消息队列NetMQ 原理分析5-StreamEngine、Encord和Decord
[TOC]
前言
介绍
[NetMQ](https://github.com/zeromq/netmq.git)是ZeroMQ的C#移植版本,它是对标准socket接口的扩展。它提供了一种异步消息队列,多消息模式,消息过滤(订阅),对多种传输协议的无缝访问。
当前有2个版本正在维护,版本3最新版为3.3.4,版本4最新版本为4.0.1。本文档是对4.0.1分支代码进行分析。
目的
对NetMQ的源码进行学习并分析理解,因此写下该系列文章,本系列文章暂定编写计划如下:
- 消息队列NetMQ 原理分析1-Context和ZObject
- 消息队列NetMQ 原理分析2-IO线程和完成端口
- 消息队列NetMQ 原理分析3-命令产生/处理、创建Socket和回收线程
- 消息队列NetMQ 原理分析4-Socket、Session、Option和Pipe
- 消息队列NetMQ 原理分析5-StreamEngine,Encord和Decord
- 消息队列NetMQ 原理分析6-TCP和Inpoc实现
- 消息队列NetMQ 原理分析7-Device
- 消息队列NetMQ 原理分析8-不同类型的Socket
- 消息队列NetMQ 原理分析9-实战
友情提示: 看本系列文章时最好获取源码,更有助于理解。
StreamEngine
SocketBase将Msg发送给SessionBase之后需要将Msg转化为byte[]进行传输,Engine就是做转换的工作,转换完成之后就会和实际的底层Socket进行消息传输。

NetMQ在Tcp协议消息转换使用的是StreamEngine。
internal sealed class StreamEngine : IEngine, IProactorEvents, IMsgSink
{
}
上一章介绍到管道事件。
发送数据
当出管道有数据可读时,会调用SessionBase的ReadActivated事件
public void ReadActivated(Pipe pipe)
{
...
if (m_engine != null)
m_engine.ActivateOut();
else
m_pipe.CheckRead();
}
然后会调用对应m_engine的ActivateOut事件
public void ActivateOut()
{
FeedAction(Action.ActivateOut, SocketError.Success, 0);
}
public void FeedAction(){
...
case State.Active:
switch (action)
{
case Action.OutCompleted:
int bytesSent = EndWrite(socketError, bytesTransferred);
// IO error has occurred. We stop waiting for output events.
// The engine is not terminated until we detect input error;
// this is necessary to prevent losing incoming messages.
if (bytesSent == -1)
{
m_sendingState = SendState.Error;
}
else
{
m_outpos.AdvanceOffset(bytesSent);
m_outsize -= bytesSent;
BeginSending();
}
break;
...
}
...
}
当TCPConnect客户端发送请求完成时,会调用OutCompleted事件
private void Loop()
{
...
switch (completion.OperationType)
{
...
case OperationType.Connect:
case OperationType.Disconnect:
case OperationType.Send:
item.ProactorEvents.OutCompleted(
completion.SocketError,
completion.BytesTransferred);
}
}
...
public void OutCompleted(SocketError socketError, int bytesTransferred)
{
...
// Create the engine object for this connection.
var engine = new StreamEngine(m_s, m_options, m_endpoint);
...
// Attach the engine to the corresponding session object.
SendAttach(m_session, engine);
...
}
此时会创建一个StreamEngine和请求的SessionBase对象进行关联。
protected override void ProcessAttach(IEngine engine)
{
Debug.Assert(engine != null);
// Create the pipe if it does not exist yet.
if (m_pipe == null && !IsTerminating)
{
ZObject[] parents = { this, m_socket };
int[] highWaterMarks = { m_options.ReceiveHighWatermark, m_options.SendHighWatermark };
int[] lowWaterMarks = { m_options.ReceiveLowWatermark, m_options.SendLowWatermark };
bool[] delays = { m_options.DelayOnClose, m_options.DelayOnDisconnect };
Pipe[] pipes = Pipe.PipePair(parents, highWaterMarks, lowWaterMarks, delays);
// Plug the local end of the pipe.
pipes[0].SetEventSink(this);
// Remember the local end of the pipe.
