HashSet,TreeSet,LinkedHashSet的比较
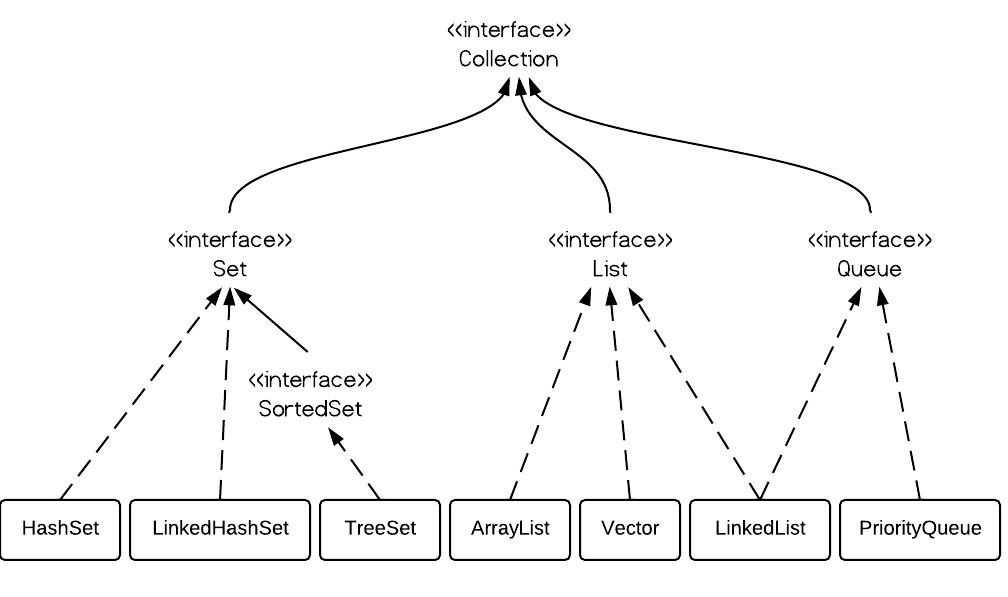
A Set contains no duplicate elements. That is one of the major reasons to use a set. There are 3 commonly used implementations of Set: HashSet, TreeSet and LinkedHashSet. When and which to use is an important question. In brief, if you need a fast set, you should use HashSet; if you need a sorted set, then TreeSet should be used; if you need a set that can be store the insertion order, LinkedHashSet should be used.
1. Set Interface
Set interface extends Collection interface. In a set, no duplicates are allowed. Every element in a set must be unique. You can simply add elements to a set, and duplicates will be removed automatically.
理解:Set中不包含重复元素.Set有三种实现方式:HashSet,TreeSet和LinkedHashSet这三种.当你需要一个操作速度较快的集合的时候,HashSet很合适;如果你需要一个元素有序的集合的时候,TreeSet很合适;当你需要保存元素的插入顺序的时候,LinkedHashSet很合适.
2. HashSet vs. TreeSet vs. LinkedHashSet
HashSet is Implemented using a hash table. Elements are not ordered. The add, remove, and contains methods have constant time complexity O(1).
TreeSet is implemented using a tree structure(red-black tree in algorithm book). The elements in a set are sorted, but the add, remove, and contains methods has time complexity of O(log (n)). It offers several methods to deal with the ordered set like first(), last(), headSet(), tailSet(), etc.
LinkedHashSet is between HashSet and TreeSet. It is implemented as a hash table with a linked list running through it, so it provides the order of insertion. The time complexity of basic methods is O(1).
理解:
- HashSet是通过哈希表来实现的.所有元素无序.增删改查操作的时间复杂度都为O(1).
- TreeSet是通过红黑树来实现的.所有元素有序,但增删改查的时间复杂度为O(log(n)).
- LinkedHashSet介于HashSet和TreeSet之间.它通过一个哈希表和一个链表来实现,基本操作的时间复杂度为O(1)
3. TreeSet Example
TreeSet<Integer> tree = new TreeSet<Integer>(); tree.add(12); tree.add(63); tree.add(34); tree.add(45); Iterator<Integer> iterator = tree.iterator(); System.out.print("Tree set data: "); while (iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.print(iterator.next() + " "); }
Output is sorted as follows:
Tree set data: 12 34 45 63
Now let's define a Dog class as follows:
class Dog { int size; public Dog(int s) { size = s; } public String toString() { return size + ""; } }
Let's add some dogs to TreeSet like the following:
import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.TreeSet; public class TestTreeSet { public static void main(String[] args) { TreeSet<Dog> dset = new TreeSet<Dog>(); dset.add(new Dog(2)); dset.add(new Dog(1)); dset.add(new Dog(3)); Iterator<Dog> iterator = dset.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.print(iterator.next() + " "); } } }
Compile ok, but run-time error occurs:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: collection.Dog cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable at java.util.TreeMap.put(Unknown Source) at java.util.TreeSet.add(Unknown Source) at collection.TestTreeSet.main(TestTreeSet.java:22)
Because TreeSet is sorted, the Dog object need to implement java.lang.Comparable'scompareTo() method like the following:
class Dog implements Comparable<Dog>{ int size; public Dog(int s) { size = s; } public String toString() { return size + ""; } @Override public int compareTo(Dog o) { return size - o.size; } }
The output is:
1 2 3
理解:当TreeMap中的Key为类对象的时候,你需要自己定义将这个类实现Comparable接口.
