python--numpy、pandas
numpy 与 pandas 都是用来对数据进行处理的模块, 前者以array 为主体,后者以 DataFrame 为主体(让我想起了Spark的DataFrame 或RDD)
有说 pandas 是 numpy 的升级版, 实际两者相辅相成,是科学数据计算处理中的两大利器
numpy 常用函数
np.linalg.qr() 计算矩阵的QR分解。把矩阵A作为QR,q是正交的,r是上三角形。
np.linalg.inv() 矩阵求逆
np.linalg.det() 矩阵求行列式(标量)
np.save和np.load。数组会以未压缩的原始二进制模式被保存,后缀为.npy:
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
def walk_in_the_stree(steps=1000):
position = 0
# walk = [position]
for s in range(steps):
# step = random.normalvariate(0,1)
step = np.random.normal()
position += step
yield position
# walk.append(position)
if __name__ == '__main__':
walk = walk_in_the_stree()
plt.plot(list(walk)[:100])
#创建各种各样的数据
import numpy as np
# 定义单个列表,这时候是只有一个维度的
lst = np.array((1,2,3),dtype=np.int32) #(3,)
print(lst.shape)
# 转成 , 3 行一列 矩阵
matrix_3_1 = lst[:,np.newaxis]
print(matrix_3_1.shape)
matrix_3_1.astype(np.float64)
# 类似于 python range 1-13 步进 1 ,并重塑为 3*4 矩阵
mat_arange = np.arange(1,13,1).reshape(3,4)
print(mat_arange)
# 1-10 区间,自己计算步长 取 12 个 值
mat_linspace=np.linspace(1,10,12) # 1-10 取 12 个
print(mat_linspace)
mat_linspace_reshape = mat_linspace.reshape(3,4)
print(mat_linspace_reshape)
# 定义 2*3 矩阵
mat = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print(mat)
# 定义 2*3 全 0 矩阵
mat_zero = np.zeros((2,3))
print(mat_zero)
# 定义 2*3 全 1 矩阵
mat_ones = np.ones((2,3))
print(mat_ones)
# 定义 2*3 接近于 0 矩阵
mat_empty = np.empty((2,3),dtype=np.float64)
print(mat_empty)
mat_empty_one_more_axis = mat_empty[:,np.newaxis]
print(mat_empty_one_more_axis.ndim) # 秩也就是几维
print(mat_empty_one_more_axis.shape) # 2*1*3 三个维度
print(mat_empty_one_more_axis.size) # 总共有多少个数据 2*1*3 = 6
np.random.normal(size=(4, 4)) # 随机生成符合正态分布的 4*4 的矩阵
from random import normalvariate
N = 1000000
sample = [normalvariate(0, 1) for _ in range(N)]
sample
多维
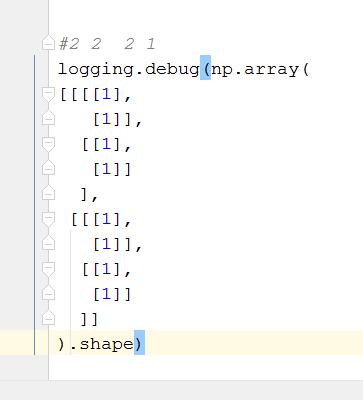
# 基本运算
# +- * 逐个 而 dot 是矩阵相乘 类似于 tensorflow的 mat_mul
import numpy as np
# +- * 逐个 而 dot 是矩阵相乘 类似于 tensorflow的 mat_mul
a = np.array([[1,2],[1,1]])
b = np.arange(4).reshape((2,2))
print('a:{}'.format(a))
print('b:{}'.format(b))
c = a * b
c_dot = a.dot(b)
print('c: {}'.format(c))
print('c_dot: {}'.format(c_dot))
output:
a:[[1 2]
[1 1]]
b:[[0 1]
[2 3]]
c: [[0 2]
[2 3]]
c_dot: [[4 7]
[2 4]]
import numpy as np
a = np.random.random((2,4))
print(a)
print(np.sum(a,axis=1)) # 按行求和
print(np.max(a,axis=0)) # 按列求最大值
print(np.min(a,axis=1)) # 按行求最小值
# 求最值所在索引,也有按列按行求
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(2,14).reshape((3,4))
print(A)
print(np.argmin(A,axis=1))
print(np.argmin(A))
print(np.argmax(A,axis=0))
print(np.argmax(A))
print(np.mean(A))
print(A.mean())
print(np.average(A))
# print(A.average()) 这个是没有的
print(np.median(A))
print(np.cumsum(A)) # 累加
print(np.diff(A)) # 累差
print(np.nonzero(A)) # 输出值的 行数, 列数 ,坐标综合指向
