第九课 — 静态链表
单链表完美解决了顺序表的问题 !
还有其它改进顺序表的方法吗?

牛人小C C 。 出场 。。。顺序表有优势 , 单链表也同样有缺点

单链表的相对劣势
单链表的实现严重依赖指针 !
数据元素中必须包含一个额外的指针域 !
没有指针的程序设计语言无法实现!
顺序表的改进


静态链表的逻辑结构


静态链表相关定义


静态链表操作




函数实现代码如下:

#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> #include "StaticList.h" #define AVAILABLE -1 /* 结点结构体的定义 */ typedef struct _tag_StaticListNode { unsigned int data; int next; } TStaticListNode; /* 静态链表结构体的定义 */ typedef struct _tag_StaticList { int capacity; TStaticListNode header; TStaticListNode node[]; } TStaticList; /* 静态链表的创建 */ StaticList* StaticList_Create(int capacity) // O(n) { TStaticList* ret = NULL; int i = 0; if( capacity >= 0 ) { ret = (TStaticList*)malloc(sizeof(TStaticList) + sizeof(TStaticListNode) * (capacity + 1)); } if( ret != NULL ) { ret->capacity = capacity; ret->header.data = 0; ret->header.next = 0; for(i=1; i<=capacity; i++) { ret->node[i].next = AVAILABLE; } } return ret; } void StaticList_Destroy(StaticList* list) // O(1) { free(list); } void StaticList_Clear(StaticList* list) // O(n) { TStaticList* sList = (TStaticList*)list; int i = 0; if( sList != NULL ) { sList->header.data = 0; sList->header.next = 0; for(i=1; i<=sList->capacity; i++) { sList->node[i].next = AVAILABLE; } } } int StaticList_Length(StaticList* list) // O(1) { TStaticList* sList = (TStaticList*)list; int ret = -1; if( sList != NULL ) { ret = sList->header.data; } return ret; } int StaticList_Capacity(StaticList* list) // O(1) { TStaticList* sList = (TStaticList*)list; int ret = -1; if( sList != NULL ) { ret = sList->capacity; } return ret; } int StaticList_Insert(StaticList* list, StaticListNode* node, int pos) // O(n) { TStaticList* sList = (TStaticList*)list; int ret = (sList != NULL); int current = 0; int index = 0; int i = 0; ret = ret && (sList->header.data + 1 <= sList->capacity); ret = ret && (pos >=0) && (node != NULL); if( ret ) { for(i=1; i<=sList->capacity; i++) { if( sList->node[i].next == AVAILABLE ) { index = i; break; } } sList->node[index].data = (unsigned int)node; sList->node[0] = sList->header; for(i=0; (i<pos) && (sList->node[current].next != 0); i++) { current = sList->node[current].next; } sList->node[index].next = sList->node[current].next; sList->node[current].next = index; sList->node[0].data++; sList->header = sList->node[0]; } return ret; } /* 获取第pos个元素的操作 */ StaticListNode* StaticList_Get(StaticList* list, int pos) // O(n) { TStaticList* sList = (TStaticList*)list; StaticListNode* ret = NULL; int current = 0; int object = 0; int i = 0; if( (sList != NULL) && (0 <= pos) && (pos < sList->header.data) ) { sList->node[0] = sList->header; for(i=0; i<pos; i++) { current = sList->node[current].next; } object = sList->node[current].next; ret = (StaticListNode*)(sList->node[object].data); } return ret; } /* 删除第pos个元素操作 */ StaticListNode* StaticList_Delete(StaticList* list, int pos) // O(n) { TStaticList* sList = (TStaticList*)list; StaticListNode* ret = NULL; int current = 0; int object = 0; int i = 0; if( (sList != NULL) && (0 <= pos) && (pos < sList->header.data) ) { sList->node[0] = sList->header; for(i=0; i<pos; i++) { current = sList->node[current].next; } object = sList->node[current].next; sList->node[current].next = sList->node[object].next; sList->node[0].data--; sList->header = sList->node[0]; sList->node[object].next = AVAILABLE; ret = (StaticListNode*)(sList->node[object].data); } return ret; }
测试代码如下:

#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "StaticList.h" /* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */ int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { StaticList* list = StaticList_Create(10); int index = 0; int i = 0; int j = 1; int k = 2; int x = 3; int y = 4; int z = 5; StaticList_Insert(list, &i, 0); StaticList_Insert(list, &j, 0); StaticList_Insert(list, &k, 0); for(index=0; index<StaticList_Length(list); index++) { int* p = (int*)StaticList_Get(list, index); printf("%d\n", *p); } printf("\n"); while( StaticList_Length(list) > 0 ) { int* p = (int*)StaticList_Delete(list, 0); printf("%d\n", *p); } printf("\n"); StaticList_Insert(list, &x, 0); StaticList_Insert(list, &y, 0); StaticList_Insert(list, &z, 0); printf("Capacity: %d Length: %d\n", StaticList_Capacity(list), StaticList_Length(list)); for(index=0; index<StaticList_Length(list); index++) { int* p = (int*)StaticList_Get(list, index); printf("%d\n", *p); } StaticList_Destroy(list); return 0; }
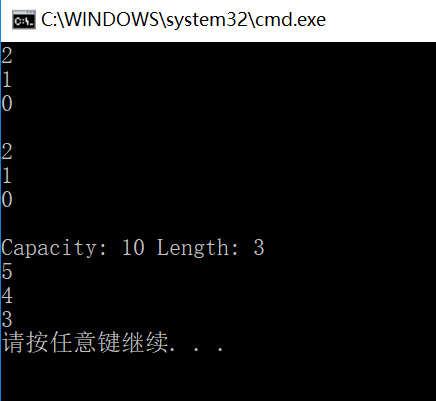
运行结果如下:
欢迎加入作者的小圈子
扫描下方左边二维码加入QQ交流群,扫描下方右边二维码关注个人微信公众号并,获取更多隐藏干货,QQ交流群:859800032 微信公众号:Crystal软件学堂


|
作者:Liu_Jing bilibili视频教程地址:https://space.bilibili.com/5782182 本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在转载文章页面给出原文连接。 如果你觉得文章对你有所帮助,烦请点个推荐,你的支持是我更文的动力。 文中若有错误,请您务必指出,感谢给予我建议并让我提高的你。 |





