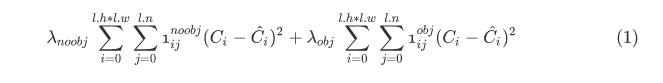YOLO v2 损失函数源码分析
-
首先来看一看region_layer 都定义了那些属性值:
layer make_region_layer(int batch, int w, int h, int n, int classes, int coords) { layer l = {0}; l.type = REGION; l.n = n; // anchors 的个数, 文章中选择为5 l.batch = batch; // batchsize l.h = h; l.w = w; l.c = n*(classes + coords + 1); // 输出的通道数 l.out_w = l.w; l.out_h = l.h; l.out_c = l.c; l.classes = classes; // 检测的类别数 l.coords = coords; l.cost = calloc(1, sizeof(float)); l.biases = calloc(n*2, sizeof(float)); // anchors的存储位置,一个anchor对应两个值 l.bias_updates = calloc(n*2, sizeof(float)); l.outputs = h*w*n*(classes + coords + 1); //输出tensor的存储空间大小 13*13*5*(20+4+1) l.inputs = l.outputs; l.truths = 30*(l.coords + 1); // ***********注1************ l.delta = calloc(batch*l.outputs, sizeof(float)); // 批量梯度 l.output = calloc(batch*l.outputs, sizeof(float));// 批量输出tensor的存储空间 int i; for(i = 0; i < n*2; ++i){ l.biases[i] = .5;//anchors的默认值设为0.5 } l.forward = forward_region_layer; // 前向计算函数 l.backward = backward_region_layer;//反向计算函数,这里delta在前向计算函数中获得了,所以该函数为空 #ifdef GPU l.forward_gpu = forward_region_layer_gpu; l.backward_gpu = backward_region_layer_gpu; l.output_gpu = cuda_make_array(l.output, batch*l.outputs); l.delta_gpu = cuda_make_array(l.delta, batch*l.outputs); #endif fprintf(stderr, "detection\n"); srand(0); return l; }
1 layer parse_region(list *options, size_params params) 2 { 3 int coords = option_find_int(options, "coords", 4); 4 int classes = option_find_int(options, "classes", 20); 5 int num = option_find_int(options, "num", 1);// 每一个cell对应的anchors个数, 文中num=5 6 7 layer l = make_region_layer(params.batch, params.w, params.h, num, classes, coords); 8 assert(l.outputs == params.inputs); 9 10 l.log = option_find_int_quiet(options, "log", 0); // 是否计算log,这个标志定义了,却未使用 11 l.sqrt = option_find_int_quiet(options, "sqrt", 0); // 输出预测值的w,h是否开方 12 13 l.softmax = option_find_int(options, "softmax", 0); // 采用softmax分类 14 l.background = option_find_int_quiet(options, "background", 0); 15 l.max_boxes = option_find_int_quiet(options, "max",30); //******** 注2 ************** 16 // 图片中最多真实boxes的个数,这个应该和make_region_layer中的30有关 17 l.jitter = option_find_float(options, "jitter", .2);//抖动,cfg中设置为.3 18 l.rescore = option_find_int_quiet(options, "rescore",0); //******** 注3 ************** 19 20 l.thresh = option_find_float(options, "thresh", .5); // .6 大于该值的时候认为包含目标 21 l.classfix = option_find_int_quiet(options, "classfix", 0); 22 l.absolute = option_find_int_quiet(options, "absolute", 0); // 1 23 l.random = option_find_int_quiet(options, "random", 0); // 1 24 25 l.coord_scale = option_find_float(options, "coord_scale", 1); // 坐标损失的权重,1 26 l.object_scale = option_find_float(options, "object_scale", 1); // 有目标的权重, 5 27 l.noobject_scale = option_find_float(options, "noobject_scale", 1); // 无目标的权重, 1 28 l.mask_scale = option_find_float(options, "mask_scale", 1); 29 l.class_scale = option_find_float(options, "class_scale", 1); // 类别权重, 1 30 l.bias_match = option_find_int_quiet(options, "bias_match",0); // 1 31 // 下面几句未执行 32 char *tree_file = option_find_str(options, "tree", 0); 33 if (tree_file) l.softmax_tree = read_tree(tree_file); 34 char *map_file = option_find_str(options, "map", 0); 35 if (map_file) l.map = read_map(map_file); 36 37 char *a = option_find_str(options, "anchors", 0); 38 if(a){ 39 int len = strlen(a); 40 int n = 1; 41 int i; 42 for(i = 0; i < len; ++i){ 43 if (a[i] == ',') ++n; 44 } 45 for(i = 0; i < n; ++i){ 46 float bias = atof(a); 47 l.biases[i] = bias; 48 a = strchr(a, ',')+1; 49 } 50 } 51 // l.biases存放了anchor的数值 52 return l; 53 }
注2: 应该和注1 相关,即再调用make_region_layer方法之前定义,并将后面的30都替换成 l.max_boxes
注3: rescore是一个标志位,推测是regression of confidence score的表示。 当该标志为1的时候,在计算损失时需要回归出被选择的anchor与真实target的iou,否则当该标志为0的时候,直接认为置信度为1。源码中该值在cfg中设置为1.