A = np.arange(14,2,-1).reshape((3,4))
print(A)
#排序
print(np.sort(A))
# 转置
print(np.transpose(A))
print(A.T)
print((A.T).dot(A))
print(np.clip(A,5,9)) # <5 截断为5 >9 截断为 9
[[ 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9]
[10 11 12 13]]
[0 0 0]
0
[2 2 2 2]
11
7.5
7.5
7.5
7.5
[ 2 5 9 14 20 27 35 44 54 65 77 90]
[[1 1 1]
[1 1 1]
[1 1 1]]
(array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2]), array([0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3]))
[[14 13 12 11]
[10 9 8 7]
[ 6 5 4 3]]
[[11 12 13 14]
[ 7 8 9 10]
[ 3 4 5 6]]
[[14 10 6]
[13 9 5]
[12 8 4]
[11 7 3]]
[[14 10 6]
[13 9 5]
[12 8 4]
[11 7 3]]
[[332 302 272 242]
[302 275 248 221]
[272 248 224 200]
[242 221 200 179]]
[[9 9 9 9]
[9 9 8 7]
[6 5 5 5]]
# numpy array 索引
# 强大的切片索引
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(26,2,-1).reshape((4,6))
print(A[1:3,2:4])
print('*'*50)
# 迭代 A 的行
for row in A:
print(row)
print('*'*50)
# 迭代 A 原本的 列
for column in A.T:
print(column)
print(A.flatten()) #试比较 .ravel 实现降维
# 迭代 A 中每一个项目
for item in A.flat:
print(item)
#output:
[[18 17]
[12 11]]
**************************************************
[26 25 24 23 22 21]
[20 19 18 17 16 15]
[14 13 12 11 10 9]
[8 7 6 5 4 3]
**************************************************
[26 20 14 8]
[25 19 13 7]
[24 18 12 6]
[23 17 11 5]
[22 16 10 4]
[21 15 9 3]
**************************************************
[26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3]
**************************************************
[[18 17]
[12 11]]
**************************************************
[26 25 24 23 22 21]
[20 19 18 17 16 15]
[14 13 12 11 10 9]
[8 7 6 5 4 3]
**************************************************
[26 20 14 8]
[25 19 13 7]
[24 18 12 6]
[23 17 11 5]
[22 16 10 4]
[21 15 9 3]
**************************************************
[26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3]
**************************************************
26,25,24,23,22,21,20,19,18,17,16,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,
# 创建多维数组 narray
res = np.random.randn(2,3) # res.shape => 2 * 3 二维数组 =》 矩阵
res * 10
res.dtype
res = np.array(range(10))
res = np.array([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10])
res[::2]
#Arithmetic with NumPy Arrays(数组计算)
# 切片索引
# 布尔索引
# Fancy Indexing(花式索引)
arr = np.arange(32).reshape((8, 4))
arr[[1, 5, 7, 2], [0, 3, 1, 2]] # 行, 列 定位元素
arr[[1, 5, 7, 2]][:, [0, 3, 1, 2]] # 先过滤出 1, 5, 7, 2 行 =》 然后全选行,然后换列顺序
# 数组转置和轴交换
data = np.arange(15).reshape(3,5)
data.T
arr = np.arange(16).reshape((2, 2, 4))
arr.transpose((1, 0, 2))
# numpy array 合并
import numpy as np
A = np.array([1,1,1])
B = np.array([2,2,3])
# 垂直合并 vertical stack,这里写出 np.newaxis是我认为vstack这操作背后首先把列表变成了有维度的结构然后进行合并
C = np.vstack((A[np.newaxis,:],B[np.newaxis,:]))
D = np.hstack((A,B)) # 水平合并 horizontal stack
