[Android] 获取音频输出getOutput
每创建一个AudioTrack,代表需要新增一个输出实例,即需要根据音频流的的stream type,音频流的音轨数量,采样率,位宽等数据来重新构建buffer,而且输出的设备也可能会有变化,由于Android设备支持的输出设备各种各样,如线控耳机,喇叭,蓝牙耳机,midi设备等,因此如果该设备是第一次被使用时,则会被初始化。
下文描述的打开输出设置并非真正的打开linux设备文件,而是输出设备相关的初始化操作
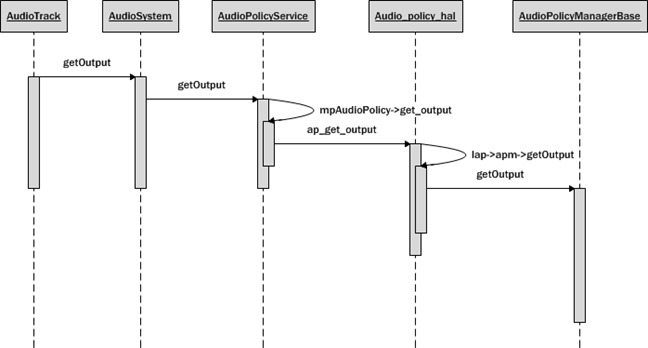
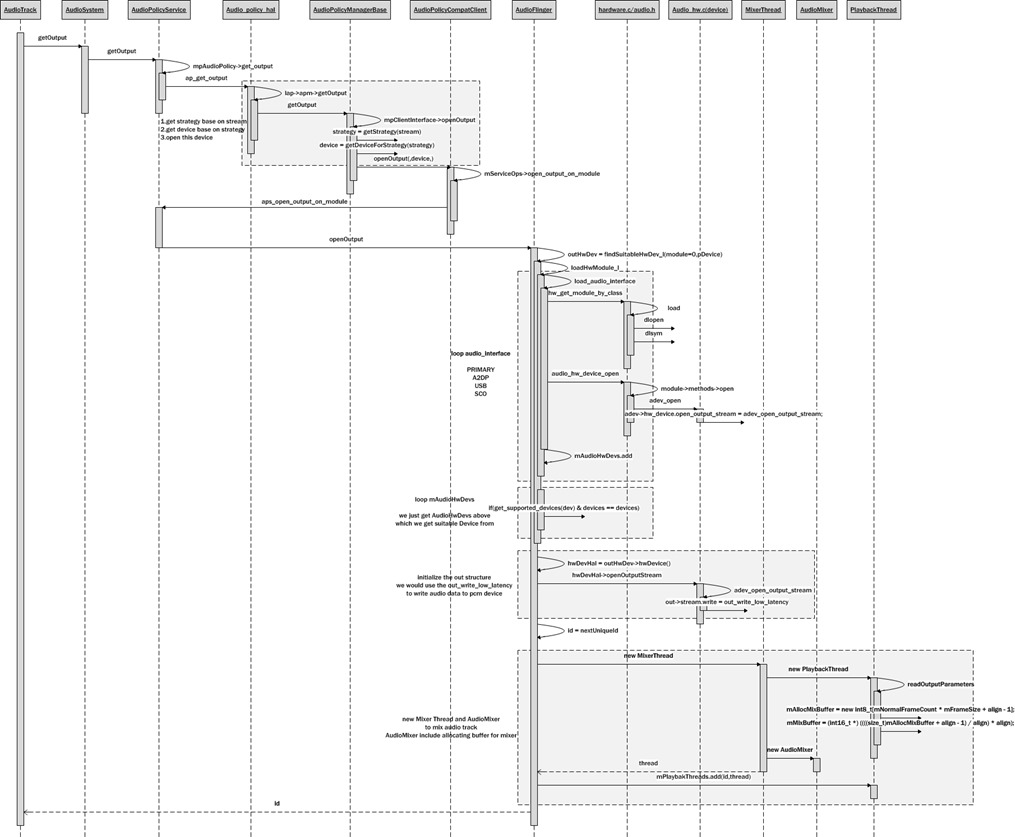
getOutput流程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | audio_io_handle_t AudioTrack::getOutput_l(){ if (mOutput) { return mOutput; } else { return AudioSystem::getOutput(mStreamType, mSampleRate, mFormat, mChannelMask, mFlags); }} |
AudioSystem是上层往底层调用audio相关功能时必经的api层
由于Output涉及到输出策略,即应该输出到哪个设备的问题,因此,需要经过AudioPolicyService来处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | audio_io_handle_t AudioPolicyService::getOutput(audio_stream_type_t stream, uint32_t samplingRate, audio_format_t format, audio_channel_mask_t channelMask, audio_output_flags_t flags, const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo){ if (mpAudioPolicy == NULL) { return 0; } ALOGV("getOutput()"); Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock); return mpAudioPolicy->get_output(mpAudioPolicy, stream, samplingRate, format, channelMask, flags, offloadInfo);} |
要理清楚Audio策略,需要先分析AudioPolicyService的构建。AudioPolicyService是在mediaserver初始化的时候创建的
1 2 3 4 5 | //main_mediaserver.cppint main(int argc, char** argv){ MediaPlayerService::instantiate();} |
在AudioPolicyService的初始化过程中,主要与策略相关的步骤有三个
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------AudioPolicyService::AudioPolicyService() : BnAudioPolicyService() , mpAudioPolicyDev(NULL) , mpAudioPolicy(NULL){ /* instantiate the audio policy manager */ rc = hw_get_module(AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module); if (rc) return; rc = audio_policy_dev_open(module, &mpAudioPolicyDev); ALOGE_IF(rc, "couldn't open audio policy device (%s)", strerror(-rc)); rc = mpAudioPolicyDev->create_audio_policy(mpAudioPolicyDev, &aps_ops, this, &mpAudioPolicy);} |
hw_get_module获取名为“AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID”的module,在audio_policy_hal.cpp中找到了同名module
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | struct legacy_ap_module HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = { module: { common: { tag: HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG, version_major: 1, version_minor: 0, id: AUDIO_POLICY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, name: "LEGACY Audio Policy HAL", author: "The Android Open Source Project", methods: &legacy_ap_module_methods, dso : NULL, reserved : {0}, }, },}; |
audio_policy_dev_open调用该module的open函数得到该module对应的设备
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | static int legacy_ap_dev_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char* name, hw_device_t** device){ struct legacy_ap_device *dev; if (strcmp(name, AUDIO_POLICY_INTERFACE) != 0) return -EINVAL; dev = (struct legacy_ap_device *)calloc(1, sizeof(*dev)); if (!dev) return -ENOMEM; dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG; dev->device.common.version = 0; dev->device.common.module = const_cast<hw_module_t*>(module); dev->device.common.close = legacy_ap_dev_close; dev->device.create_audio_policy = create_legacy_ap; dev->device.destroy_audio_policy = destroy_legacy_ap; *device = &dev->device.common; return 0;} |
