- 管理迭代器
–当使用迭代器或指向容器元素的引用时,最小化要求迭代器必须保持有效的程序片段
–由于向迭代器添加元素时或者删除元素的时候可能会使迭代器失效,因此在容器内做插入删除等操作的时必须重新定位迭代器位置对于vector 、deque、string等线性存储结构尤为重要,但是对于链式存储不影响,他的迭代器,指针和引用都不会失效。
- 如果在一个循环中插入或者删除deque、string、或者vector中的元素,不要缓存end()返回的迭代器。因为会发生变化。迭代器失效。而且这是不好的思路。
-
接下来就是代码演示,在代码关键位置会有注释说明。清晰易懂,其中代码不会每行都有注释,代码注释的作用是让读者能够更清晰明了的读懂程序,而不是画蛇添足导致过多的赘述。
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <list>
#include <forward_list>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <deque>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test_and_insert(forward_list<string>&sflst, const string &s1, const string &s2)
{
auto prev = sflst.before_begin();
auto fbengin = sflst.begin();
bool inserted = false;
while (fbengin != sflst.end())
if (*fbengin == s1)
{
fbengin = sflst.insert_after(fbengin, s2);
inserted = true;
}
else
{
prev = fbengin;
fbengin++;
}
if (!inserted)
{
sflst.insert_after(prev, s2);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
list<int >lst{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 2, 35, 76, 43, 1 };
auto it = lst.begin();
while (it != lst.end())
{
cout << *it<< " ";
if (*it % 2)
it = lst.erase(it);
else
++it;
}
it = lst.begin();
cout << endl;
while (it != lst.end())
{
cout << *it++<< " ";
}
cout << endl;
int ia[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 23, 7, 7 };
vector<int>iv;
list<int>il;
iv.assign(ia, ia + 10);
il.assign(ia, ia + 10);
auto iiv = iv.begin();
while (iiv != iv.end())
if (!(*iiv & 1))
iiv = iv.erase(iiv);
else
iiv++;
auto iil = il.begin();
while (iil != il.end())
if (*iil & 1)
iil = il.erase(iil);
else
iil++;
for (iiv = iv.begin(); iiv != iv.end(); iiv++)
cout << *iiv << " ";
cout << endl;
for (iil = il.begin(); iil != il.end(); iil++)
cout << *iil << " ";
cout << endl;
forward_list<int>forlist{ 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 5, 3, 56, 32, 65, 324, 6 };
auto prev = forlist.before_begin();
auto fbegin = forlist.begin();
while (fbegin != forlist.end())
if (!(*fbegin % 2))
fbegin=forlist.erase_after(prev);
else
{
prev = fbegin;
fbegin++;
}
fbegin = forlist.begin();
while (fbegin != forlist.end())
cout << *fbegin++ << " ";
cout << endl;
forward_list<string>flist{ "hello", "myheart", "dear", "hai" };
test_and_insert(flist, "hello", "heihei1");
auto fllist = flist.begin();
cout << *(++fllist) << endl;
list<int>ilst{ 23, 45, 2, 3, 21, 45, 23, 234, 433, 5, 6, 76, 4, 2, 2, 5 };
auto curr = ilst.begin();
while (curr!=ilst.end())
{
if (*curr & 1)
{
curr = ilst.insert(curr,*curr);
curr++;
curr++;
}
else
curr = ilst.erase(curr);
}
for (curr = ilst.begin(); curr != ilst.end();curr++)
{
cout << *curr << " ";
}
cout << endl;
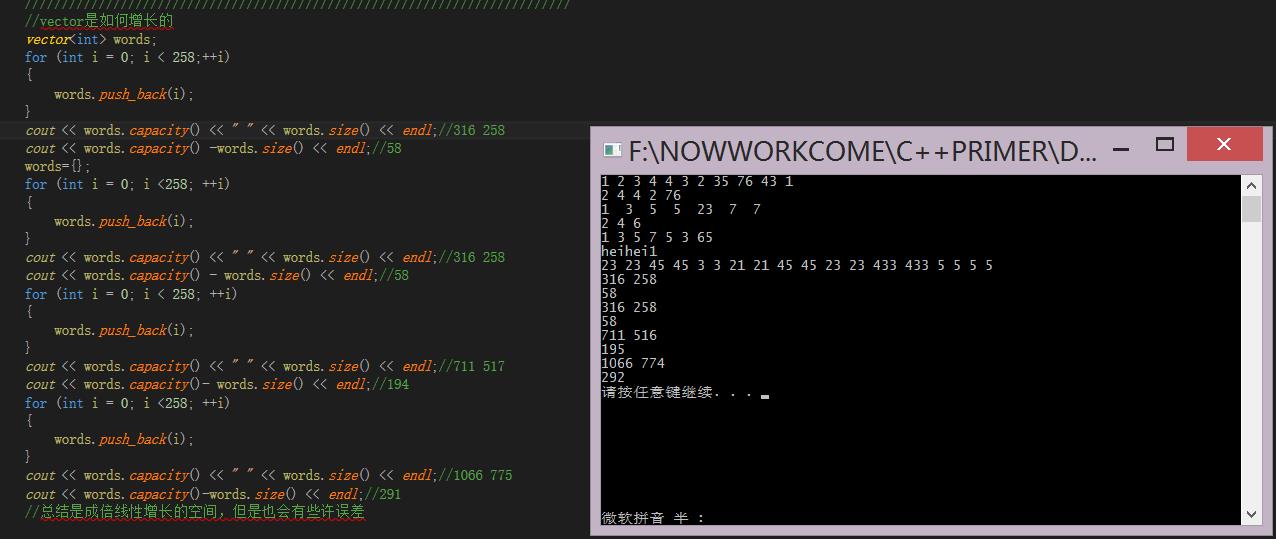
vector<int> words;
for (int i = 0; i < 258;++i)
{
words.push_back(i);
}
cout << words.capacity() << " " << words.size() << endl;
cout << words.capacity() -words.size() << endl;
words={};
for (int i = 0; i <258; ++i)
{
words.push_back(i);
}
cout << words.capacity() << " " << words.size() << endl;
cout << words.capacity() - words.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 258; ++i)
{
words.push_back(i);
}
cout << words.capacity() << " " << words.size() << endl;
cout << words.capacity()- words.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i <258; ++i)
{
words.push_back(i);
}
cout << words.capacity() << " " << words.size() << endl;
cout << words.capacity()-words.size() << endl;
system("pause");
}