Debug.Assert(m_pipe == null);
m_pipe = pipes[0];
// Ask socket to plug into the remote end of the pipe.
SendBind(m_socket, pipes[1]);
}
// Plug in the engine.
Debug.Assert(m_engine == null);
m_engine = engine;
m_engine.Plug(m_ioThread, this);
}
接收数据
当完成端口通知数据接收完成时,会调用Proactor的InCompleted事件,实际就是调用的对应的StreamEngine的InCompleted事件
public void InCompleted(SocketError socketError, int bytesTransferred)
{
FeedAction(Action.InCompleted, socketError, bytesTransferred);
}
public void FeedAction(){
...
case State.Active:
switch (action)
{
case Action.InCompleted:
m_insize = EndRead(socketError, bytesTransferred);
ProcessInput();
break;
...
}
...
}
接收完成后会对接收到的数据进行处理
private void ProcessInput()
{
...
if (m_options.RawSocket)
{
if (m_insize == 0 || !m_decoder.MessageReadySize(m_insize))
{
processed = 0;
}
else
{
processed = m_decoder.ProcessBuffer(m_inpos, m_insize);
}
}
else
{
// Push the data to the decoder.
processed = m_decoder.ProcessBuffer(m_inpos, m_insize);
}
...
// Flush all messages the decoder may have produced.
m_session.Flush();
...
}
public override bool MessageReadySize(int msgSize)
{
m_inProgress = new Msg();
m_inProgress.InitPool(msgSize);
