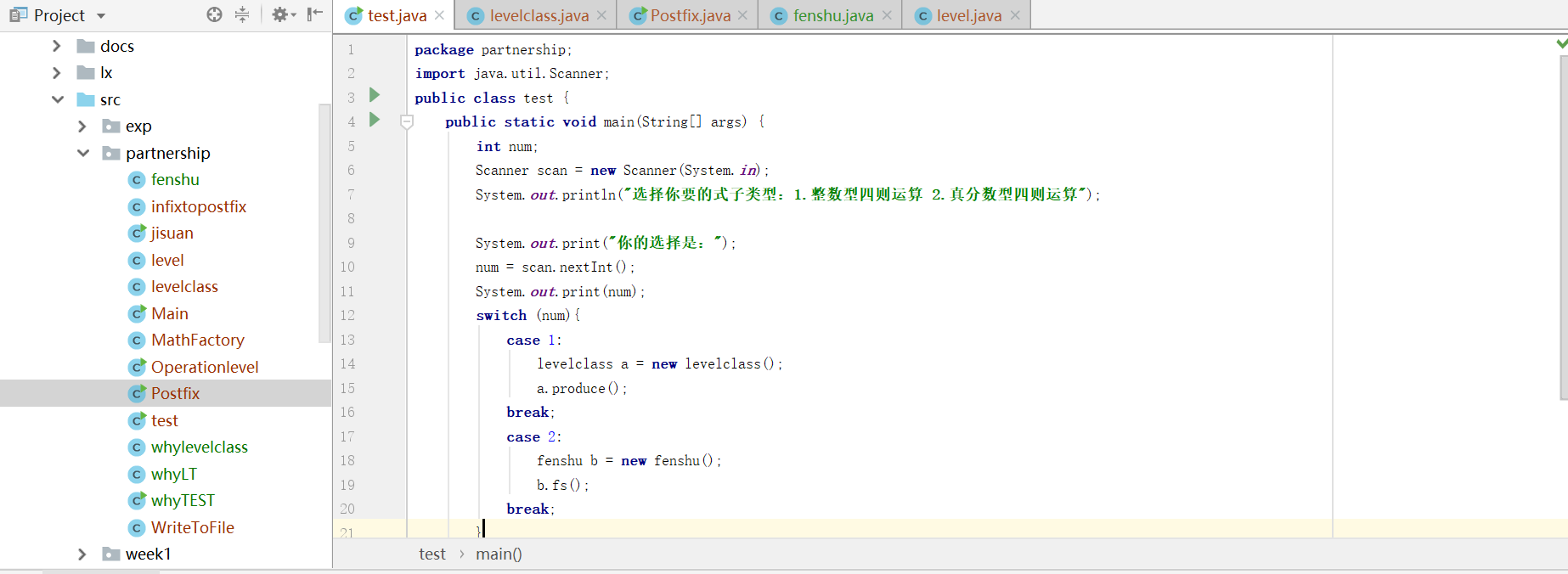
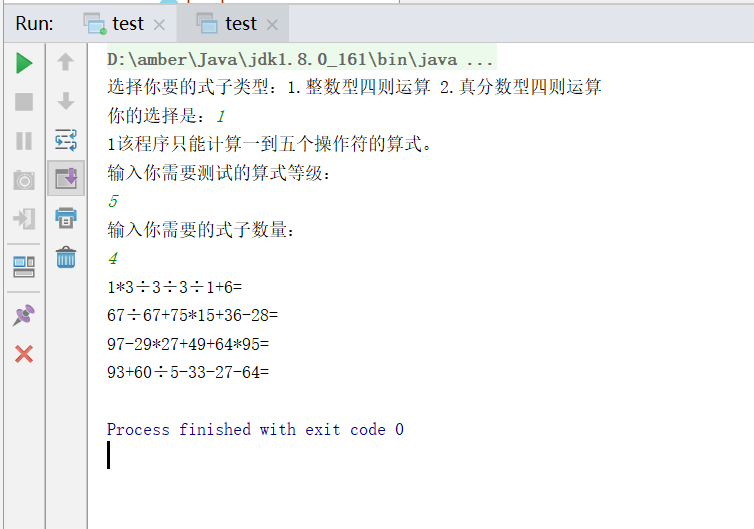
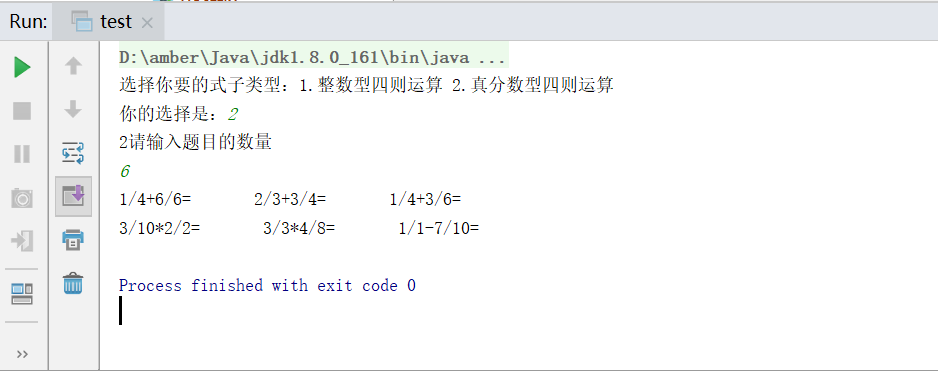
生成题目类驱动类的运行截图
-
后缀表达式计算的驱动类运行截图
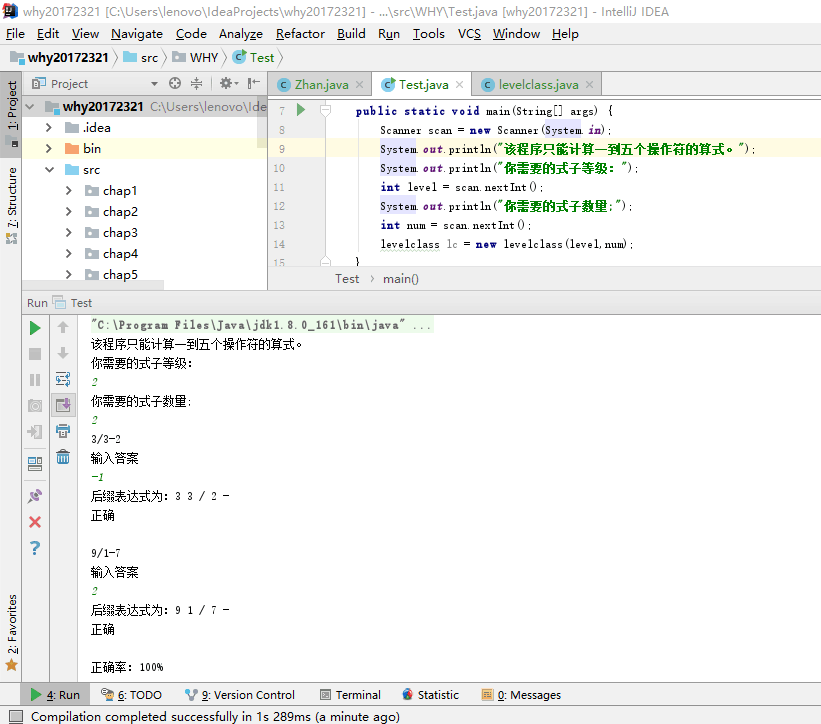

关键代码解释
- 在一个驱动类
test里可以测试两个类,一个是随机生成整数题目的leveltest类,另一个是随机生成真分数型题目的fenshu类
leveltest类代码如下:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class levelclass {
public levelclass(){
char[] operator = new char[]{'+', '-', '*', '÷'};
Random random = new Random();
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int num;
int level;
System.out.println("该程序只能计算一到五个操作符的算式。");
System.out.println("输入你需要测试的算式等级:");
level = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入你需要的式子数量:");
num = scan.nextInt();
switch (level)
{
//一级算式
case 1:
ArrayList<String> expression1 = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
int n = random.nextInt(1) + 1; //1个运算符
int[] number = new int[n + 1];
String ex = new String();
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
number[j] = random.nextInt(100) + 1; //2个数字
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int s = random.nextInt(4);//随机选择某个运算符
ex += String.valueOf(number[j]) + String.valueOf(operator[s]);
if (s == 3) {
number[j + 1] = decide(number[j], number[j + 1]);
}
}
ex += String.valueOf(number[n]);
ex += "=";
expression1.add(ex);
}
for(int ii = 0; ii < expression1.size() ; ii++)
{
System.out.print(expression1.get(ii) + "\n");
}
// System.out.println(expression1);
break;
}
private static int decide(int x,int y){//通过递归实现整除
Random random=new Random();
if(x%y!=0){
y=random.nextInt(100)+1;
return decide(x,y);