print(A.shape,C.shape)
print('*'*50)
print(C)
print('*'*50)
print(D)
E = np.concatenate((A,B,B,A),axis=0)
print('*'*50)
print(E)
print('*'*50)
F = np.concatenate((A[:,np.newaxis],B[:,np.newaxis]),axis=1)
print(F)
output:
(3,) (2, 3)
**************************************************
[[1 1 1]
[2 2 3]]
**************************************************
[1 1 1 2 2 3]
**************************************************
[1 1 1 2 2 3 2 2 3 1 1 1]
**************************************************
[[1 2]
[1 2]
[1 3]]
# numpy array 分割
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(12).reshape((3,4))
print(A)
print('*'*50)
B = np.split(A,3,axis=0) # 行操作分割
print(B)
C = np.split(A,2,axis=1) # 行操作分给为 2 部分
print('*'*50)
print(C)
print('*'*50)
# 不等量分割
print(np.array_split(A,3,axis=1)) # 列操作 不等量分给为 3 列
print('*'*50)
# 简化版
print(np.vsplit(A,3))
print('*'*50)
print(np.hsplit(A,2))
output:
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
**************************************************
[array([[0, 1, 2, 3]]), array([[4, 5, 6, 7]]), array([[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])]
**************************************************
[array([[0, 1],
[4, 5],
[8, 9]]), array([[ 2, 3],
[ 6, 7],
[10, 11]])]
**************************************************
[array([[0, 1],
[4, 5],
[8, 9]]), array([[ 2],
[ 6],
[10]]), array([[ 3],
[ 7],
[11]])]
**************************************************
[array([[0, 1, 2, 3]]), array([[4, 5, 6, 7]]), array([[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])]
**************************************************
[array([[0, 1],
[4, 5],
[8, 9]]), array([[ 2, 3],
[ 6, 7],
[10, 11]])]
# numpy 深浅拷贝 跟 from copy import copy 里一个道理 ,赋值 < copy.copy < copy.deepcopy()
import numpy as np
a = numpy.arange(4)
b = a
c = a
d = b
a[0] = 11
print(b) # 直接赋值 abcd 都是同一个 a is b = True ,这时候改变a ,其他的bcd 都会被一起改变
b = a.copy() # 深拷贝
print('b: %s' %hex(id(b)),'!=','a: %s' %hex(id(a)))
out:
[11 1 2 3]
b: 0x7f4ad44f1210 != a: 0x7f4ad44e58a0
pandas 感觉能一打十 , pandas 抓住 一维 (Series np.linspace(1,12)),二维(np.linspace(1,12).reshape([3,4])) 分别去理解
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series([1,3,6,np.nan,44,1])
s
dates = pd.date_range('20160601',periods=6)
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(6,4),index=dates,columns=['a','b','c','d'])
df
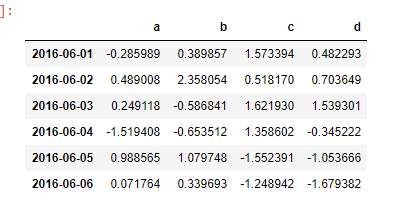
# 第二种方法生成 DataFrame
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'A':1.,
'B':pd.Timestamp('20130102'),
'C':pd.Series(1,index=list(range(4)),dtype='float32'),
'D':np.array([3]*4,dtype='int32'),
'E':pd.Categorical(["test","training","test","train"]),
'F':'foo',
'G':'Bar'
})
df2
df2.dtypes
df2.index
df2.columns
df2.values
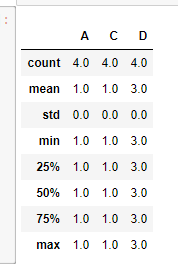
df2.describe()