NextStep(new ByteArraySegment(m_inProgress.Data, m_inProgress.Offset),
m_inProgress.Size, RawMessageReadyState);
return true;
}
读取数据到Msg后会调用Decoder的ProcessBuffer方法
PS:由于
NetMQ有自己的传输协议格式,因此当使用NetMQ和其他程序进行Socket传输时,必须使用StreamSocket。
public int ProcessBuffer(ByteArraySegment data, int size)
{
...
while (m_toRead == 0)
{
if (!Next())
{
if (State < 0)
{
return -1;
}
return size;
}
}
return size;
...
}
protected override bool Next()
{
if (State == RawMessageReadyState)
{
return RawMessageReady();
}
return false;
}
private bool RawMessageReady()
{
...
bool isMessagedPushed = m_msgSink.PushMsg(ref m_inProgress);
if (isMessagedPushed)
{
// NOTE: This is just to break out of process_buffer
// raw_message_ready should never get called in state machine w/o
// message_ready_size from stream_engine.
NextStep(new ByteArraySegment(m_inProgress.Data, m_inProgress.Offset),
1, RawMessageReadyState);
}
return isMessagedPushed;
...
}
对读到的数据进行处理调用RawDecoder的Next的方法,将获取到的Msg放入到SeesionBase的管道中。
流程分析
读写数据流程图如下图所示:
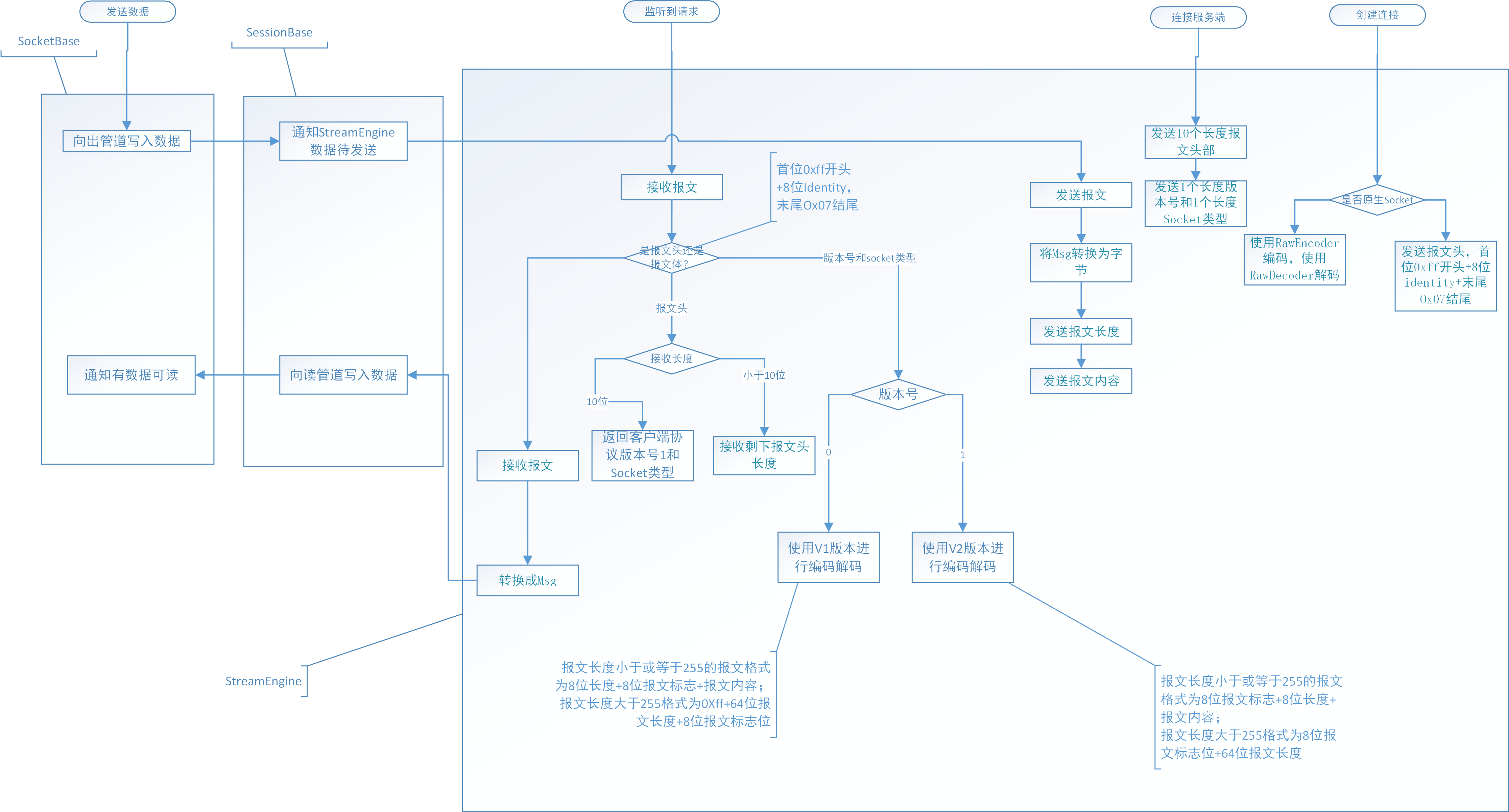
我们使用WireShark进行验证。
我们监听15557地址,然后创建一个客户端连接15557地址
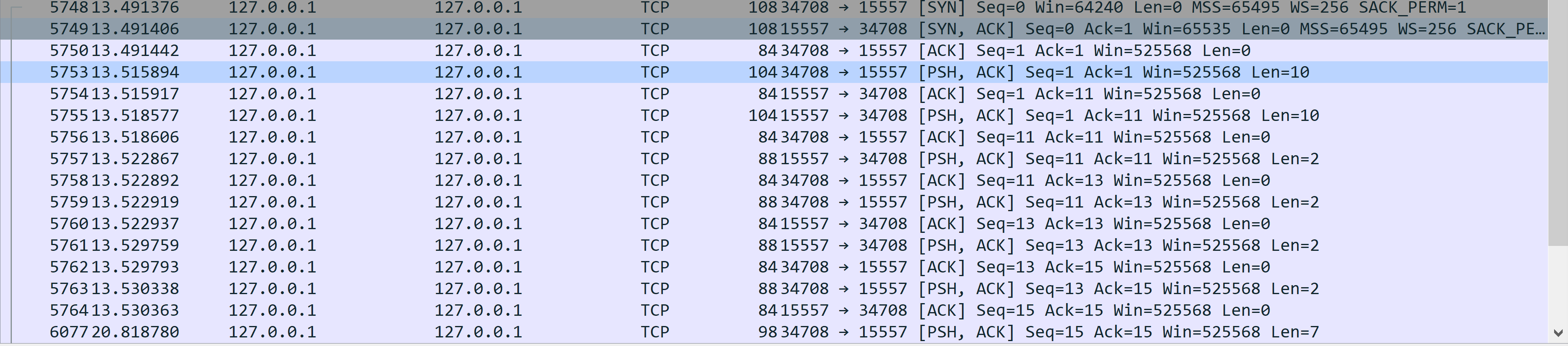
前面3条是三次握手。第四条是客户端向服务器发送了10字节长度的请求头部,以0xff开头,0x7f结尾。中间是8字节是Identitysize长度
...
