种类并查集
Zjnu Stadium HDU - 3047
逾期说是种类并查集,其实更像是权值并查集,以一个点作为基准,通过路径压缩把所有的座位关系都变成与基准有直接关系的,查询的过程也是不断维护集合的过程,没有当前查询的信息,就插入查询的信息,如果有,则判断是否与集合中的信息冲突。
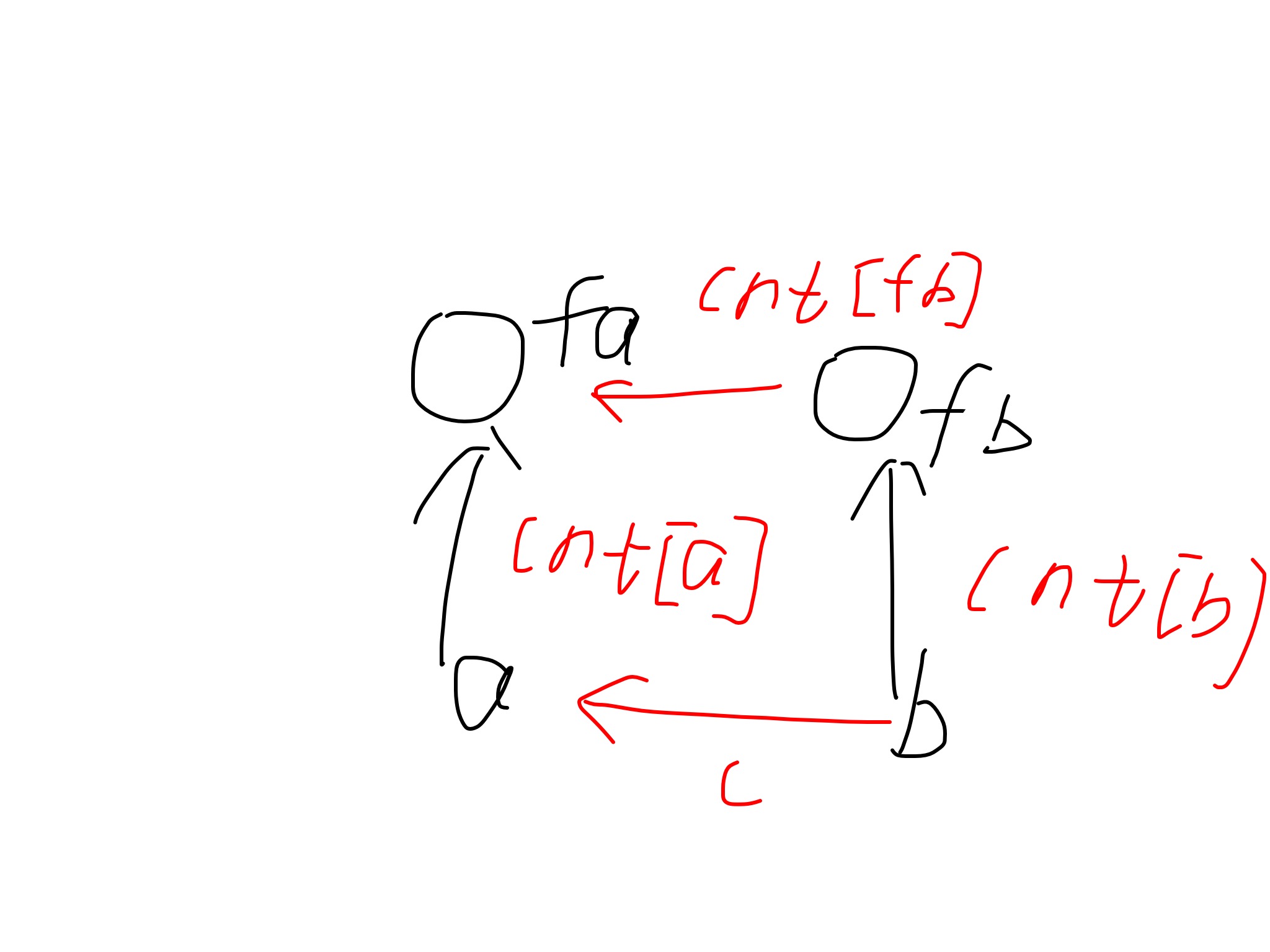
对于每次加入的时候都有下面这个关系,根据这个等价关系,求出cnt[fb],然后通过find函数进行路径压缩和更新,这大致是权值并查集的通常做法。无论这个权值是区间和或者是奇偶分析等,只要能通过这个关系更新的就可以做。

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int maxn=1e5+5; 4 int n,m; 5 int f[maxn],cnt[maxn]; 6 void init() 7 { 8 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) 9 f[i]=i,cnt[i]=0; 10 } 11 int find(int x){ 12 if(x!=f[x]){ 13 int fa=f[x]; 14 f[x]=find(f[x]); 15 cnt[x]=(cnt[x]+cnt[fa])%300; 16 } 17 return f[x]; 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 22 while(cin>>n>>m) 23 { 24 init();long long ans=0; 25 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ 26 //cout <<i<<" "<<m<<endl; 27 int a;int b;int c; 28 cin>>a>>b>>c; 29 int fa=find(a); 30 int fb=find(b); 31 32 if(fa!=fb){ 33 f[fb]=fa; 34 cnt[fb]=(c+cnt[a]-cnt[b])%300; 35 }else 36 { 37 if((cnt[b]-cnt[a]+300)%300!=c%300) ans++; 38 } 39 } 40 cout <<ans<<endl; 41 } 42 return 0; 43 }
B - 食物链 POJ - 1182
之前被这道题支配了好久,做完上面那道题后,发现这不是一模一样嘛,通过被吃关系或吃关系建立一个圈,那就和上面的操场那个完全一样了,只是这个有两种操作。
我们回顾并查集,最初的并查集是作为种类分类的集合,但是到后来的权值并查集显然就不是这个作用了,它通过以根为基准建立了一套偏移系,通过路径压缩,能够把每个元素的偏移直接与根连接上,查询就很容易计算。不在这个集合中的就先加进来。种类并查集只是有一个mod系的权值并查集,而且还比较好写。这个题用cin关同步T了,快读500ms,scanf200ms。
ps:这些东西一旦想明白了很简单,想不明白是真的很自闭。
附代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int maxn=1e5+5; 4 int n,m; 5 int f[maxn],cnt[maxn]; 6 void init() 7 { 8 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) 9 f[i]=i,cnt[i]=0; 10 } 11 int find(int x){ 12 if(x!