4. HashSet Example
HashSet<Dog> dset = new HashSet<Dog>(); dset.add(new Dog(2)); dset.add(new Dog(1)); dset.add(new Dog(3)); dset.add(new Dog(5)); dset.add(new Dog(4)); Iterator<Dog> iterator = dset.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.print(iterator.next() + " "); }
Output:
5 3 2 1 4
Note the order is not certain.
理解:HashSet迭代输出的元素是无序的.
5. LinkedHashSet Example
LinkedHashSet<Dog> dset = new LinkedHashSet<Dog>(); dset.add(new Dog(2)); dset.add(new Dog(1)); dset.add(new Dog(3)); dset.add(new Dog(5)); dset.add(new Dog(4)); Iterator<Dog> iterator = dset.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.print(iterator.next() + " "); }
The order of the output is certain and it is the insertion order:
2 1 3 5 4
6. Performance testing
The following method tests the performance of the three class on add() method.
public static void main(String[] args) { Random r = new Random(); HashSet<Dog> hashSet = new HashSet<Dog>(); TreeSet<Dog> treeSet = new TreeSet<Dog>(); LinkedHashSet<Dog> linkedSet = new LinkedHashSet<Dog>(); // start time long startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { int x = r.nextInt(1000 - 10) + 10; hashSet.add(new Dog(x)); } // end time long endTime = System.nanoTime(); long duration = endTime - startTime; System.out.println("HashSet: " + duration); // start time startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { int x = r.nextInt(1000 - 10) + 10; treeSet.add(new Dog(x)); } // end time endTime = System.nanoTime(); duration = endTime - startTime; System.out.println("TreeSet: " + duration); // start time startTime = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { int x = r.nextInt(1000 - 10) + 10; linkedSet.add(new Dog(x)); } // end time endTime = System.nanoTime(); duration = endTime - startTime; System.out.println("LinkedHashSet: " + duration); }
From the output below, we can clearly wee that HashSet is the fastest one.
HashSet: 2244768 TreeSet: 3549314 LinkedHashSet: 2263320
* The test is not precise, but can reflect the basic idea that TreeSet is much slower because it is sorted.
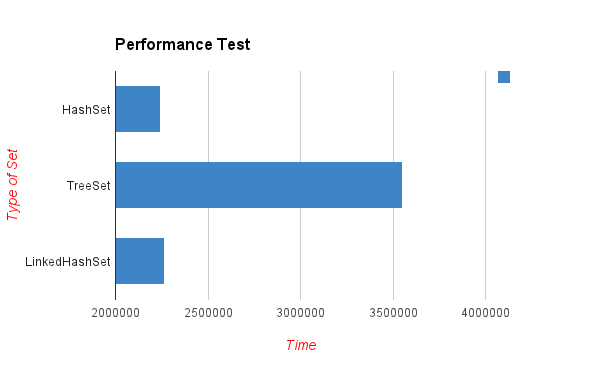
理解:TreeSet的操作最为耗时.
下面是从另一篇文章粘贴过来的,作为补充:
1) Synchronization
All three i.e. HashSet, TreeSet and LinkedHashSet are not synchronized. They can not be shared between multiple threads, until specifically synchronized. It's easy to create synchronized Set though, all you need to do is use java.util.Collections utility class as shown below :
Synchronizing HashSet in Java
Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet(...));
Synchronizing LinkedHashSet in Java
Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new LinkedHashSet(...));
Synchronizing TreeSet in Java
Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new TreeSet(...));
理解:HashSet,TreeSet和LinkedHashSet都是非同步的,它不能被多线程共享,但可以通过Collection工具类来实现.
2) Null Element
This property can be deduced form HashMap, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap, since HashSet internally uses HashMap, LinkedHashSet internally uses LinkedHashMap and TreeSet internally uses TreeMap. Both HashMap and LinkedHashMap allows one null key and so are these two Set implementation. On the other hand since TreeMap doesn't allow null keys, TreeSet doesn't allow null elements and throws java.lang.NullPointerException when you try to add a null object. Main reason of this is use of compareTo() and compare() method, which throws NullPointerException if one element is null, but it truly depends upon implementation.
理解:HashSet内部使用HashMap,LinkedHashSet内部使用LinkedHashMap,TreeSet内部使用TreeMap.由于HashMap和LinkedHashMap允许null元素,所以相应的HashSet和LinkedHashSet也允许null元素.TreeMap不允许有null键值,所以TreeSet不允许有null键值,否则会抛出NullPointerException异常.主要原因是compareTo和compare方法的参数为null时会抛出NullPointerException异常.
5) Iterator
Iterator retuned by all three Set implementations are fail-fast, which means if you modify collection once iteration begins i.e. add or delete elements without using Iterator's remove method, it will throw ConcurrentModificationException. Also Iterator of HashSet doesn't guarantee any order, while Iterator of LinkedHashSet let you iterate in the order elements are added. You can also see this article to learn more about different types of Iterator in Java.
理解:这三个集合返回的迭代器均为fail-fast类型的.也就是说当你对集合进行迭代操作之后,又调用了集合的add或delete操作对集合进行了修改(而不是调用迭代器的add和delete方法),就会抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常.HashSet的迭代器不保证任何顺序,而LinkedHashSet的迭代器会按照元素的插入顺序进行迭代.