得到该设备对应的音频策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 | static int create_legacy_ap(const struct audio_policy_device *device, struct audio_policy_service_ops *aps_ops, void *service, struct audio_policy **ap){ struct legacy_audio_policy *lap; int ret; if (!service || !aps_ops) return -EINVAL; lap = (struct legacy_audio_policy *)calloc(1, sizeof(*lap)); if (!lap) return -ENOMEM; lap->policy.set_device_connection_state = ap_set_device_connection_state; lap->policy.get_device_connection_state = ap_get_device_connection_state; lap->policy.set_phone_state = ap_set_phone_state; lap->policy.set_ringer_mode = ap_set_ringer_mode; lap->policy.set_force_use = ap_set_force_use; lap->policy.get_force_use = ap_get_force_use; lap->policy.set_can_mute_enforced_audible = ap_set_can_mute_enforced_audible; lap->policy.init_check = ap_init_check; lap->policy.get_output = ap_get_output; lap->policy.start_output = ap_start_output; lap->policy.stop_output = ap_stop_output; lap->policy.release_output = ap_release_output; lap->policy.get_input = ap_get_input; lap->policy.start_input = ap_start_input; lap->policy.stop_input = ap_stop_input; lap->policy.release_input = ap_release_input; lap->policy.init_stream_volume = ap_init_stream_volume; lap->policy.set_stream_volume_index = ap_set_stream_volume_index; lap->policy.get_stream_volume_index = ap_get_stream_volume_index; lap->policy.set_stream_volume_index_for_device = ap_set_stream_volume_index_for_device; lap->policy.get_stream_volume_index_for_device = ap_get_stream_volume_index_for_device; lap->policy.get_strategy_for_stream = ap_get_strategy_for_stream; lap->policy.get_devices_for_stream = ap_get_devices_for_stream; lap->policy.get_output_for_effect = ap_get_output_for_effect; lap->policy.register_effect = ap_register_effect; lap->policy.unregister_effect = ap_unregister_effect; lap->policy.set_effect_enabled = ap_set_effect_enabled; lap->policy.is_stream_active = ap_is_stream_active; lap->policy.is_stream_active_remotely = ap_is_stream_active_remotely; lap->policy.is_source_active = ap_is_source_active; lap->policy.dump = ap_dump; lap->policy.is_offload_supported = ap_is_offload_supported; lap->service = service; lap->aps_ops = aps_ops; lap->service_client = new AudioPolicyCompatClient(aps_ops, service); if (!lap->service_client) { ret = -ENOMEM; goto err_new_compat_client; } lap->apm = createAudioPolicyManager(lap->service_client); if (!lap->apm) { ret = -ENOMEM; goto err_create_apm; } *ap = &lap->policy; return 0;err_create_apm: delete lap->service_client;err_new_compat_client: free(lap); *ap = NULL; return ret;} |
可见,函数中一大堆的成员赋值都是policy相关的