按横纵轴排序
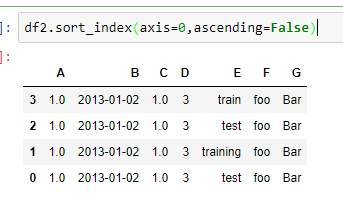
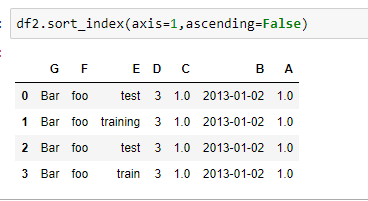
按某一列的值进行排序
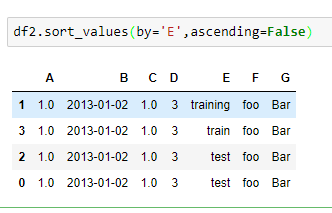
看到这里,忍不住说一句卧槽~ 这不干了 sql 的事情了么。。。
# 使用 pandas 筛选数据,简直碉堡!!!
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
dates = pd.date_range('2018-05-01',periods=6)
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(24).reshape(6,4),index=dates,columns=['A','B','C','D'])
df['A'] # 筛选某一列,按列名
print(df)
print(df.A)
print(df[0:3]) # 筛选某几行,按通用索引切片
print('*'*50)
print(df['20180501':'20180503']) # 筛选某几行,按自定义索引切片
print('*'*50)
# select by label: loc
print(df.loc['20180501':'20180503'])
print(df.loc['20180501':'20180503','A':'C'])
# df.loc[:,3]这样查找第三行是错误的 ,loc只能用自定义的索引来查找 如果要用到 0-3 这种需要使用 iloc ==>index local
print('*'*50)
# select by position
print(df.iloc[3]) # 第三行
print('*'*50)
# print(df.iloc[3:5,'B':'D']) 这样 用 column 名字查找也是不对的 iloc 只能用索引 0:5 这种
print(df.iloc[3:5,1:3])
print('*'*50)
# mixed selection: ix 标签与索引混合筛选
print(df.ix[2:4,['A','C']])
# Boolean indexing ,类似于 filter where df.A > 8
print(df[df.A>8])
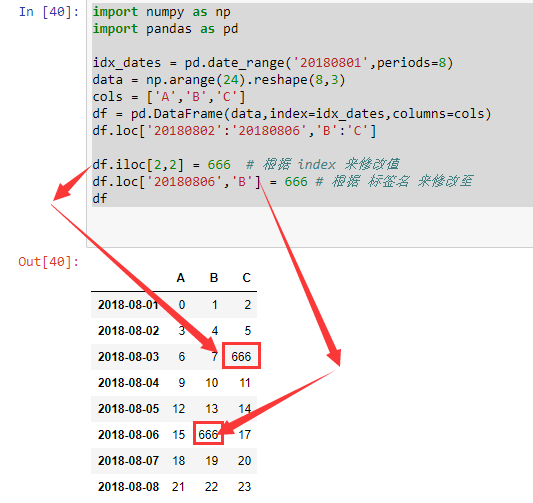
# 修改 值总结
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
idx_dates = pd.date_range('20180801',periods=8)
data = np.arange(24).reshape(8,3)
cols = ['A','B','C']
df = pd.DataFrame(data,index=idx_dates,columns=cols)
df.loc['20180802':'20180806','B':'C']
df.iloc[2,2] = 666 # 根据 index 来修改值
df.loc['20180806','B'] = 666 # 根据 标签名 来修改至
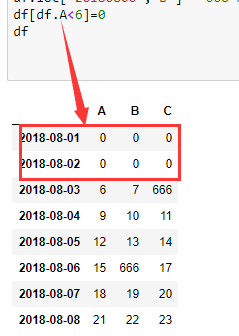
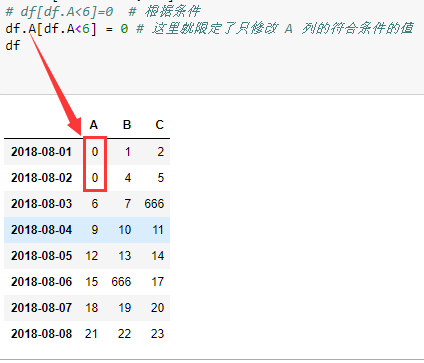
# df[df.A<6]=0 # 根据条件
df.A[df.A<6] = 0 # 这里就限定了只修改 A 列的符合条件的值
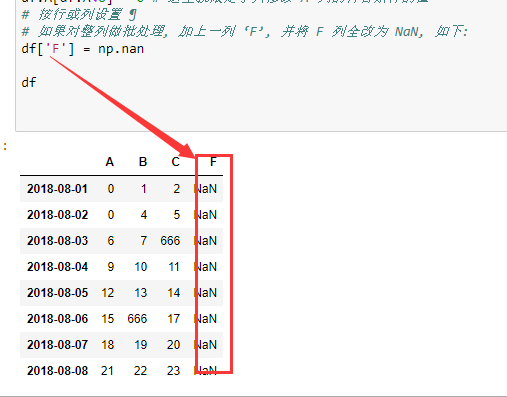
# 按行或列设置 ¶
# 如果对整列做批处理, 加上一列 ‘F’, 并将 F 列全改为 NaN, 如下:
# df['F'] = np.nan
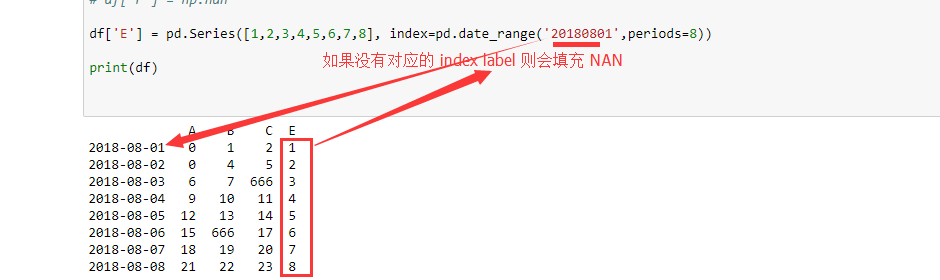
df['E'] = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8], index=pd.date_range('20180801',periods=8))
print(df)
#
金融数据模块 获取股票
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import pandas_datareader.data as web
import datetime
cmd = 'cmd /k D:\"Program Files (x86)"\python\python.exe "$(FULL_CURRENT_PATH)" &pause &exit'
#os.system(cmd)
print(cmd)
data = range(1,11)
index = [chr(i) for i in range(97,107,1)]
s = pd.Series(data,index=index)
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5))
s = pd.Series(dict(a=1,b=2,c=3))
print(s)
print(s.values)
print(s.index)
df = pd.DataFrame({'col1':[1,2,3],'col2':[4,5,6]},index=range(3))
print(df)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3,4),index=['row1','row2','row3'],columns=['col1','col2','col3','col4'])
# 根据标签来定位
print(df1.loc[['row2','row3'],['col3','col4']])
# 根据index 来定位
print(df1.iloc[1:,2:])
# ix 混合定位
print(df1.ix[1:,['col2','col4']])
df_csvsave = web.DataReader("601233.SS","yahoo",datetime.datetime(2019,1,1),datetime.date.today())