在看这部分源码之前,先了解一下数据的存储结构,方便看懂源码中寻找各种值得索引。
首先net.truth,及真实target的存储格式 : x,y,w,h,class,x,y,w,h,class,...
然后是*output的存储格式: 维度 w->h>entry->n->batch, 其中entry对应着每个anchor生成的向量维度,文章中就是长度为(4+1+20)的向量,该向量中存储顺序为 box, confidence,classes
1 void forward_region_layer(const layer l, network net) 2 { 3 int i,j,b,t,n; 4 memcpy(l.output, net.input, l.outputs*l.batch*sizeof(float)); 5 6 #ifndef GPU 7 for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b){ 8 for(n = 0; n < l.n; ++n){ 9 int index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h, 0); 10 activate_array(l.output + index, 2*l.w*l.h, LOGISTIC); 11 index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h, l.coords); 12 fprintf(stderr,"background %s \n", l.background) 13 if(!l.background) activate_array(l.output + index, l.w*l.h, LOGISTIC); 14 } 15 } 16 if (l.softmax_tree){ 17 int i; 18 int count = l.coords + 1; 19 for (i = 0; i < l.softmax_tree->groups; ++i) { 20 int group_size = l.softmax_tree->group_size[i]; 21 softmax_cpu(net.input + count, group_size, l.batch, l.inputs, l.n*l.w*l.h, 1, l.n*l.w*l.h, l.temperature, l.output + count); 22 count += group_size; 23 } 24 } else if (l.softmax){ 25 int index = entry_index(l, 0, 0, l.coords + !l.background); 26 softmax_cpu(net.input + index, l.classes + l.background, l.batch*l.n, l.inputs/l.n, l.w*l.h, 1, l.w*l.h, 1, l.output + index); 27 } 28 #endif 29 30 memset(l.delta, 0, l.outputs * l.batch * sizeof(float)); // 梯度清零 31 if(!net.train) return; // 非训练模式直接返回 32 float avg_iou = 0; // average iou 33 float recall = 0; // 召回数 34 float avg_cat = 0; // 平均的类别辨识率 35 float avg_obj = 0; 36 float avg_anyobj = 0; 37 int count = 0; // 该batch内检测的target数 38 int class_count = 0; 39 *(l.cost) = 0; // 损失 40 for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b) { // 遍历batch内数据 41 if(l.softmax_tree){// 不执行 42 int onlyclass = 0; 43 for(t = 0; t < 30; ++t){ 44 box truth = float_to_box(net.truth + t*(l.coords + 1) + b*l.truths, 1); 45 if(!truth.x) break; 46 int class = net.truth[t*(l.coords + 1) + b*l.truths + l.coords]; 47 float maxp = 0; 48 int maxi = 0; 49 if(truth.x > 100000 && truth.y > 100000){ 50 for(n = 0; n < l.n*l.w*l.h; ++n){ 51 int class_index = entry_index(l, b, n, l.coords + 1); 52 int obj_index = entry_index(l, b, n, l.coords); 53 float scale = l.output[obj_index]; 54 l.delta[obj_index] = l.noobject_scale * (0 - l.output[obj_index]); 55 float p = scale*get_hierarchy_probability(l.output + class_index, l.softmax_tree, class, l.w*l.h); 56 if(p > maxp){ 57 maxp = p; 58 maxi = n; 59 } 60 } 61 int class_index = entry_index(l, b, maxi, l.coords + 1); 62 int obj_index = entry_index(l, b, maxi, l.coords); 63 delta_region_class(l.output, l.delta, class_index, class, l.classes, l.softmax_tree, l.class_scale, l.w*l.h, &avg_cat); 64 if(l.output[obj_index] < .3) l.delta[obj_index] = l.object_scale * (.3 - l.output[obj_index]); 65 else l.delta[obj_index] = 0; 66 l.delta[obj_index] = 0; 67 ++class_count; 68 onlyclass = 1; 69 break; 