回到输出策略,从上面policy相关的赋值中,能知道mpAudioPolicy->get_output最终会调用到ap_get_output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | static audio_io_handle_t ap_get_output(struct audio_policy *pol, audio_stream_type_t stream, uint32_t sampling_rate, audio_format_t format, audio_channel_mask_t channelMask, audio_output_flags_t flags, const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo){ struct legacy_audio_policy *lap = to_lap(pol); ALOGV("%s: tid %d", __func__, gettid()); return lap->apm->getOutput((AudioSystem::stream_type)stream, sampling_rate, (int) format, channelMask, (AudioSystem::output_flags)flags, offloadInfo);} |
这里的lap->apm又是什么?我们在上面创建AudioPolicy时也能找到其创建的地方
1 | lap->apm = createAudioPolicyManager(lap->service_client); |
1 2 3 4 | extern "C" AudioPolicyInterface* createAudioPolicyManager(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface){ return new AudioPolicyManagerDefault(clientInterface);} |
AudioPolicyManagerDefault是AudioPolicyManagerBase的子类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | class AudioPolicyManagerDefault: public AudioPolicyManagerBase{public: AudioPolicyManagerDefault(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface) : AudioPolicyManagerBase(clientInterface) {} virtual ~AudioPolicyManagerDefault() {}}; |
因此最终还是调用到AudioPolicyManagerBase::getOutput,绕了这么大一圈,先来回顾一下getOutput走过的流程
- AudioSystem,API层
- AudioPolicyService,策略层
- Audio_policy_hal,module层
- AudioPolicyManagerBase,实际上的策略实现层
getOutput实现
getOutput的实现分为三个步骤
- 根据传进来的stream type获得策略。
- 根据策略获得输出设备。策略的作用,就是根据策略与目前的状态来选取输出的设备。
- 打开该输出设备
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | audio_io_handle_t AudioPolicyManagerBase::getOutput(AudioSystem::stream_type stream, uint32_t samplingRate, uint32_t format, uint32_t channelMask, AudioSystem::output_flags flags, const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo){ audio_io_handle_t output = 0; uint32_t latency = 0; routing_strategy strategy = getStrategy((AudioSystem::stream_type)stream); audio_devices_t device = getDeviceForStrategy(strategy, false /*fromCache*/); mTestOutputs[mCurOutput] = mpClientInterface->openOutput(0, &outputDesc->mDevice, &outputDesc->mSamplingRate, &outputDesc->mFormat, &outputDesc->mChannelMask, &outputDesc->mLatency, outputDesc->mFlags, offloadInfo); return output;} |
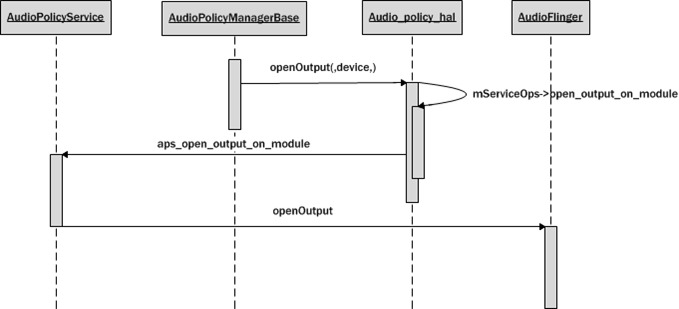
openOutput
在打开设备的时候调用了mpClientInterface->openOutput,而mpClientInterface是在构造AudioPolicyManagerBase的时候传进来的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------// AudioPolicyManagerBase// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------AudioPolicyManagerBase::AudioPolicyManagerBase(AudioPolicyClientInterface *clientInterface) :#ifdef AUDIO_POLICY_TEST Thread(false),#endif //AUDIO_POLICY_TEST mPrimaryOutput((audio_io_handle_t)0), mAvailableOutputDevices(AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE), mPhoneState(AudioSystem::MODE_NORMAL), mLimitRingtoneVolume(false), mLastVoiceVolume(-1.0f), mTotalEffectsCpuLoad(0), mTotalEffectsMemory(0), mA2dpSuspended(false), mHasA2dp(false), mHasUsb(false), mHasRemoteSubmix(false), mSpeakerDrcEnabled(false){ mpClientInterface = clientInterface;} |
我们前回顾一下,传进来的是
