Gym 101810
友情提示:
这篇题解并没有GJKL,因为我也不会,而且看别人代码也看不懂,而且问学长还不给我讲!hmc:这个题巨麻烦,我只能说balabala。我不学了我退役了啊!
A:这傻逼题我从开头wa了四个小时然后我发现我写了各种奇葩东西,
嗯不说了。很明显要么在某线段起点开始要么在某线段终点结束。然后枚举段点二分就行。

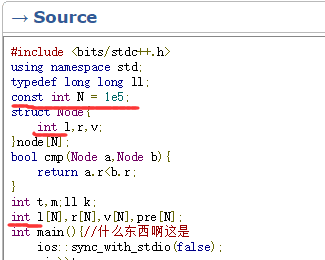
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 const int N = 1e5+5; 5 struct Node{ 6 ll l,r,v; 7 }node[N]; 8 bool cmp(Node a,Node b){ 9 return a.r<b.r; 10 } 11 ll t,m;ll k; 12 ll l[N],r[N],v[N],pre[N]; 13 int main(){//什么东西啊这是 14 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 15 cin>>t; 16 while (t--){ 17 cin>>m>>k; 18 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ 19 cin>>node[i].l>>node[i].r>>node[i].v; 20 } 21 sort(node+1,node+1+m,cmp); 22 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ 23 l[i]=node[i].l; 24 r[i]=node[i].r; 25 v[i]=node[i].v; 26 pre[i]=pre[i-1]+(r[i]-l[i]+1)*v[i]; 27 } 28 l[m+1]=2e9+2;r[m+1]=2e9+2; 29 pre[m+1]=pre[m]+0; 30 ll ans = 0; 31 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ 32 int id = lower_bound(r,r+m+1,l[i]+k-1)-r;// 33 ll tmp = pre[id-1]-pre[i-1]; 34 if(l[i]+k-1>=l[id]) 35 tmp+=(l[i]+k-l[id])*v[id]; 36 ans = max(ans,tmp); 37 } 38 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ 39 int id = lower_bound(l,l+m+1,r[i]-k+1)-l; 40 ll tmp = pre[i]-pre[id-1]; 41 if(r[i]-k+1<=r[id-1]){ 42 tmp+=(r[id-1]-(r[i]-k+1)+1)*v[id-1]; 43 } 44 ans = max(ans,tmp); 45 } 46 cout<<ans<<endl; 47 } 48 } 49 /** 50 1 51 1 1000000000 52 2 1000000000 1000000000 53 */
B:这。。。傻逼题吧。。。

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define mk(a,b) make_pair(a,b) 3 #define pii pair<int,int> 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef long long ll; 6 int t; 7 ll x,n; 8 ll ans[1005]; 9 int main(){ 10 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 11 cin>>t; 12 while (t--){ 13 memset(ans,0, sizeof(ans)); 14 cin>>x>>n; 15 if(n==1){ 16 cout<<x<<endl; 17 continue; 18 } 19 ll tmp = x/(2*n-2); 20 x%=2*n-2; 21 ans[1]+=tmp;ans[n]+=tmp; 22 for(int i=2;i<n;i++) 23 ans[i]+=tmp*2; 24 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 25 if(x<=0) break; 26 ans[i]++;x--; 27 } 28 for(int i=n-1;i>=1;i--){ 29 if(x<=0) break; 30 ans[i]++,x--; 31 } 32 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 33 cout<<ans[i]<<' '; 34 } 35 cout<<endl; 36 } 37 }
C:读错题wa自闭了。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define mk(a,b) make_pair(a,b) #define pii pair<int,int> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int t;ll n; cin>>t; while (t--){ cin>>n; bool flag = false; int ans = 0; for(int i=0;i<=32;i++){ if(!(n&(1ll<<i))){ ans++; } else break; } cout<<ans+1<<endl; } }
D:别想什么横着竖着花里胡哨的,就一排一排的交错放就行。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define mk(a,b) make_pair(a,b) #define pii pair<int,int> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; int t; ll n,m; int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin>>t; while (t--){ cin>>n>>m; ll ans = 1e17; if(n==1){ cout<<(m+1)/2<<endl; continue; } if(m==1){ cout<<(n+1)/2<<endl; continue; } if(n%2==0){ if(m%2==0){ ans = min(ans,n/2*(m+1)); ans = min(ans,m/2*(n+1)); } else{ ans = min(ans,n/2*(m+1)); ans = min(ans,m*n/2+m/2); } } else{ if(m%2==0){ ans = min(ans,m/2*(n+1)); ans = min(ans,n*m/2+n/2); } else{ ans = min(ans,n*(m+1)/2); ans = min(ans,m*(n+1)/2); } } cout<<ans<<endl; } }
E:运用小学数学知识可以很轻松的发现这个递推式吧,写在代码里了。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define mk(a,b) make_pair(a,b) #define pii pair<int,int> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const ll mod = 1e9+7; const int N = 1E5+5; int t; int n; ll a[N]; ll pre[N]; ll f[N]; int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin>>t; while (t--){ cin>>n; pre[0]=1ll; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { cin >> a[i]; pre[i] = pre[i - 1] * a[i] % mod; } f[1]=a[1]-1; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ f[i]=(a[i]*f[i-1]+pre[i-1]*(a[i]-1))%mod; } cout<<f[n]<<endl; } }
F:我很知趣的没用memset,被这个东西坑死太多次了,然后枚举每个ai就完了