print(df_csvsave)
#--------------------Numpy 实操-----------------------#
import numpy as np
nd_array = np.arange(12).reshape(3,4)
# [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
nd_array_2 = np.random.randn(2,3)
# [[-0.41325135 -0.02692777 -0.32209818]
# [-0.2165073 -0.2670806 -0.81044977]]
nd_array_3 = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
# [[1 2 3]
# [4 5 6]]
nd_array_3.ndim # 不是很好
nd_array_3.shape # 最好打印的 维度
nd_array_3.dtype # 自动推断类别
#还有 一个 asarray 函数将输入转换为 ndarray ,但如果输入已经是 ndarray 则不再复制,可见 numpy 如何节省内存
nd_array = np.zeros((2,3,4))
nd_array_empty = np.empty((1,2,3)) # 想要用 np.emtpy 来生成 一个全0的数组并不安全,有时候他可能会返回未初始化的垃圾数值
nd_array_ones = np.ones((2,3,4))
ones_like
zeros_like
empty_like
full # 根据给定的形状和数据类型生成指定数值的数组
full_like #根据所给的数组生成一个形状一样但内容是制定熟知的数组
eye, identity 生成一个 N x N 的特征矩阵 (对角线位置都是 1, 其余位置是 0 )
# dtype 是 NumPy 能够与其他系统数据灵活交互的原因。
bool 用一位存储的布尔类型(值为TRUE或FALSE)
inti 由所在平台决定其精度的整数(一般为int32或int64)
int8 整数,范围为128至127
int16 整数,范围为32 768至32 767
int32 整数,范围为231至231 1
int64 整数,范围为263至263 1
uint8 无符号整数,范围为0至255
uint16 无符号整数,范围为0至65 535
uint32 无符号整数,范围为0至2321
uint64 无符号整数,范围为0至2641
float16 半精度浮点数(16位):其中用1位表示正负号,5位表示指数,10位表示尾数
float32 单精度浮点数(32位):其中用1位表示正负号,8位表示指数,23位表示尾数
float64或float 双精度浮点数(64位):其中用1位表示正负号,11位表示指数,52位表示尾数
complex64 复数,分别用两个32位浮点数表示实部和虚部
complex128或complex 复数,分别用两个64位浮点数表示实部和虚部
nd_array = np.arange(1,13,1).reshape((3,4))
# [[ 1 2 3 4]
# [ 5 6 7 8]
# [ 9 10 11 12]]
assert nd_array[1,0] == 5
#切片索引
#布尔索引
names = np.array(['Bob', 'Joe', 'Will', 'Bob', 'Will', 'Joe' ,'Joe'])
data = np.random.randn(7,4)
"""
[[-0.95318864 -1.74423099 -0.81897377 -0.70390841]
[-0.29549586 0.01167501 0.96874759 1.46136914]
[-1.12905232 -0.278389 0.3696933 0.61565096]
[ 0.13841785 -0.31665318 0.3529398 0.89718371]
[-1.69152047 -0.84335155 0.04088088 1.42676566]
[ 0.26460153 -0.47009072 -1.41669296 -0.15561476]
[ 0.43348994 0.58136748 -0.11474831 1.27946868]]
"""
# print(names == 'Bob')
print(data[names == 'Bob'])
"""
[[-0.95318864 -1.74423099 -0.81897377 -0.70390841]
[ 0.13841785 -0.31665318 0.3529398 0.89718371]]
"""
# 神奇索引
arr = np.empty((8,4))
for i in range(len(arr)):
arr[i] = i
print(arr)
[[0.00000000e+000 0.00000000e+000 0.00000000e+000 0.00000000e+000]
[1.00000000e+000 1.00000000e+000 1.00000000e+000 1.00000000e+000]
[6.01347002e-154 6.01347002e-154 2.02570722e+174 9.79882228e+252]
[4.05612391e+228 6.11148662e-154 6.01347002e-154 4.90927656e+252]
[8.89486967e+252 9.08367237e+223 1.43981165e+214 6.01347002e-154]
[4.18641660e+034 4.81436178e+199 9.78749662e+199 4.27250819e+180]
[2.17603461e+243 6.01347002e-154 3.04040975e+180 1.15824468e-152]
[2.76455339e+257 1.97107051e+161 6.01386414e-154 6.01347002e-154]]
print(arr[[4,3,0,6]])
[[4. 4. 4. 4.]
[3. 3. 3. 3.]
[0. 0. 0. 0.]