switch (m_handshakeState)
{
case HandshakeState.Closed:
switch (action)
{
case Action.Start:
// Send the 'length' and 'flags' fields of the identity message.
// The 'length' field is encoded in the long format.
m_greetingOutputBuffer[m_outsize++] = 0xff;
m_greetingOutputBuffer.PutLong(m_options.Endian, (long)m_options.IdentitySize + 1, 1);
m_outsize += 8;
m_greetingOutputBuffer[m_outsize++] = 0x7f;
...
}
...
}
...

第6条是服务器向客户端发送的10字节长度的请求头部,以0xff开头,0x7f结尾。中间是8字节是identitysize的信息
I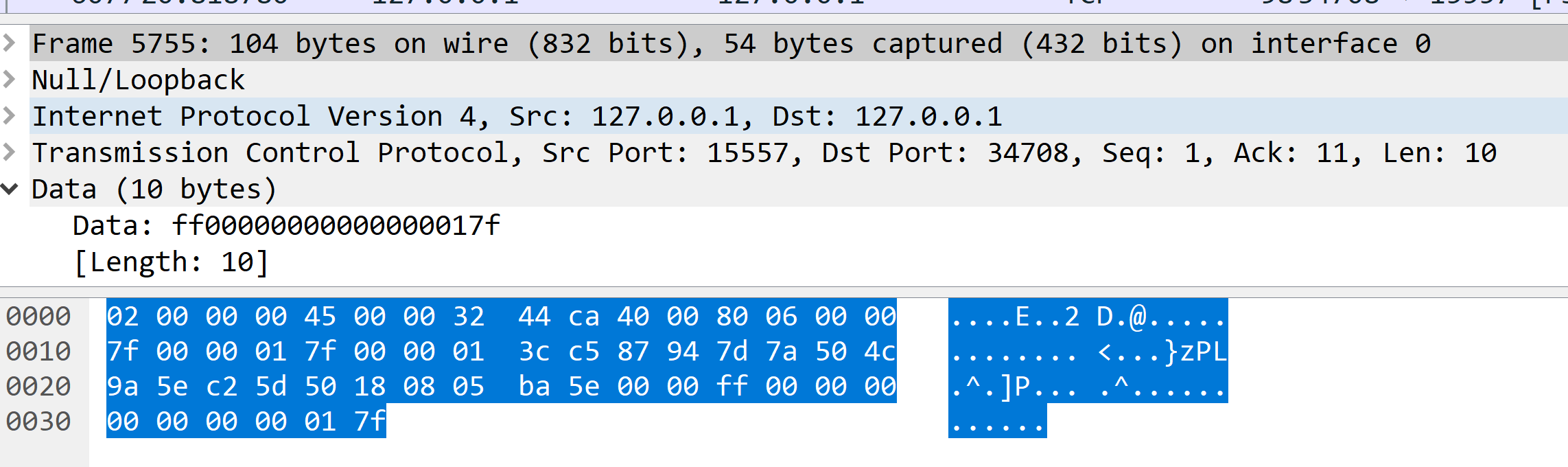
第8条是服务器向客户端发送的版本号和Socket类型,01表示版本号1,06表示当前是RouterSocket
...
case HandshakeState.ReceivingGreeting:
switch (action)
{
case Action.InCompleted:
...
if (m_greeting[0] != 0xff || (m_greetingBytesRead == 10 && (m_greeting[9] & 0x01) == 0)){
...