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define mk(a,b) make_pair(a,b) #define pii pair<int,int> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int N = 1e5+5; int t,n,a[N]; int vis[10*N]; int qaq(int x){ int tmp = x; for(int i=1;i*i<=x;i++){ if(x%i==0){ if(vis[i]) { tmp = min(tmp, i); break; } if(vis[x/i]) { tmp = min(tmp, x/i); } } } return tmp; } vector<int> v;//*** int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin>>t; while (t--){ cin>>n; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ cin>>a[i]; vis[a[i]]=1; v.push_back(a[i]); } ll sum = 0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ a[i] = qaq(a[i]); sum+=a[i]; } for(auto a:v){ vis[a]=0; } v.clear(); cout<<sum<<endl; } }
H:。。。

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define mk(a,b) make_pair(a,b) 3 #define pii pair<int,int> 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef long long ll; 6 int main(){ 7 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 8 int t,n,a[2005]; 9 cin>>t; 10 while (t--){ 11 cin>>n; 12 for(int i=1;i<=2*n;i++) 13 cin>>a[i]; 14 int maxx = 0; 15 for(int i=1;i<=2*n;i++){ 16 maxx = max(maxx,a[i]+a[2*n-i+1]); 17 } 18 cout<<maxx<<endl; 19 } 20 }
I:。。。

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define mk(a,b) make_pair(a,b) 3 #define pii pair<int,int> 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef long long ll; 6 int t,x,n; 7 int main(){ 8 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 9 cin>>t; 10 while (t--){ 11 cin>>x>>n; 12 int tmp = x/n; 13 if(tmp==0){ 14 cout<<-1<<endl; 15 continue; 16 } 17 if(x%n==0){ 18 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<tmp<<' '; 19 } else{ 20 vector<int> ans; 21 for(int i=1;i<=x%n;i++) 22 ans.push_back(tmp+1); 23 for(int i=x%n;i<n;i++) 24 ans.push_back(tmp); 25 reverse(ans.begin(),ans.end()); 26 for(auto a: ans) cout<<a<<' '; 27 } 28 cout<<endl; 29 } 30 }
M:lca板子题,用的cincout然后tle三发自闭了。快读大法好

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 const int N = 1e5+3; 5 inline int read() { 6 int X=0,w=1; char c=getchar(); 7 while (c<'0'||c>'9') { if (c=='-') w=-1; c=getchar(); } 8 while (c>='0'&&c<='9') X=(X<<3)+(X<<1)+c-'0',c=getchar(); 9 return X*w; 10 } 11 struct Node{ 12 int to,v1,v2; 13 }; 14 vector<Node>g[N]; 15 int s1[N],s2[N]; 16 int t,n,q; 17 int par[N][21],dep[N],deg[N]; 18 void dfs(int v,int fa){ 19 dep[v]=dep[fa]+1; 20 par[v][0]=fa; 21 for(int i=1;(1<<i)<=dep[fa];i++) 22 par[v][i]=par[par[v][i-1]][i-1]; 23 for(int i=0;i<g[v].size();i++){ 24 int u = g[v][i].to; 25 if(u==fa) 26 continue; 27 s1[u]=s1[v]+g[v][i].v1;//下来 28 s2[u]=s2[v]+g[v][i].v2;//上去 29 //down[v]+=g[v][i].v1+g[v][i].v2; 30 dfs(u,v); 31 //down[v]+=down[u]; 32 } 33 } 34 int lca(int x,int y){ 35 if(dep[x]>dep[y]) 36 swap(x,y); 37 for(int i=20;i>=0;i--) 38 if(dep[x]<=dep[y]-(1<<i)) 39 y = par[y][i]; 40 if(x==y) 41 return x; 42 for(int i=20;i>=0;i--) { 43 if (par[x][i] == par[y][i]) 44 continue; 45 else 46 x=par[x][i],y=par[y][i]; 47 } 48 return par[x][0]; 49 } 50 void init(){ 51 for(int i=1;i<=1e5;i++) 52 g[i].clear(); 53 memset(par,0, sizeof(par)); 54 memset(dep,0, sizeof(dep)); 55 memset(deg,0, sizeof(deg)); 56 memset(s1,0, sizeof(s1)); 57 memset(s2,0, sizeof(s2)); 58 } 59 int main(){ 60 t = read(); 61 while (t--){ 62 init(); 63 cin>>n; 64 int u,v,c1,c2; 65 int all = 0; 66 for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ 67 u=read();v=read();c1=read();c2=read(); 68 deg[u]++; 69 deg[v]++; 70 all+=c1+c2; 71 g[u].push_back(Node{v,c1,c2}); 72 g[v].push_back(Node{u,c2,c1}); 73 } 74 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 75 if(deg[i]==1){ 76 dfs(i,0); 77 break; 78 } 79 } 80 q=read(); 81 while (q--){ 82 u=read();v=read(); 83 int baba = lca(u,v); 84 int ans = all; 85 ans -= s2[v]-s2[baba]; 86 ans -= s1[u]-s1[baba]; 87 printf("%d\n",ans); 88 } 89 } 90 }




