《Entity Framework 6 Recipes》中文翻译系列 (46) ------ 第八章 POCO之领域对象测试和仓储测试
翻译的初衷以及为什么选择《Entity Framework 6 Recipes》来学习,请看本系列开篇
8-8 测试领域对象
问题
你想为领域对象创建单元测试。
这主要用于,测试特定的数据访问功能。
解决方案
对于这个解决方案,使用POCO模板来创建你的实体。使用POC模板能减少你需要编写的代码量,还能让你的解决方案非常清晰。当然,在解决方案中,你将运用手工创建的POCO类和下面的步骤。
假设你有如图8-9所示的模型。
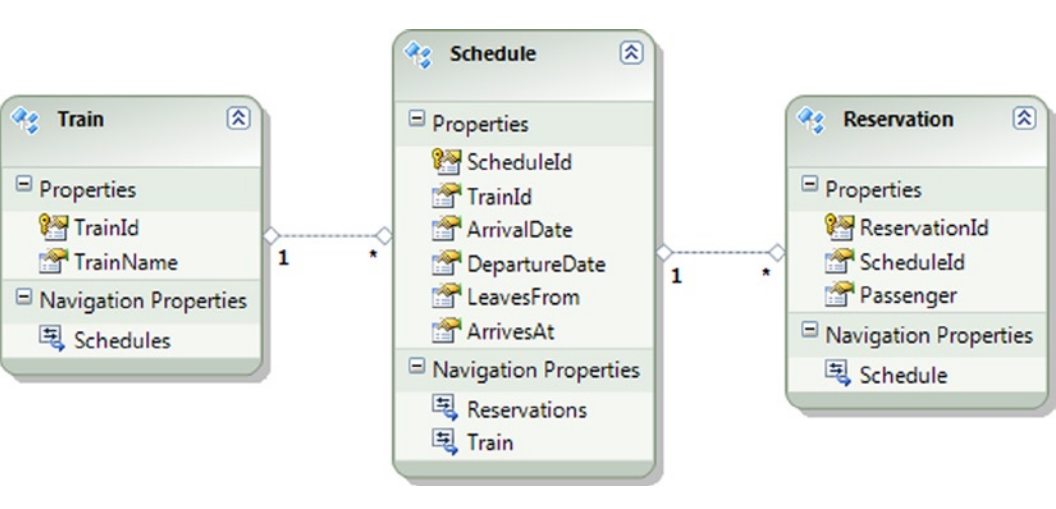
图8-9. 一个包含reservation、schedule和train的模型
这个模型表示预订火车出行。每个预定都是一个特定的出行计划。按下面的步骤创建模型和为应用准备单元测试:
1、创建一个空的解决方案。右键解决方案,选择Add(新增) ➤New Project(新建项目)。添加一个类库项目。将它命名为TrainReservation;
2、右键TrainReservation项目,选择Add(新增) ➤New Item(新建项)。添加一个ADO.NET实体数据模型。导入表Train,Schedule和Reservation。最终的模型如图8-9所示。
3、添加一个Ivalidate接口和ChangeAction枚举,如代码清单8-11所示。
代码清单8-11. IValidate接口
public enum ChangeAction { Insert, Update, Delete } interface IValidate { void Validate(ChangeAction action); }
4、将代码8-12中的代码添加到项目中,它添加了类Reservation和Schedule的验证代码(实现接口IValidate)。
代码清单8-12. 类Reservation和Schedule类实现IValidate接口
1 public partial class Reservation : IValidate 2 { 3 public void Validate(ChangeAction action) 4 { 5 if (action == ChangeAction.Insert) 6 { 7 if (Schedule.Reservations.Count(r => 8 r.ReservationId != ReservationId && 9 r.Passenger == this.Passenger) > 0) 10 throw new InvalidOperationException( 11 "Reservation for the passenger already exists"); 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 16 public partial class Schedule : IValidate 17 { 18 public void Validate(ChangeAction action) 19 { 20 if (action == ChangeAction.Insert) 21 { 22 if (ArrivalDate < DepartureDate) 23 { 24 throw new InvalidOperationException( 25 "Arrival date cannot be before departure date"); 26 } 27 28 if (LeavesFrom == ArrivesAt) 29 { 30 throw new InvalidOperationException( 31 "Can't leave from and arrive at the same location"); 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 }
5、使用代码清单8-13中的代码重写DbContext中的SaveChanges()方法,这将允许你在保存数据到数据库前验证更改。
代码清单8-13. 重写SaveChages()方法
1 public override int SaveChanges() 2 { 3 this.ChangeTracker.DetectChanges(); 4 var entries = from e in this.ChangeTracker.Entries().Where(e => e.State == (System.Data.Entity.EntityState.Added | EntityState.Modified | EntityState.Deleted)) 5 where (e.Entity != null) && 6 (e.Entity is IValidate) 7 select e; 8 foreach (var entry in entries) 9 { 10 switch (entry.State) 11 { 12 case EntityState.Added: 13 ((IValidate)entry.Entity).Validate(ChangeAction.Insert); 14 break; 15 case EntityState.Modified: 16 ((IValidate)entry.Entity).Validate(ChangeAction.Update); 17 break; 18 case EntityState.Deleted: 19 ((IValidate)entry.Entity).Validate(ChangeAction.Delete); 20 break; 21 } 22 } 23 return base.SaveChanges(); 24 }