=f[x]){ 13 int fa=f[x]; 14 f[x]=find(f[x]); 15 cnt[x]=(cnt[x]+cnt[fa])%300; 16 } 17 return f[x]; 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 22 while(cin>>n>>m) 23 { 24 init();long long ans=0; 25 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ 26 //cout <<i<<" "<<m<<endl; 27 int a;int b;int c; 28 cin>>a>>b>>c; 29 int fa=find(a); 30 int fb=find(b); 31 32 if(fa!=fb){ 33 f[fb]=fa; 34 cnt[fb]=(c+cnt[a]-cnt[b])%300; 35 }else 36 { 37 if((cnt[b]-cnt[a]+300)%300!=c%300) ans++; 38 } 39 } 40 cout <<ans<<endl; 41 } 42 return 0; 43 }
这个题卡了巨长时间。最后玄学的把C++换成G++过了。
模二系种类并查集+方法01dp。先找出每个集合,因为这几个集合无法统一基准,所以要选择哪种组合可以满足题目,01背包算出用这cnt个集合凑p1个人方法数。然后反向推回去,记录每一步的选择情况。实现起来比较困难。需要找好一一对应的关系

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <map> 4 #define deg(x) cout <<"x= "<<x<<endl 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int n,p1,p2; 8 int f[1000],cnt[1000]; 9 struct node{ 10 int num1; 11 int num0; 12 }bag[1000]; 13 int dp[1000][1000]; 14 void init(){ 15 memset(bag,0,sizeof(bag)); 16 memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); 17 for(int i=0;i<=p1+p2;i++){ 18 cnt[i]=0;f[i]=i; 19 } 20 } 21 22 int find(int x) 23 { 24 25 if(x!=f[x]) 26 { 27 int fa=f[x]; 28 f[x]=find(f[x]); 29 cnt[x]=(cnt[x]+cnt[fa])%2; 30 } 31 return f[x]; 32 } 33 34 bool read() 35 { 36 37 char s[5];int a,b; 38 int sign=1; 39 /*for(int i=1;i<=p1+p2;i++) 40 { 41 cout <<f[i]<<" "; 42 }*/ 43 //cout <<endl; 44 //std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 45 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 46 { 47 cin>>a>>b>>s; 48 int fa=find(a);int fb=find(b); 49 if(s[0]=='y') 50 { 51 if(fa!=fb) 52 { 53 f[fb]=fa; 54 cnt[fb]=(cnt[a]-cnt[b]+2)%2; 55 }else 56 { 57 if(cnt[b]%2!=cnt[a]%2) 58 sign=0; 59 //cout <<"in"<<i<<endl; 60 } 61 62 }else 63 { 64 if(fa!=fb) 65 { 66 f[fb]=fa; 67 cnt[fb]=(cnt[a]+1-cnt[b]+2)%2; 68 } else 69 { 70 //cout <<"in"<<i<<endl; 71 if((cnt[a]+1)%2!