}
else{
return y;
}
}
public void produce(){
}
}
因为case是重复的所以只用一个做例子。用户输入的式子等级n在外层循环里创建了一个可以放置n+1个数字的数组,一个内循环是用来给之前创建的数组赋值,另一个内循环将随机选中的数字数组中的某一索引中的值和操作数组中某一索引的值连起来拼成一个表达式。
fenshu类代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class fenshu {
public fenshu() {
String formula = null;
int a, b,c,d;
System.out.println("请输入题目的数量");
Scanner scan2 = new Scanner(System.in);
c = scan2.nextInt();
String sz[] = new String[c];
int x1, x2, m1, m2;
for (d = 0; d < c; d++) {
m1 = 1 + (int) (Math.random() * 10);
x1 = 1 + (int) (Math.random() * m1);
m2 = 1 + (int) (Math.random() * 10);
x2 = 1 + (int) (Math.random() * m2);
int operate = (int) (Math.random() * 3);//生成运算符
if (operate == 0) {
b = x1 * m2 + x2 * m1;
a = m1 * m2;
formula = yuefen(b, a);
System.out.print(x1 + "/" + m1 + "+" + x2 + "/" + m2 + "= ");
}
if (operate == 1) {
b = x1 * m2 - x2 * m1;
a = m1 * m2;
formula = yuefen(b, a);
System.out.print(x1 + "/" + m1 + "-" + x2 + "/" + m2 + "= ");
}
if (operate == 2) {
b = x1 * x2;
a = m1 * m2;
formula = yuefen(b, a);
System.out.print(x1 + "/" + m1 + "*" + x2 + "/" + m2 + "= ");
}
if (operate == 3) {
b = m1 * x2;
a = m2 * x1;
formula = yuefen(b, a);
System.out.print(x1 + "/" + m1 + "/" + x2 + "/" + m2 + "= ");
}
if ((d + 1) % 3 == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
sz[d] = formula;
}
}
public static String yuefen(int a,int b){
int y = 1;
for(int i=a;i>=1;i--){
if(a%i==0&&b%i==0){
y = i;
break;
}
}
int z = a/y;
int m = b/y;
if(z==0) {
return "0";
}
return ""+z+"/"+m;
}
public void fs(){
}
}
- 对正误的判断并且统计正确率
int wrong = 0;
for(String st :expression)
{