6、使用代码清单8-14中的代码创建IReservationContext接口,我们将使用这个接口来帮助测试。它是一个虚假的上下文对象,它不会将更改真正地保存到数据库。
代码清单8-14. 使用接口IReservationContext来定义DbContext中需要的方法
public interface IReservationContext : IDisposable { IDbSet<Train> Trains { get; } IDbSet<Schedule> Schedules { get; } IDbSet<Reservation> Reservations { get; } int SaveChanges(); }
7、POCO模板生成了POCO类和实现了ObjectContext的上下文类。我们需要这个上下文类实现IReservationContext接口。 为了实现这个要求,我们编辑Recipe8.Context.tt模板文件,在生成上下文对象名称处添加IReservationContext。 这一行完整代码如下:
<#=Accessibility.ForType(container)#> partial class <#=code.Escape(container)#> : DbContext,IReservationContext
8、使用代码清单8-15创建仓储类,这个类的构造函数接受一个IReservationContext类型的参数。
代码清单8-15. 类ReservationRepository的构造函数接受一个IReservationContext类型的参数
1 public class ReservationRepository 2 { 3 private IReservationContext _context; 4 5 public ReservationRepository(IReservationContext context) 6 { 7 if (context == null) 8 throw new ArgumentNullException("context is null"); 9 _context = context; 10 } 11 public void AddTrain(Train train) 12 { 13 _context.Trains.Add(train); 14 } 15 16 public void AddSchedule(Schedule schedule) 17 { 18 _context.Schedules.Add(schedule); 19 } 20 21 public void AddReservation(Reservation reservation) 22 { 23 _context.Reservations.Add(reservation); 24 } 25 26 public void SaveChanges() 27 { 28 _context.SaveChanges(); 29 } 30 31 public List<Schedule> GetActiveSchedulesForTrain(int trainId) 32 { 33 var schedules = from r in _context.Schedules 34 where r.ArrivalDate.Date >= DateTime.Today && 35 r.TrainId == trainId 36 select r; 37 return schedules.ToList(); 38 } 39 }
9、右键解决方案,选择Add(新增) ➤New Project(新建项目)。添加一个测试项目到解决方案。将这个项目命名为Tests,并添加System.Data.Entity的引用。
10、使用代码清单8-16,创建一个虚拟对象集和一个虚拟的DbContext,以方便你在没有数据库的情况下隔离测试业务规则。
代码清单8-16.实现虚拟对象集和虚拟的上下文对象
1 public class FakeDbSet<T> : IDbSet<T> 2 where T : class 3 { 4 HashSet<T> _data; 5 IQueryable _query; 6 7 public FakeDbSet() 8 { 9 _data = new HashSet<T>(); 10 _query = _data.AsQueryable(); 11 } 12 13 public virtual T Find(params object[] keyValues) 14 { 15 throw new NotImplementedException("Derive from FakeDbSet<T> and override Find"); 16 } 17 18 public T Add(T item) 19 { 20 _data.Add(item); 21 return item; 22 } 23 24 public T Remove(T item) 25 { 26 _data.Remove(item); 27 return item; 28 } 29 30 public T Attach(T item) 31 { 32 _data.Add(item); 33 return item; 34 } 35 36 public T Detach(T item) 37 { 38 _data.Remove(item); 39 return item; 40 } 41 42 public T Create() 43 { 44 return Activator.CreateInstance<T>(); 45 } 46 47 public TDerivedEntity Create<TDerivedEntity>() where TDerivedEntity : class, T 48 { 49 return Activator.CreateInstance<TDerivedEntity>(); 50 } 51 52 public System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.DbLocalView<T> Local 53 { 54 get { return null; } 55 } 56 57 public System.Threading.Tasks.Task<T> FindAsync(System.Threading.CancellationToken token,params object[] keyValues) 58 { 59 throw new NotImplementedException("Derive from FakeDbSet<T> and override Find"); 60 } 61 62 Type IQueryable.ElementType 63 { 64 get { return _query.ElementType; } 65 } 66 System.Linq.Expressions.Expression IQueryable.Expression 67 { 68 get { return _query.Expression; } 69 } 70 71 IQueryProvider IQueryable.Provider 72 { 73 get { return _query.Provider; } 74 } 75 System.Collections.IEnumerator System.Collections.IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() 76 { 77 return _data.GetEnumerator(); 78 } 79 IEnumerator<T> IEnumerable<T>.GetEnumerator() 80 { 81 return _data.GetEnumerator(); 82 } 83 } 84 public class FakeReservationContext : IReservationContext, IDisposable 85 { 86 private IDbSet<Train> trains; 87 private IDbSet<Schedule> schedules; 88 private IDbSet<Reservation> reservations; 89 public FakeReservationContext() 90 { 91 trains = new FakeDbSet<Train>(); 92 schedules = new FakeDbSet<Schedule>(); 93 reservations = new FakeDbSet<Reservation>(); 94 } 95 96 public IDbSet<Train> Trains 97 { 98 get { return trains; } 99 } 100 101 public IDbSet<Schedule> Schedules 102 { 103 get { return schedules; } 104 } 105 106 public IDbSet<Reservation> Reservations 107 { 108 get { return reservations; } 109 } 110 111 public int SaveChanges() 112 { 113 foreach (var schedule in Schedules.Cast<IValidate>()) 114 { 115 schedule.Validate(ChangeAction.Insert); 116 } 117 foreach (var reservation in Reservations.Cast<IValidate>()) 118 { 119 reservation.Validate(ChangeAction.Insert); 120 } 121 return 1; 122 } 123 public void Dispose() 124 { 125 } 126 }
11、我们不想使用真正的数据库来测试,所以我们需要创建一个虚拟的DbContext,用它来模拟DbContext,它使用内存集合来扮演我们的数据存储。将代码清单8-17中的单元测试代码添加到项目中。
代码清单8-18. 我们测试项目中的代码清单