=cnt[b]%2) 72 sign=0; 73 } 74 } 75 // cout <<sign<<"sing"<<endl; 76 77 } 78 return sign; 79 } 80 81 int main() 82 { 83 //freopen("a.txt","r",stdin); 84 //std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 85 while(cin>>n>>p1>>p2) 86 { 87 if(n==0&&p1==0&&p2==0) break; 88 init();int sign=read(); 89 /* for(int i=1;i<=p1+p2;i++) 90 { 91 cout <<i<<" "<<f[i]<<" "<<cnt[i]<<endl; 92 } 93 cout <<"sign="<<sign<<endl;*/ 94 if(sign==0) cout <<"no\n"; 95 else 96 { 97 map <int,int> M; 98 for(int i=1;i<=p1+p2;i++) 99 { 100 int fa=find(i); 101 if(cnt[i]==1) bag[fa].num1++; 102 else bag[fa].num0++; 103 } 104 int ct=0; 105 for(int i=1;i<=p1+p2;i++){ 106 //deg(bag[i].num0); 107 //deg(bag[i].num1); 108 } 109 for(int i=1;i<=p1+p2;i++) 110 { 111 if(bag[i].num0==0&&bag[i].num1==0) continue; 112 ct++; 113 bag[ct].num0=bag[i].num0;bag[ct].num1=bag[i].num1; 114 M[i]=ct;//根对应背包编号 115 } 116 /* for(int i=1;i<=ct;i++) 117 { 118 cout <<bag[i].num0<<" "<<bag[i].num1<<endl; 119 }*/ 120 dp[0][0]=1; 121 for(int i=1;i<=ct;i++) 122 { 123 for(int j=0;j<=p1;j++) 124 { 125 if(j>=bag[i].num0) dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-bag[i].num0]; 126 if(j>=bag[i].num1) dp[i][j]+=dp[i-1][j-bag[i].num1]; 127 } 128 } 129 if(dp[ct][p1]!=1) { 130 cout <<"no\n"; 131 continue; 132 } 133 int choose[1000]={0};int y=p1; 134 for(int i=ct;i>=1;i--){ 135 //cout <<"tia"<<dp[i-1][y-bag[i].num0]<<" "<<dp[i-1][y-bag[i].num1]<<endl; 136 if(dp[i][y]==dp[i-1][y-bag[i].num0]) 137 { 138 choose[i]=0;y=y-bag[i].num0; 139 } 140 else if(dp[i][y]==dp[i-1][y-bag[i].num1]) 141 { 142 choose[i]=1;y=y-bag[i].num1; 143 } 144 } 145 /*for(int i=1;i<=ct;i++) 146 { 147 cout <<choose[i]<<endl; 148 }*/ 149 for(int i=1;i<=p1+p2;i++){ 150 int fa=find(i); 151 int z=M[fa]; 152 if(choose[z]==cnt[i]) 153 cout <<i<<'\n'; 154 } 155 cout <<"end\n"; 156 } 157 158 } 159 return 0; 160 }