1 | lap->apm = createAudioPolicyManager(lap->service_client); |
1 2 | lap->service_client = new AudioPolicyCompatClient(aps_ops, service); |
调用了AudioPolicyCompatClient的openOutput
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | audio_io_handle_t AudioPolicyCompatClient::openOutput(audio_module_handle_t module, audio_devices_t *pDevices, uint32_t *pSamplingRate, audio_format_t *pFormat, audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask, uint32_t *pLatencyMs, audio_output_flags_t flags, const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo){ return mServiceOps->open_output_on_module(mService, module, pDevices, pSamplingRate, pFormat, pChannelMask, pLatencyMs, flags, offloadInfo);} |
然后又回调到了AudioPolicyManager的open_output_on_module
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | struct audio_policy_service_ops aps_ops = { open_output : aps_open_output, open_duplicate_output : aps_open_dup_output, close_output : aps_close_output, suspend_output : aps_suspend_output, restore_output : aps_restore_output, open_input : aps_open_input, close_input : aps_close_input, set_stream_volume : aps_set_stream_volume, set_stream_output : aps_set_stream_output, set_parameters : aps_set_parameters, get_parameters : aps_get_parameters, start_tone : aps_start_tone, stop_tone : aps_stop_tone, set_voice_volume : aps_set_voice_volume, move_effects : aps_move_effects, load_hw_module : aps_load_hw_module, open_output_on_module : aps_open_output_on_module, open_input_on_module : aps_open_input_on_module,}; |
最终调用的是AudioFlinger的openOutput,实在是比较绕
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | static audio_io_handle_t aps_open_output_on_module(void *service, audio_module_handle_t module, audio_devices_t *pDevices, uint32_t *pSamplingRate, audio_format_t *pFormat, audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask, uint32_t *pLatencyMs, audio_output_flags_t flags, const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo){ sp<IAudioFlinger> af = AudioSystem::get_audio_flinger(); if (af == 0) { ALOGW("%s: could not get AudioFlinger", __func__); return 0; } return af->openOutput(module, pDevices, pSamplingRate, pFormat, pChannelMask, pLatencyMs, flags, offloadInfo);} |
AudioFlinger的openOutput是真正实现打开输出设备(模块)的地方,其中有三个步骤:
- 加载音频硬件设备(audio.primary.rtd294x.so)
- 硬件设备输出方法初始化(选择恰当的输出函数)
- 创建MixerThread
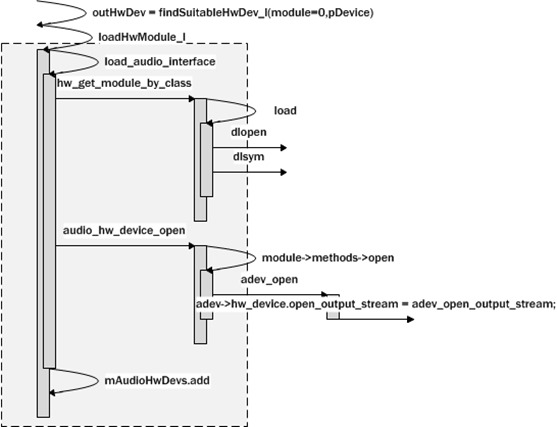
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------audio_io_handle_t AudioFlinger::openOutput(audio_module_handle_t module, audio_devices_t *pDevices, uint32_t *pSamplingRate, audio_format_t *pFormat, audio_channel_mask_t *pChannelMask, uint32_t *pLatencyMs, audio_output_flags_t flags, const audio_offload_info_t *offloadInfo){ outHwDev = findSuitableHwDev_l(module, *pDevices); audio_hw_device_t *hwDevHal = outHwDev->hwDevice(); audio_io_handle_t id = nextUniqueId() status_t status = hwDevHal->open_output_stream(hwDevHal, id, *pDevices, (audio_output_flags_t)flags, &config, &outStream); thread = new MixerThread(this, output, id, *pDevices); return id;} |