}
else if (m_greetingBytesRead < 10)
{
var greetingSegment = new ByteArraySegment(m_greeting, m_greetingBytesRead);
BeginRead(greetingSegment, PreambleSize - m_greetingBytesRead);
}
else
{
...
m_outpos[m_outsize++] = 1; // Protocol version
m_outpos[m_outsize++] = (byte)m_options.SocketType;
...
}
...
}
...
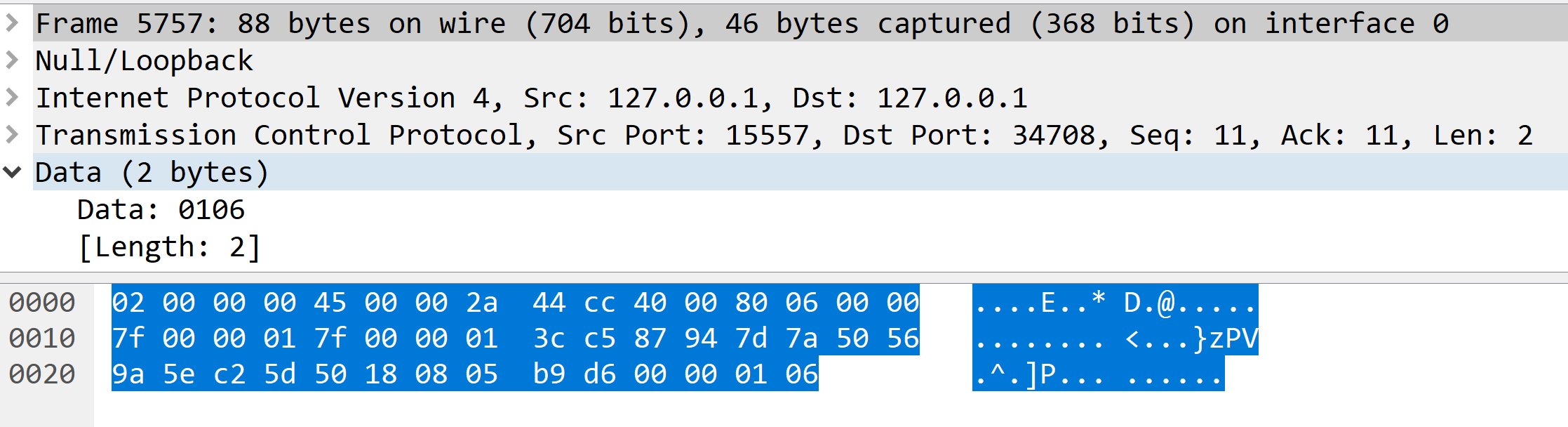
第10条是客户端向服务器发送的版本号和socket类型,05表示当前是DealSocket
...
case HandshakeState.ReceivingRestOfGreeting:
switch (action)
{
case Action.InCompleted:
...
if (m_greeting[VersionPos] == 0)
{
// ZMTP/1.0 framing.
m_encoder = new V1Encoder(Config.OutBatchSize, m_options.Endian);
m_encoder.SetMsgSource(m_session);
m_decoder = new V1Decoder(Config.InBatchSize, m_options.MaxMessageSize, m_options.Endian);
m_decoder.SetMsgSink(m_session);
}
else
{
// v1 framing protocol.
m_encoder = new V2Encoder(Config.OutBatchSize, m_session, m_options.Endian);
m_decoder = new V2Decoder(Config.InBatchSize, m_options.MaxMessageSize, m_session, m_options.Endian);
}
Activate();
...