1 [TestClass] 2 public class ReservationTest 3 { 4 private IReservationContext _context; 5 6 [TestInitialize] 7 public void TestSetup() 8 { 9 var train = new Train { TrainId = 1, TrainName = "Polar Express" }; 10 var schedule = new Schedule 11 { 12 ScheduleId = 1, 13 Train = train, 14 ArrivalDate = DateTime.Now, 15 DepartureDate = DateTime.Today, 16 LeavesFrom = "Dallas", 17 ArrivesAt = "New York" 18 }; 19 var reservation = new Reservation 20 { 21 ReservationId = 1, 22 Passenger = "Phil Marlowe", 23 Schedule = schedule 24 }; 25 _context = new FakeReservationContext(); 26 var repository = new ReservationRepository(_context); 27 repository.AddTrain(train); 28 repository.AddSchedule(schedule); 29 repository.AddReservation(reservation); 30 repository.SaveChanges(); 31 } 32 33 [TestMethod] 34 [ExpectedException(typeof(InvalidOperationException))] 35 public void TestForDuplicateReservation() 36 { 37 var repository = new ReservationRepository(_context); 38 var schedule = repository.GetActiveSchedulesForTrain(1).First(); 39 var reservation = new Reservation 40 { 41 ReservationId = 2, 42 Schedule = schedule, 43 Passenger = "Phil Marlowe" 44 }; 45 repository.AddReservation(reservation); 46 repository.SaveChanges(); 47 } 48 49 [TestMethod] 50 [ExpectedException(typeof(InvalidOperationException))] 51 public void TestForArrivalDateGreaterThanDepartureDate() 52 { 53 var repository = new ReservationRepository(_context); 54 var schedule = new Schedule 55 { 56 ScheduleId = 2, 57 TrainId = 1, 58 ArrivalDate = DateTime.Today, 59 DepartureDate = DateTime.Now, 60 ArrivesAt = "New York", 61 LeavesFrom = "Chicago" 62 }; 63 repository.AddSchedule(schedule); 64 repository.SaveChanges(); 65 } 66 67 [TestMethod] 68 [ExpectedException(typeof(InvalidOperationException))] 69 public void TestForArrivesAndLeavesFromSameLocation() 70 { 71 var repository = new ReservationRepository(_context); 72 var schedule = new Schedule 73 { 74 ScheduleId = 3, 75 TrainId = 1, 76 ArrivalDate = DateTime.Now, 77 DepartureDate = DateTime.Today, 78 ArrivesAt = "Dallas", 79 LeavesFrom = "Dallas" 80 }; 81 repository.AddSchedule(schedule); 82 repository.SaveChanges(); 83 } 84 } 85 }
测试项目有三个单元测试,它测试下面几个业务规则:
1、一个乘客不能超过一个出行预定;
2、到达时间必须晚于出发时间;
3、出发地和目的地不能相同;
原理
我们使用相当数量的代码创建了一个完整的解决方案,它包含一个接口(IReservationContext),我们用它来抽象对DbContext的引用,一个虚拟的DbSet(FakeDbSet<T>),一个虚拟的DbContext(FakeReservationContext),以及比较小的单元测试集。我们使用虚拟的DbContext,是为了不与数据库发生交互。测试的目的是,测试业务规则,而不是数据库交互。
解决方案中的一个关键点是,我们创建一个简化的仓储,用它来管理对象的插入和查询。仓储的构造函数接受一个IReservationContext类型的参数。为了测试领域对象,我们给它传递了一个FakeReservationContext的实例。如果允许将领域对象持久化到数据库中,我们需要传递一个真正的DBContext的实例:EFRecipesEntities。