[6. 6. 6. 6.]]
arr = np.arange(32).reshape((8,4))
arr_3 = arr[[1,5,7,2]][:, [0,3,1,2]]
arr_2 = arr[[1,5,7,2], [0,3,1,2]] # 行列查找
# 转置 | 换轴
arr = np.arange(15).reshape((3,5))
print(np.dot(arr.T,arr))
对于更高维度的数组, transpose 方法可以接受包含周边好的元组, 用于置换轴
arr = np.arange(16).reshape((2,2,4))
print(arr)
print("*"*20)
print(arr.transpose((1,0,2)))
"""
[[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]]
[[ 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15]]]
********************
[[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[[ 4 5 6 7]
[12 13 14 15]]]
"""
换轴
arr = np.arange(16).reshape((2,2,4))
arr_swapped = arr.swapaxes(1,2)
print(arr_swapped)
"""
[[[ 0 4]
[ 1 5]
[ 2 6]
[ 3 7]]
[[ 8 12]
[ 9 13]
[10 14]
[11 15]]]
"""
numpy universal func --> ufunc
分为 一元 , 二元 , 等
一元通用函数有
abs , fabs 逐元素地计算证书, 浮点数或复数的绝对值
sqrt 计算每个元素的平方根 (与 arr** 0.5 相等)
square 计算每个元素的平方
exp 计算每个元素的自然指数值 e^x
log , log10 log2 log1p
剩下的查字典
二元通用函数
add
subtract
multiply
divide, floor_divide
power
maximum, fmax
minimum , fmin
mod
copysign
等等。。。
使用素组进行面向数组编程
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
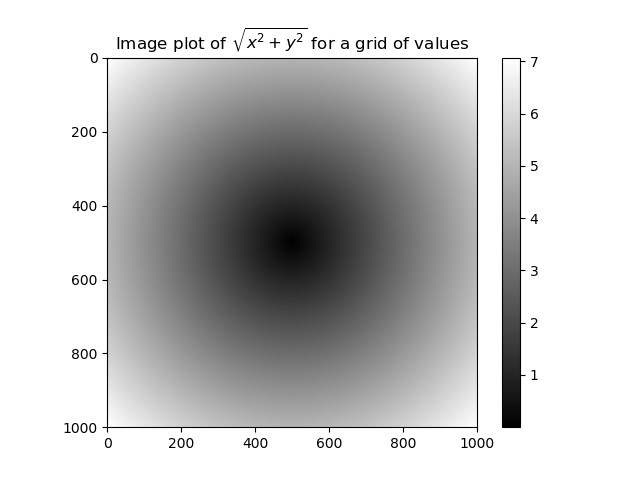
points = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.01)
xs, ys = np.meshgrid(points, points)
z = np.sqrt(xs **2 + ys ** 2)
plt.imshow(z, cmap = plt.cm.gray);
plt.colorbar()
plt.title("Image plot of $\sqrt{x^2 + y ^2}$ for a grid of values")
plt.show()
print(z)
将 条件逻辑作为数组操作
xarr = np.array([1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5])
yarr = np.array([2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5])
cond = np.array([True, False, True, True, False])
result = [(x if c else y) for x, y , c in zip(xarr, yarr, cond)] # 低效, 因为所有的工作都是通过解释器解释 python 代码完成
# print(result)
# [1.1, 2.2, 1.3, 1.4, 2.5]
result_2 = np.where(cond, xarr, yarr) # 高效一些因为是 C 实现的
print(result_2)
arr = np.random.randn(4,4)
arr_2 = np.where(arr>0, 2, -2)
print(arr_2)
"""
[[-2 2 2 -2]
[ 2 -2 2 2]
[ 2 2 -2 2]
[ 2 2 -2 2]]
"""
arr = np.random.randn(5,4)
arr.mean()
arr.sum()
arr.std()
arr.mean(axis=0) # 按行求均值
arr.mean(axis=1) # 按列求均值
基础数组统计方法
sum 沿着轴向计算所有元素的累和, 0 长度的数组, 累和胃 0
mean 数学平均, 0 长度的数组平均值为 NaN
std , var 标准差和方差, 可以选择自由度 调整 (默认坟墓是 n)
min, max 最小值和 最大值
argmin , argmax 最小值和最大值的 位置
cumsum 从 0 开始元素累计和
cumprod 从1 开始元素累计积
布尔值 数组的方法
arr = np.random.randn(100)
(arr > 0).sum()
对于布尔值数组, 有两个非常有用的方法 any 和 all ,。
bools = np.array([False, False, True, False])
bools.any()
bools.all()
### 排序
arr = np.random.randn(6)
arr.sort()
print(arr)
arr = np.random.randn(5,3)
arr.sort(1)
print(arr)
唯一值与其他集合操作
names = np.array(['Frank','May','Tom','Frank'])
np.unique(names)
判断一个数组中的值是否在另外以恶搞数组中, 并返回一个 布尔值数组
values = np.array([6,0,0,3,2,5,6])
bools = np.in1d(values, [2,3,6])
print(bools)
[ True False False True True False True]
数组的集合操作
unique(x) 计算 x 中的 唯一值, 并排序
intersect1d(x, y) 计算 x 和 y的交集, 并排序
union1d(x,y) 并集 并排序
in1d(x,y) 计算 x 中的元素是否包含在y 中, 返回一个布尔值数组
setdiff1(x,y) 茶几, 在 x 中 但不再 y 中的 x 的元素
setxor1d(x,y) 异或集, 在 x 或 y 中, 但不属于 x, y 交集的元素
numpy 使用数组进行 二进制文件的 输入和输出, 文本文件 一般用 pandas 操作
values = np.array([6,0,0,3,2,5,6])
np.save('values_ndarray',values)
# 会保存为 values_ndarray.npy 这不就是序列化么
values_loaded = np.load('values_ndarray.npy')
print(values_loaded)
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,6,1)
b = np.arange(6,11,1)
np.savez('test',a=a,b=b)
arch = np.load('test.npz')
c = arch['a']
d = arch['b']
print('{}\n{}'.format(c,d))