1. 加载硬件设备
当然是只有设备第一次使用的时候才会加载,后续可以直接从已加载的设备中获取。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | AudioFlinger::AudioHwDevice* AudioFlinger::findSuitableHwDev_l( audio_module_handle_t module, audio_devices_t devices){ if (module == 0) { for (size_t i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(audio_interfaces); i++) { loadHwModule_l(audio_interfaces[i]); } // then try to find a module supporting the requested device. for (size_t i = 0; i < mAudioHwDevs.size(); i++) { AudioHwDevice *audioHwDevice = mAudioHwDevs.valueAt(i); audio_hw_device_t *dev = audioHwDevice->hwDevice(); if ((dev->get_supported_devices != NULL) && (dev->get_supported_devices(dev) & devices) == devices) return audioHwDevice; } } else { // check a match for the requested module handle AudioHwDevice *audioHwDevice = mAudioHwDevs.valueFor(module); if (audioHwDevice != NULL) { return audioHwDevice; } } return NULL;} |
而且音频设备可能不止一个,audio_interfaces中就定义了几个需要加载的设备,当然,并不是所有定义的都能加载成功,这取决于方案厂商实现了几个设备模块
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | static const char * const audio_interfaces[] = { AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_PRIMARY, AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_A2DP, AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_USB,#ifdef BLUETOOTH_RTK_VR AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_VOHOG, /*BOARD_HAVE_BLUETOOTH_RTK_VR*/#endif#ifdef BLUETOOTH_RTK_SCO AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_SCO,#endif}; |
如果加载成功,那么会进行音量的设置,并把这个设备加入设备数组中进行维护
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | // loadHwModule_l() must be called with AudioFlinger::mLock heldaudio_module_handle_t AudioFlinger::loadHwModule_l(const char *name){ int rc = load_audio_interface(name, &dev); dev->set_master_volume(dev, mMasterVolume) audio_module_handle_t handle = nextUniqueId(); mAudioHwDevs.add(handle, new AudioHwDevice(name, dev, flags)); return handle;} |
加载,实际上就是把设备相关的lib文件加载进来,并且加载lib文件内的相关函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------static int load_audio_interface(const char *if_name, audio_hw_device_t **dev){ rc = hw_get_module_by_class(AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, if_name, &mod); rc = audio_hw_device_open(mod, dev);} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 | /* *加载lib文件的名字遵循下面的格式: *class_id : audio *inst : primary (参考上面的设备名数组,有primary,A2DP,USB等) *prop : rtd294x (这个是平台相关的名称,如ro.product.board等) *path :优先查找/system/lib/hw下的,后查找vendor/lib/hw下的 *最后load开始加载lib */int hw_get_module_by_class(const char *class_id, const char *inst, const struct hw_module_t **module){ int status; int i; const struct hw_module_t *hmi = NULL; char prop[PATH_MAX]; char path[PATH_MAX]; char name[PATH_MAX]; if (inst) snprintf(name, PATH_MAX, "%s.