70 } 71 } 72 if(onlyclass) continue; 73 } 74 for (j = 0; j < l.h; ++j) { 75 for (i = 0; i < l.w; ++i) { 76 for (n = 0; n < l.n; ++n) { 77 int box_index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 0); 78 //带入 entry_index, 由output tensor的存储格式可以知道这里是第n类anchor在(i,j)上对应box的首地址 79 box pred = get_region_box(l.output, l.biases, n, box_index, i, j, l.w, l.h, l.w*l.h); 80 // 在cell(i,j)上相对于anchor n的预测结果, 相对于feature map的值 81 float best_iou = 0; 82 for(t = 0; t < 30; ++t){//net.truth存放的是真实数据 83 // net.truth存储格式:x,y,w,h,c,x,y,w,h,c,.... 84 box truth = float_to_box(net.truth + t*(l.coords + 1) + b*l.truths, 1); 85 //读取一个真实目标框 86 if(!truth.x) break;//遍历完所有真实box则跳出循环 87 float iou = box_iou(pred, truth);//计算iou 88 if (iou > best_iou) { 89 best_iou = iou;//找到与当前预测box的最大iou 90 } 91 } 92 int obj_index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, l.coords); 93 // 存储第n个anchor在cell (i,j)的预测的confidence的index 94 avg_anyobj += l.output[obj_index]; // 有目标的概率 95 96 l.delta[obj_index] = l.noobject_scale * (0 - l.output[obj_index]); 97 // *********** 注4 ********** 98 // 所有的predict box都当做noobject,计算其损失梯度,主要是为了计算速度考虑 99 if(l.background) l.delta[obj_index] = l.noobject_scale * (1 - l.output[obj_index]);//未执行 100 if (best_iou > l.thresh) {//该预测框中有目标 101 // *********** 注5 *********** 102 l.delta[obj_index] = 0; 103 } 104 105 if(*(net.seen) < 12800){// net.seen 已训练样本的个数 106 // *********** 注6 *********** 107 box truth = {0}; // 当前cell为中心对应的第n个anchor的box 108 truth.x = (i + .5)/l.w; // cell的中点 // 对应tx=0.5 109 truth.y = (j + .5)/l.h; //ty=0.5 110 truth.w = l.biases[2*n]/l.w; //相对于feature map的大小 // tw=0 111 truth.h = l.biases[2*n+1]/l.h; //th=0 112 delta_region_box(truth, l.output, l.biases, n, box_index, i, j, l.w, l.h, l.delta, .01, l.w*l.h); 113 //将预测的tx,ty,tw,th和上面的box差值存入l.delta 114 } 115 } 116 } 117 } 118 for(t = 0; t < 30; ++t){ 119 box truth = float_to_box(net.truth + t*(l.coords + 1) + b*l.truths, 1); 120 //对应的真实值,归一化的真实值 121 122 if(!truth.x) break; 123 float best_iou = 0; 124 int best_n = 0; 125 i = (truth.x * l.w);// 类型的强制转换,计算该truth所在的cell的i,j坐标 126 j = (truth.y * l.h); 127 //printf("%d %f %d %f\n", i, truth.x*l.w, j, truth.y*l.h); 128 box truth_shift = truth; 129 truth_shift.x = 0; 130 truth_shift.y = 0; 131 //printf("index %d %d\n",i, j); 132 for(n = 0; n < l.n; ++n){ // 遍历对应的cell预测出的n个anchor 133 // 即通过该cell对应的anchors与truth的iou来判断使用哪一个anchor产生的predict来回归 134 int box_index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 0); 135 box pred = get_region_box(l.output, l.biases, n, box_index, i, j, l.w, l.h, l.w*l.h); 136 // 预测box,归一化的值 137 //下面这几句是将truth与anchor中心对齐后,计算anchor与truch的iou 138 if(l.bias_match){ // ********* 注7 *************** 139 pred.w = l.biases[2*n]/l.w; // 因为是和anchor比较,所以直接使用anchor的相对大小 140 pred.h = l.biases[2*n+1]/l.h; 141 } 142 //printf("pred: (%f, %f) %f x %f\n", pred.x, pred.y, pred.w, pred.h); 143 pred.x = 0; 144 pred.y = 0; 145 float iou = box_iou(pred, truth_shift); 146 if (iou > best_iou){ 147 