np.savez_compressed('test.npz', a=c,b=d) # 塞入已经压缩的文件中
4.5 线性代数
dot , @ 中缀操作符用于 点乘矩阵
np.dot(x,y) x@y
常用 numpy.linalg 函数
diag 将一个仿真的对焦 (或非对焦) 元素作为一维数组返回, 或者将一维数组砖会员成一个仿真, 并且在非对角线上有 零点
dot 矩阵点乘
trace 计算对角元素和
det 计算矩阵的行列式
eig 计算方阵的特征值 和特征向量
inv 计算方阵的逆矩阵
pinv 计算矩阵的 Moore-Penrose 伪逆
qr 计算QR分解
svd 计算奇异值分解
solve 求解 x 的线性系统 Ax= b , 其中 A 是方阵
lstsq 计算 Ax = b 的最小二乘解
伪随机数 生成
numpy.random
seed # 向随机数生成器传递随即状态种子
permutation # 返回一个序列的随机排列,或者 返回一个 乱序的整数范围序列
shuffle # 随机排列一个序列
rand # 从均匀分布中抽取样本
randint # 根据给定的由低到高的范围抽取随机整数
randn # MATLAB 型接口
binomial # 从二项分布中 抽取样本
normal 从正态(高斯) 分布中抽取样本
beta 从 beta 分布中 抽取样本
chjsquare 从卡方分布中抽取样本
gamma 从伽马分布中 抽取样本
uniform 从均匀 (0,10) 分布中抽取样本
随机漫步
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
position = 0
walk = [position]
steps = 1000
for i in range(steps):
step = 1 if random.randint(0,1) else -1
position += step
walk.append(position)
print(walk)
plt.plot(walk[:100])
plt.show()
一次性模拟多次随机漫步
import numpy as np
nwalks = 5000
nsteps = 1000
draws = np.random.randint(0,2, size=(nwalks, nsteps)) # 5k x 1k
steps = np.where(draws > 0, 1, -1)
walks = steps.cumsum(1)
walks_max = walks.max()
walks_min = walks.min()
print('max: {}\nmin: {}'.format(walks_max, walks_min))
"""
max: 129
min: -120
"""
hits30 = (np.abs(walks) >= 30).any(1)
print(hits30)
正式开始 pandas 之旅
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series, DataFrame
import numpy as np
obj = Series(np.arange(10))
assert (obj.index.all() == obj.values.all())
# Series 可以看做是长度固定且有序的字典
from pandas import Series, DataFrame
from collections import defaultdict
default_dict = defaultdict(int, dict(a=1,b=2,c=None))
series = Series(default_dict)
series.isnull()
"""
a False
b False
c True
"""
series.notnull()
"""
a True
b True
c False
"""
pandas DataFrame 操作
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series, DataFrame
from collections import defaultdict
person_1 = {'name': 'frank','age':18,'gender':'male'}
person_2 = {'name': 'tom','age':20,'gender':'male'}
person_3 = {'name': 'jim','age':16,'gender':'male'}
person_4 = {'name': 'may','age':18,'gender':'female'}
series = Series(person_1)
# print(series)
df = DataFrame([Series(person_1), Series(person_2), Series(person_3)], index=['person_1','person_2','person_3'])
print(df.head(10))
json_dict = {'person_1': {'name': 'frank', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'male'},
'person_2': {'name': 'tom', 'age': 20, 'gender': 'male'},
'person_3': {'name': 'jim', 'age': 16, 'gender': 'male'},
'person_4': {'name': 'may', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'female'}
}
df2 = DataFrame(json_dict)
print(df2.head(10).T)
name age gender
person_1 frank 18 male
person_2 tom 20 male
person_3 jim 16 male
age gender name
person_1 18 male frank
person_2 20 male tom
person_3 16 male jim
person_4 18 female may
dataframe --> index (行) columns (列) values (拿出具体内容 不包含 index , columns)
# reindex 可以 纵向 (row) 也可以横向 重建索引 参数为 columns=state
json_dict = {'person_1': {'name': 'frank', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'male'},
'person_2': {'name': 'tom', 'age': 20, 'gender': 'male'},
'person_3': {'name': 'jim', 'age': 16, 'gender': 'male'},
'person_4': {'name': 'may', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'female'}
}
df2 = DataFrame(json_dict).T
indice = pd.Index(['person_'+str(i) for i in np.arange(4)])
print(df2.reindex(indice)) # columns=indice 并且返回新对象