我们需要DbSets通过虚拟的DbContext,返回一个和真实上下文EFRecipesEntities返回相匹配的数据。为了实现需求,我们修改了T4模板,让它生成的上下文返回IDbSet<T>来代替DbSet<T>。为了确保虚拟的DbContext也返回IDbSet<T>类型的DbSet,我们实现了自己的FakeDbset<T>,它派生至IDbSet<T>。
在测试项目中,我创建一个基于FakeReservationContext实例的ReservationRepository进行测试。单元测试与虚拟的FakReservationContext交互代替了与真实DbContext的交互。
最佳实践
有两个测试方法:定义一个仓储接口,真正的仓储和用于测试的一个或多个仓储都需要实现它。 通过实现该接口,与持久化框架的交互可以被隐藏在具体的实现中。不需要创建基础设施其余部分的虚拟对象。它能简化测试代码的实现,但这可能会让仓储自身的代码未被测试。
定义一个DbContext的接口,它公布IDbSet<T>类型的属性和SaveChanges()方法,正如本节所做的那样。真正的DbContext和所有虚拟的DbContext必须实现这个接口。使用这种方法,你不需要虚拟整个仓储,它可能会在某些情况下不同。你的虚拟DbContext不需要模拟整个DbContext类的行为;这可能会是一个挑战。你需要在你的接口中限制你的代码,够用即可。
8-9 使用数据库测试仓储
问题
你想使用数据库测试你的仓储。
这种方法经常被用来做集成测试,它测试完整的数据访问功能。
解决方案
你创建了一个仓储,管理所有的查询、插入、更新和删除。你想使用一个真正的数据库实例来测试这个仓储。假设你有如图8-10的所示的模型。因为我们测试时会创建和删除数据库,所以让我们从一个测试数据库开始吧。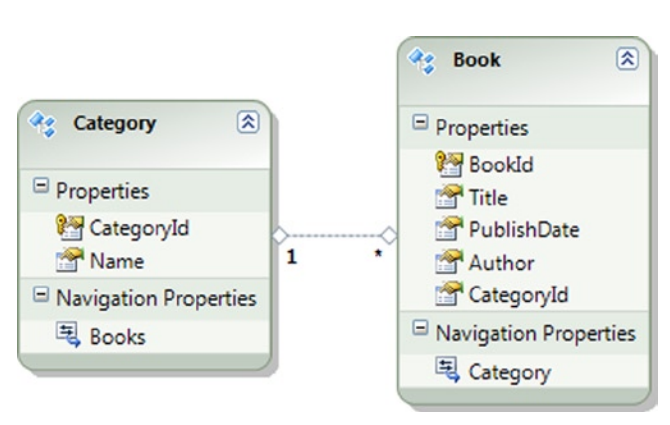
图8-10. 一个关于书及目录的模型
按下面的步骤测试仓储:
1、创建一个空的解决方案。右键解决方案,选择Add(新增) ➤New Project(新建项目)。添加一个类库项目。将它命名为BookRepository;
2、创建一个数据库,命名为Test。我们会在单元测试中创建和删除这个数据库。所以你要确保重新创建一个空的数据库;
3、添加表Book、Category及其关系到图8-10所示的模型中。导入这些表到一个新的模型中,或者,你可以使用Model First创建一个模型,然后用生成的数据库脚本来创建数据库;
4、添加代码清单8-18中的代码,创建一个BookRepository类,它通过模型处理插入和查询;
代码清单8-18. BookRepository类,通过模型处理插入和查询;
1 public class BookRepository 2 { 3 private TestEntities _context; 4 5 public BookRepository(TestEntities context) 6 { 7 _context = context; 8 } 9 10 public void InsertBook(Book book) 11 { 12 _context.Books.Add(book); 13 } 14 15 public void InsertCategory(Category category) 16 { 17 _context.Categories.Add(category); 18 } 19 20 public void SaveChanges() 21 { 22 _context.SaveChanges(); 23 } 24 25 public IQueryable<Book> BooksByCategory(string name) 26 { 27 return _context.Books.Where(b => b.Category.Name == name); 28 } 29 30 public IQueryable<Book> BooksByYear(int year) 31 { 32 return _context.Books.Where(b => b.PublishDate.Year == year); 33 } 34 }
5、右键解决方案,选择Add(新增) ➤New Project(新建项目)。添加一个测试项目。并添加System.Data.Entity和项目BookRepository的引用。
6、右键测试项目,选择Add(新增) ➤New Test(新建测试)。添加一个单元测试到项目中。使用代码清单8-19中的代码创建测试类。
代码清单8-19. 单元测试类BookRepositoryTest