System.out.println(st);
String str;
str = st;
Zhan lt = new Zhan();
List<String> list = lt.work(str);
List<String> list2 = lt.InfixToPostfix(list);
System.out.println("输入答案");
int daan = scan.nextInt();
System.out.print("后缀表达式为:");
lt.printList(list2);
System.out.println(" ");
if(daan != lt.doCal(list2)){
System.out.println("错误 正确答案为:"+lt.doCal(list2));
System.out.println(" ");
wrong = wrong+1;}
else{
System.out.println("正确");
System.out.println(" ");}
}
int sum=100-(wrong*100/num);
System.out.println("正确率:"+sum+"%");
遇到的困难及解决办法
- 问题一:
问题就是当客户输入测试等级3时,出来的题目会是客户需要的题目输入的三倍,如图所示
当客户输入测试等级4时,出来的题目会是客户需要的题目输入的两倍,如图所示
其他的情况下都是正确的,我debug发现,在case3和case4时程序会分别循环3遍和两遍。可是在这两个case里的代码和case1、2、5中的代码是一样的。我和吴恒佚想了很久都不知道为什么。
这是上周遇到的一个问题。
- 问题一解决方案:why发现是case3、4、5都没有写break,case5没有影响,但是其他的就出现上图所示的问题了。
- 问题二:这周的一个bug,很难遇到,是在偶然中发现的,当生成的题目一个÷后连着一个x时,计算结果就会出现问题,例如5÷5x25时,给出的正确答案不是25而是1。
- 问题二解决办法:其实不是解决办法,只有一个思路,大概是因为除法乘法同时出现时会先计算乘法,然后变成一个类似于真分数计算的表达式,最后又取整数部分当作计算结果了。

项目地址
PSP时间统计:
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 50 | ||
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 60 | ||
| Development | 开发 | 600 | ||
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 150 | ||
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 45 | ||
| Design UML | 设计项目UML类图 | 20 | ||
| Coding | 具体编码 | 180 | ||
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 60 | ||
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 100 | ||
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量(实际时间) | 30 | ||
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | ||
| 合计 | 1315 |