best_iou = iou; 148 best_n = n;// 最优iou对应的anchor索引,然后使用该anchor预测的predict box计算与真实box的误差 149 } 150 } 151 //printf("%d %f (%f, %f) %f x %f\n", best_n, best_iou, truth.x, truth.y, truth.w, truth.h); 152 153 int box_index = entry_index(l, b, best_n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 0); 154 float iou = delta_region_box(truth, l.output, l.biases, best_n, box_index, i, j, l.w, l.h, l.delta, l.coord_scale * (2 - truth.w*truth.h), l.w*l.h); 155 // 注意这里的关于box的损失权重 ************* 注 8 ********************** 156 if(l.coords > 4){// 不执行 157 int mask_index = entry_index(l, b, best_n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 4); 158 delta_region_mask(net.truth + t*(l.coords + 1) + b*l.truths + 5, l.output, l.coords - 4, mask_index, l.delta, l.w*l.h, l.mask_scale); 159 } 160 if(iou > .5) recall += 1;// 如果iou> 0.5, 认为找到该目标,召回数+1 161 avg_iou += iou; 162 163 //l.delta[best_index + 4] = iou - l.output[best_index + 4]; 164 int obj_index = entry_index(l, b, best_n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, l.coords);// 对应predict预测的confidence 165 avg_obj += l.output[obj_index]; 166 l.delta[obj_index] = l.object_scale * (1 - l.output[obj_index]);//有目标时的损失 167 if (l.rescore) { //定义了rescore表示同时对confidence score进行回归 168 l.delta[obj_index] = l.object_scale * (iou - l.output[obj_index]); 169 } 170 if(l.background){//不执行 171 l.delta[obj_index] = l.object_scale * (0 - l.output[obj_index]); 172 } 173 174 int class = net.truth[t*(l.coords + 1) + b*l.truths + l.coords];// 真实类别 175 if (l.map) class = l.map[class];//不执行 176 int class_index = entry_index(l, b, best_n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, l.coords + 1);//预测的class向量首地址 177 delta_region_class(l.output, l.delta, class_index, class, l.classes, l.softmax_tree, l.class_scale, l.w*l.h, &avg_cat); 178 ++count; 179 ++class_count; 180 } 181 } 182 //printf("\n"); 183 *(l.cost) = pow(mag_array(l.delta, l.outputs * l.batch), 2);//MSEloss 184 printf("Region Avg IOU: %f, Class: %f, Obj: %f, No Obj: %f, Avg Recall: %f, count: %d\n", avg_iou/count, avg_cat/class_count, avg_obj/count, avg_anyobj/(l.w*l.h*l.n*l.batch), recall/count, count); 185 }
注6:
>Also, in every image many grid cells do not contain any object. This pushes the donfidence scores of thos cells towards zero, ofthen overpowering the gradient from cells that do contain objects. This can lead to model instability, causing training to diverge early on.
在yolo中有这么一段
> Sum-squred error also equally weights errors in large boxes and small boxes. Our error metric should reflect that small derivations in large boxes matter less than in small boxes. To partially address this we predict the square root of the bounding box width and height instead of the width and height directly.
即yolo v1中使用w和h的开方还和该问题,而在yolo v2中则通过赋值一个和w,h相关的权重函数达到该目的。
3. 所以总结起来,代码中计算的损失包括:其中最后一项只在训练初期使用

-
计算包含目标和不包含目标的anchors的iou损失
-
12800样本之前计算未预测到target的anchors的梯度
-
针对于每一个target,计算最接近的anchor的coord梯度
-
计算类别预测的损失和梯度。