%s", class_id, inst); else strlcpy(name, class_id, PATH_MAX); /* * Here we rely on the fact that calling dlopen multiple times on * the same .so will simply increment a refcount (and not load * a new copy of the library). * We also assume that dlopen() is thread-safe. */ /* Loop through the configuration variants looking for a module */ for (i=0 ; i<HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT+1 ; i++) { if (i < HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT) { if (property_get(variant_keys[i], prop, NULL) == 0) { continue; } snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.%s.so", HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2, name, prop); if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) break; snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.%s.so", HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1, name, prop); if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) break; } else { snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.default.so", HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2, name); if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) break; snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.default.so", HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1, name); if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) break; } } status = -ENOENT; if (i < HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT+1) { /* load the module, if this fails, we're doomed, and we should not try * to load a different variant. */ status = load(class_id, path, module); } return status;} |
1 | |
load调用dlopen与dlsym加载函数接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | /** * Load the file defined by the variant and if successful * return the dlopen handle and the hmi. * @return 0 = success, !0 = failure. */static int load(const char *id, const char *path, const struct hw_module_t **pHmi){ handle = dlopen(path, RTLD_NOW); hmi = (struct hw_module_t *)dlsym(handle, sym);} |
audio_hw_device_open会调用刚刚加载的lib中的adev_open函数,adev_open函数的职责是把后续所需要的功能函数赋值到某个结构体中进行维护,以便后续调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 | static inline int audio_hw_device_open(const struct hw_module_t* module, struct audio_hw_device** device){ return module->methods->open(module, AUDIO_HARDWARE_INTERFACE, (struct hw_device_t**)device);}static int adev_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char* name, hw_device_t** device){ struct tuna_audio_device *adev; int ret; if (strcmp(name, AUDIO_HARDWARE_INTERFACE) != 0) return -EINVAL; adev = calloc(1, sizeof(struct tuna_audio_device)); if (!adev) return -ENOMEM; adev->hw_device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG; adev->hw_device.common.version = AUDIO_DEVICE_API_VERSION_2_0; adev->hw_device.common.module = (struct hw_module_t *) module; adev->hw_device.common.close = adev_close; adev->hw_device.init_check = adev_init_check; adev->hw_device.set_voice_volume = adev_set_voice_volume; adev->hw_device.set_master_volume = adev_set_master_volume; adev->hw_device.get_master_volume = adev_get_master_volume; adev->hw_device.set_master_mute = adev_set_master_mute; adev->hw_device.get_master_mute = adev_get_master_mute; adev->hw_device.set_mode = adev_set_mode; adev->hw_device.set_mic_mute = adev_set_mic_mute; adev->hw_device.get_mic_mute = adev_get_mic_mute; adev->hw_device.set_parameters = adev_set_parameters; adev->hw_device.get_parameters = adev_get_parameters; adev->hw_device.get_input_buffer_size = adev_get_input_buffer_size; adev->hw_device.open_output_stream = adev_open_output_stream; adev->hw_device.close_output_stream = adev_close_output_stream; adev->hw_device.open_input_stream = adev_open_input_stream; adev->hw_device.close_input_stream = adev_close_input_stream; adev->hw_device.dump = adev_dump; adev->mixer = mixer_open(0); if (!adev->mixer) { free(adev); ALOGE("Unable to open the mixer, aborting."); return -EINVAL; } /* Set the default route before the PCM stream is opened */ pthread_mutex_lock(&adev->lock); set_route_by_array(adev->mixer, defaults, 1); adev->mode = AUDIO_MODE_NORMAL; adev->out_device = AUDIO_DEVICE_OUT_SPEAKER; adev->in_device = AUDIO_DEVICE_IN_BUILTIN_MIC & ~AUDIO_DEVICE_BIT_IN; select_output_device(adev); adev->pcm_modem_dl = NULL; adev->pcm_modem_ul = NULL; adev->voice_volume = 1.0f; adev->tty_mode = TTY_MODE_OFF; adev->device_is_toro = is_device_toro(); adev->bluetooth_nrec = true; adev->wb_amr = 0; adev->AI_open_count = 0; adev->AO_open_count = 0; /* RIL */ // ril_open(&adev->ril); pthread_mutex_unlock(&adev->lock); /* register callback for wideband AMR setting */ // ril_register_set_wb_amr_callback(audio_set_wb_amr_callback, (void *)adev); *device = &adev->hw_device.common; return 0;} |
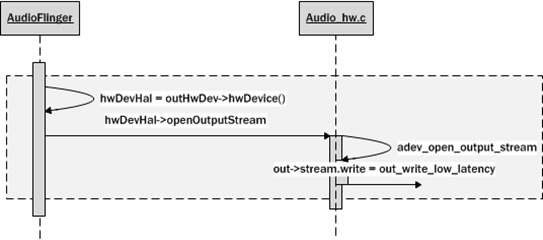
2. 选择恰当输出方法
调用刚刚加载lib中的open_output_stream方法,即adev_open_output_stream,目的是选择合适的Audio输出方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | static int adev_open_output_stream(struct audio_hw_device *dev, audio_io_handle_t handle, audio_devices_t devices, audio_output_flags_t flags, struct audio_config *config, struct audio_stream_out **stream_out){ output_type = OUTPUT_LOW_LATENCY; out->stream.common.get_buffer_size = out_get_buffer_size_low_latency; out->stream.common.get_sample_rate = out_get_sample_rate; out->stream.get_latency = out_get_latency_low_latency; out->stream.write = out_write_low_latency;} |
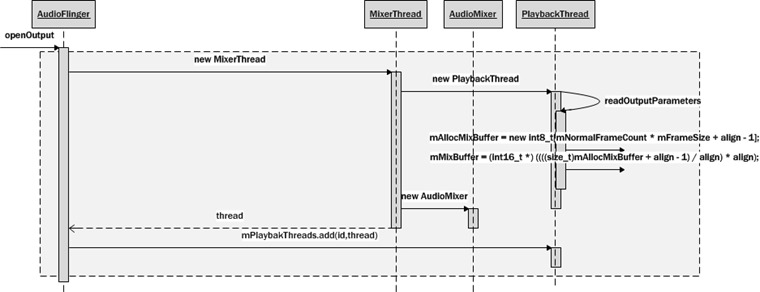
3. 创建MixerThread
MixerThread是PlaybackThread的子类,因此,也会一同创建PlaybackThread
首先会判断能否用硬件设备模块设置音量,可以的话就不会采用Android的AudioMixer来混音MasterVolume了,不过streamVolume还是会用AudioMixer进行混音。然后调用readOutputParameters来创建混音所使用的buffer。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 | // ----------------------------------------------------------------------------// Playback// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::PlaybackThread(const sp<AudioFlinger>& audioFlinger, AudioStreamOut* output, audio_io_handle_t id, audio_devices_t device, type_t type) : ThreadBase(audioFlinger, id, device, AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE, type), mNormalFrameCount(0), mMixBuffer(NULL), mAllocMixBuffer(NULL), mSuspended(0), mBytesWritten(0), mActiveTracksGeneration(0), // mStreamTypes[] initialized in constructor body