1 [TestClass] 2 public class BookRepositoryTest 3 { 4 private TestEntities _context; 5 6 [TestInitialize] 7 public void TestSetup() 8 { 9 _context = new TestEntities(); 10 if (_context.Database.Exists()) 11 { 12 _context.Database.Delete(); 13 } 14 _context.Database.Create(); 15 } 16 17 [TestMethod] 18 public void TestsBooksInCategory() 19 { 20 var repository = new BookRepository.BookRepository(_context); 21 var construction = new Category { Name = "Construction" }; 22 var book = new Book 23 { 24 Title = "Building with Masonary", 25 Author = "Dick Kreh", 26 PublishDate = new DateTime(1998, 1, 1) 27 }; 28 book.Category = construction; 29 repository.InsertCategory(construction); 30 repository.InsertBook(book); 31 repository.SaveChanges(); 32 33 // test 34 var books = repository.BooksByCategory("Construction"); 35 Assert.AreEqual(books.Count(), 1); 36 } 37 38 [TestMethod] 39 public void TestBooksPublishedInTheYear() 40 { 41 var repository = new BookRepository.BookRepository(_context); 42 var construction = new Category { Name = "Construction" }; 43 var book = new Book 44 { 45 Title = "Building with Masonary", 46 Author = "Dick Kreh", 47 PublishDate = new DateTime(1998, 1, 1) 48 }; 49 book.Category = construction; 50 repository.InsertCategory(construction); 51 repository.InsertBook(book); 52 repository.SaveChanges(); 53 54 // test 55 var books = repository.BooksByYear(1998); 56 Assert.AreEqual(books.Count(), 1); 57 } 58 }
7、右键测试项目,选择Add(新增) ➤New Item(新建项)。从General Templates(常规)中选择应用程序配置文件。从BookRepository项目中的app.config文件中复制<connectionStrings>到测试项目的App.config文件中。
8、右键测试项目,选择设置为启动项目。选择Debug(调试) ➤Start Debugging(开始调试) 或者按F5执行测试。确保没有数据库连接连到测试数据库。否则会导致DropDatabase()方法失败。
原理
实体框架有两种常用的测试方法。第一种是测试你的业务逻辑,对于这个方法,你会用一个”虚拟“的数据库层,因为你的焦点是在业务逻辑上,这些逻管理着对象间的交互,以及保存到数据库的规则。我们在8-8节中演示了这种方法。
第二种方法是测试你的业务逻辑和数据持久化。这个方法用得比较广泛,同时也需要更多的时间和资源。当它实现自动测试工具时,像经常被用到持续集成环境中的测试工具,你需要自动创建和删除测试数据库。
每次迭代测试都需要一个新的数据库状态。后继的测试不能被前面的测试数据影响。这种创建,删除数据库的端到端的测试,比起8-8中演示的逻辑测试需要更多的资源。
代码清单8-19中的单元测试代码,在测试初始化阶段,我们检查了数据库是否存在。如果存在,就使用DropDatabase()方法(译注:代码中使用的是Delete方法)将其删除。然后使用CreateDatabase()方法(译注:代码中使用的是Create方法)创建新的数据库。这些方法都使用配置文件App.config中的连接字符串。本来,这个连接字符串和开发库中的连接字符串应该不一样。为了简单起见,我们对它们使用相同的连接字符串。
至此第八章结束。转眼一个月就过去了,不知不觉中就更新了46篇了。回头看,真是不容易。首先,感谢大家的阅读,特别是为我指出错字别字,及翻译上不当的朋友。其次,我得感谢我的老婆QTT和儿子FYH,因为,在这一个月的时间的,我差不多用了全部的业余时间。如果没有她的支持,肯定不可能有这个系列的。同时,儿子才一岁多,正是需要爸爸陪着玩的时候,结果我整天抱着电脑,对此表示歉意。最后,感谢博客园为我们提供这样一个学习的平台。本系列的翻译也不得不结束了。因为,听朋友说,这种完整的翻译会涉及版权问题。无论是出于对作者权益的维护,还是自身权益的维护,我都不得不终止翻译。不过,大家也不用担心,前八章已经基本介绍完了EF的知识点,后面是一些高级的,很少使用的知识。比如存储过程、自定义上下文对象等。 如果对它们感兴趣的话,只好烦麻大家阅读原书了。欢迎大家一起学习讨论。后续,我将继续介绍EF相关的知识,特别是EF7的知识和运用。感谢大家继续关注!
实体框架交流QQ群: 458326058,欢迎有兴趣的朋友加入一起交流
谢谢大家的持续关注,我的博客地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/VolcanoCloud/






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?