}
...
Encoder
###V2Encoder
接下来就是数据传输。
public V2Encoder(int bufferSize, IMsgSource session, Endianness endian)
: base(bufferSize, endian)
{
m_inProgress = new Msg();
m_inProgress.InitEmpty();
m_msgSource = session;
// Write 0 bytes to the batch and go to message_ready state.
NextStep(m_tmpbuf, 0, MessageReadyState, true);
}
由于NetMQ使用的是版本1,用的是V2Encoder和V2Decoder进行编码和解码。
在初始化Encoder的时候会向报文写入2个0字节数据,暂时不明白为何要这样做。
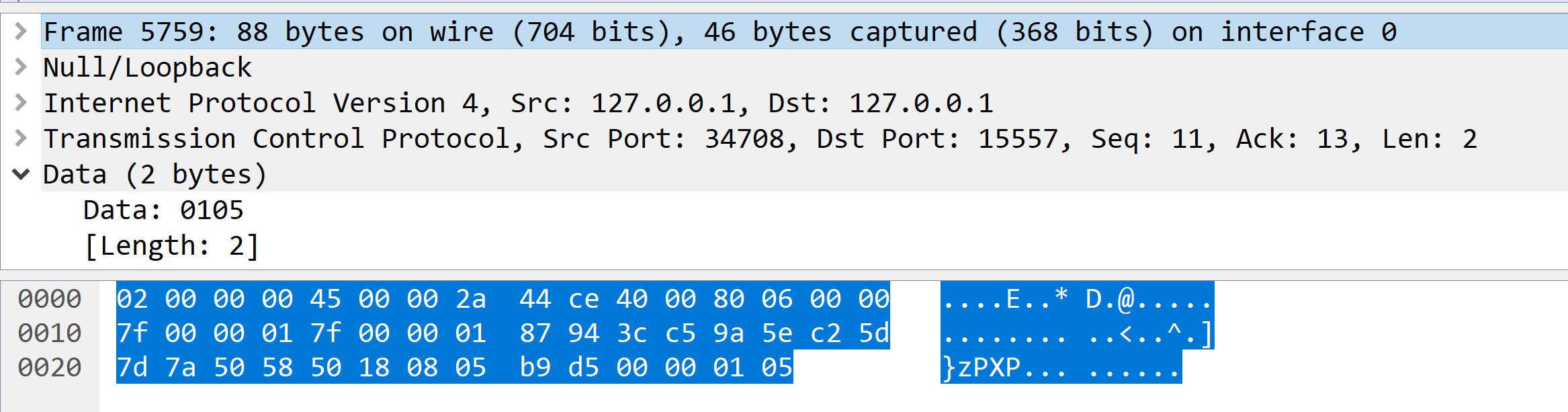
int protocolFlags = 0;
if (m_inProgress.HasMore)
protocolFlags |= V2Protocol.MoreFlag;
if (m_inProgress.Size > 255)
protocolFlags |= V2Protocol.LargeFlag;
m_tmpbuf[0] = (byte)protocolFlags;
// Encode the message length. For messages less then 256 bytes,
// the length is encoded as 8-bit unsigned integer. For larger
// messages, 64-bit unsigned integer in network byte order is used.