mOutput(output), mLastWriteTime(0), mNumWrites(0), mNumDelayedWrites(0), mInWrite(false), mMixerStatus(MIXER_IDLE), mMixerStatusIgnoringFastTracks(MIXER_IDLE), standbyDelay(AudioFlinger::mStandbyTimeInNsecs), mBytesRemaining(0), mCurrentWriteLength(0), mUseAsyncWrite(false), mWriteAckSequence(0), mDrainSequence(0), mSignalPending(false), mScreenState(AudioFlinger::mScreenState), // index 0 is reserved for normal mixer's submix mFastTrackAvailMask(((1 << FastMixerState::kMaxFastTracks) - 1) & ~1), // mLatchD, mLatchQ, mLatchDValid(false), mLatchQValid(false){ snprintf(mName, kNameLength, "AudioOut_%X", id); mNBLogWriter = audioFlinger->newWriter_l(kLogSize, mName); // Assumes constructor is called by AudioFlinger with it's mLock held, but // it would be safer to explicitly pass initial masterVolume/masterMute as // parameter. // // If the HAL we are using has support for master volume or master mute, // then do not attenuate or mute during mixing (just leave the volume at 1.0 // and the mute set to false). mMasterVolume = audioFlinger->masterVolume_l(); mMasterMute = audioFlinger->masterMute_l(); if (mOutput && mOutput->audioHwDev) { if (mOutput->audioHwDev->canSetMasterVolume()) { mMasterVolume = 1.0; } if (mOutput->audioHwDev->canSetMasterMute()) { mMasterMute = false; } } readOutputParameters(); // mStreamTypes[AUDIO_STREAM_CNT] is initialized by stream_type_t default constructor // There is no AUDIO_STREAM_MIN, and ++ operator does not compile for (audio_stream_type_t stream = (audio_stream_type_t) 0; stream < AUDIO_STREAM_CNT; stream = (audio_stream_type_t) (stream + 1)) { mStreamTypes[stream].volume = mAudioFlinger->streamVolume_l(stream); mStreamTypes[stream].mute = mAudioFlinger->streamMute_l(stream); } // mStreamTypes[AUDIO_STREAM_CNT] exists but isn't explicitly initialized here, // because mAudioFlinger doesn't have one to copy from} |
创建mixer buffer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | void AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread::readOutputParameters(){ mAllocMixBuffer = new int8_t[mNormalFrameCount * mFrameSize + align - 1]; mMixBuffer = (int16_t *) ((((size_t)mAllocMixBuffer + align - 1) / align) * align); memset(mMixBuffer, 0, mNormalFrameCount * mFrameSize);} |
在MixerThread构造函数内创建了混音器AudioMixer。如果采用FastMixer的话,也会在MixerThread内创建,而且还会创建FastMixer的mixer buffer SourceAudioBufferProvider并进行各种初始化设置,这里不做讨论。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | AudioFlinger::MixerThread::MixerThread(const sp<AudioFlinger>& audioFlinger, AudioStreamOut* output, audio_io_handle_t id, audio_devices_t device, type_t type) : PlaybackThread(audioFlinger, output, id, device, type), // mAudioMixer below // mFastMixer below mFastMixerFutex(0) // mOutputSink below // mPipeSink below // mNormalSink below{ mAudioMixer = new AudioMixer(mNormalFrameCount, mSampleRate);} |
创建完MixerThread后把它加紧mPlaybackThreads进行管理
1 2 | thread = new MixerThread(this, output, id, *pDevices);mPlaybackThreads.add(id, thread); |
总体流程如下:


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步