int size = m_inProgress.Size;
if (size > 255)
{
m_tmpbuf.PutLong(Endian, size, 1);
NextStep(m_tmpbuf, 9, SizeReadyState, false);
}
else
{
m_tmpbuf[1] = (byte)(size);
NextStep(m_tmpbuf, 2, SizeReadyState, false);
}
第一个字节是Flags用于标记该报文是否为大报文,超过过255个字节就会标记为大包标记,是否还有更多报文。若报文长度小于256,则第二个字节用于存储报文长度。但是若是大报文,则会8个字节保存报文长度。
下面就开始发送数据
我们用客户端发一个字符串test1,然后服务端原样返回该字符串
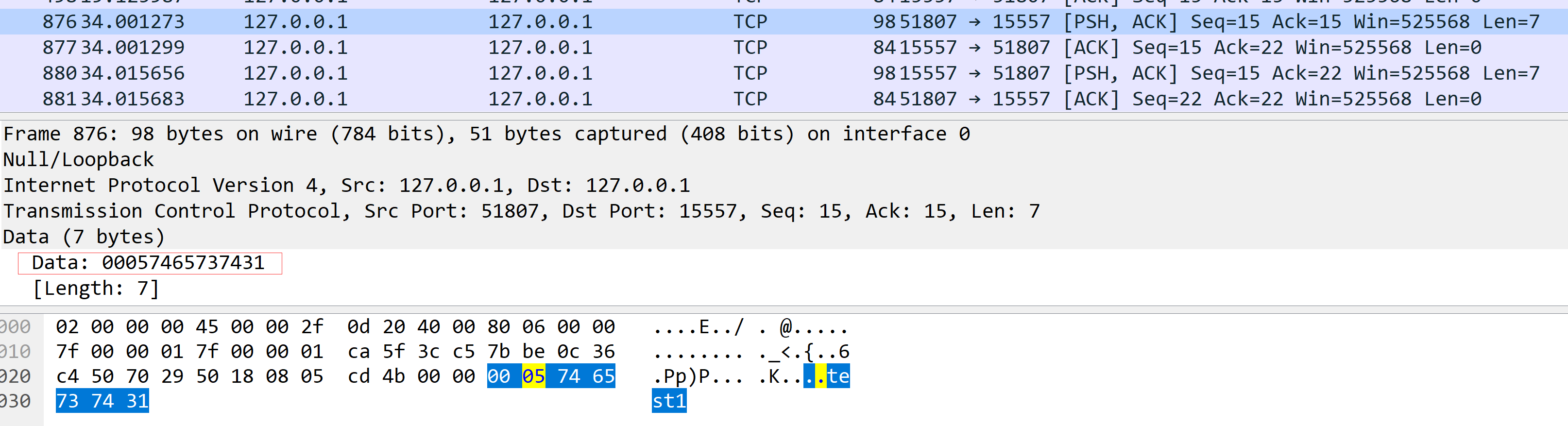
可以看到如我们上面分析的一样,第一个字节为0,第二个字节为大小test1为5个字节长度。由于CMD命令单行输入最长字符限制长度为255,因此我们没办法在CMD命令下输入更长数据进行测试。暂时就不做验证。
###V1Encoder
V1Encoder编码如下所示
if (size < 255)
{
m_tmpbuf[0] = (byte)size;
m_tmpbuf[1] = (byte)(m_inProgress.Flags & MsgFlags.More);
NextStep(m_tmpbuf, 2, SizeReadyState, false);
}
else
{
m_tmpbuf[0] = 0xff;
m_tmpbuf.PutLong(Endian, size, 1);
m_tmpbuf[9] = (byte)(m_inProgress.Flags & MsgFlags.More);
NextStep(m_tmpbuf, 10, SizeReadyState, false);
}
当小于255字符,首字符是长度,第二个字符是Flags,超过255字符,首字符为0xff,然后跟着8个字符长度的长度值,接下来是Flags
###RawEncoder
使用RawEncoder会将原始数据原样发送不会增加任何其他字符。
Decoder
###V2Decoder
接收到数据会先接收第一个字节Flags判断是否有后续包以及是小包还是打包,若是小包,则解析第一个字节长度位,否则读取8个字节长度位。
###V1Decoder
接收到数据收先会判断第一个字节是不是Oxff,若为Oxff则表示为打包,获取8位字节长度,否则获取1位字节长度处理。
###RawDecoder
使用RawDecoder会读取数据保存到管道中。
总结
本片介绍了NetMQ的报文格式并阐述了底层Msg如何转换为流进行发送和接收。
微信扫一扫二维码关注订阅号杰哥技术分享
本文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Jack-Blog/p/7283897.html
作者博客:杰哥很忙
欢迎转载,请在明显位置给出出处及链接