### 需要谨慎 重建索引,只有原本有的 索引列才会有值,其他填充 NaN
"""
age gender name
person_0 NaN NaN NaN
person_1 18 male frank
person_2 20 male tom
person_3 16 male jim
"""
# drop 也是同样道理 参数为 axis=1 或者 axis='columns' ,这是可以 inplace =True 操作
json_dict = {'person_1': {'name': 'frank', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'male'},
'person_2': {'name': 'tom', 'age': 20, 'gender': 'male'},
'person_3': {'name': 'jim', 'age': 16, 'gender': 'male'},
'person_4': {'name': 'may', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'female'}
}
df2 = DataFrame(json_dict).T
df2.drop(['age','gender'], axis='columns' or 1,inplace=True)
print(df2)
"""
name
person_1 frank
person_2 tom
person_3 jim
person_4 may
"""
loc , iloc 是作者 推崇的 ,至于 ix 混合索引 ,因为其有很多神奇索引 会看起来很怪异,作者不是很推荐
# 函数应用和映射
from pandas import DataFrame
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0,10,(4, 3)), columns=list('bde'), index=range(4))
print(df,'\n','*'*20)
print(df.apply(lambda x: x.max() - x.min(),axis=1)) # 按 columns 轴 横向统计每一行
常见操作
from pandas import DataFrame
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from functools import reduce
df = DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape((3,4)))
print(df.head(10))
print('{}'.format('*'*20))
df['col_sum'] = df.apply(sum,axis=1) # sum 每一行的值,并添加为最后一列 col_sum
df.loc['row_sum'] = df.apply(sum,axis=0) # sum 每一列的值, 并添加为最后一行
print(df.head(10))
"""
0 1 2 3
0 0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6 7
2 8 9 10 11
********************
0 1 2 3 col_sum
0 0 1 2 3 6
1 4 5 6 7 22
2 8 9 10 11 38
row_sum 12 15 18 21 66
"""
# 排序
from pandas import DataFrame
import numpy as np
df = DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape((3,4)), index=['a','c','b'])
print(df.head(10))
df = df.sort_index()
print(df.head(10))
from pandas import DataFrame
import numpy as np
df = DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape((3,4)), index=['a','c','b'], columns=['col2','col1','col3','col4'])
print(df.head(10))
df = df.sort_index(axis=1) # 按照列进行排序
print(df.head(10))
"""
col2 col1 col3 col4
a 0 1 2 3
c 4 5 6 7
b 8 9 10 11
col1 col2 col3 col4
a 1 0 2 3
c 5 4 6 7
b 9 8 10 11
"""
import numpy as np
df = DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape((3,4)), index=['a','c','b'], columns=['col2','col1','col3','col4'])
print(df.head(10))
df = df.sort_index(axis=0) # 按照列进行排序
print(df.head(10))
print('*'*20,'按照Series 值排序','*'*20)
df = df.sort_values(by=['col1'])
print(df.head(10))
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def my_print(text,star_cnt=20):
stars = '*'*star_cnt
print('{stars}{text}{stars}'.format(stars=stars,text=text))
df = pd.DataFrame({'colA' : list('AABCA'), 'colB' : ['X',np.nan,'Ya','Xb','Xa'],'colC' : [100,50,30,50,20], 'colD': [90,60,60,80,50]})
print(df.head(10))
my_print('正则操作')
df2 = df[df['colA'].str.contains(r'a|A')]
print(df2)
"""
colA colB colC colD
0 A X 100 90
1 A NaN 50 60
2 B Ya 30 60
3 C Xb 50 80
4 A Xa 20 50
********************正则操作********************
colA colB colC colD
0 A X 100 90
1 A NaN 50 60
4 A Xa 20 50
"""
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def my_print(text,star_cnt=20):
stars = '*'*star_cnt
print('{stars}{text}{stars}'.format(stars=stars,text=text))
df = pd.DataFrame({'colA' : list('AABCA'), 'colB' : ['X',np.nan,'Ya','Xb','Xa'],'colC' : [100,50,30,50,20], 'colD': [90,60,60,80,50]})
print(df.head(10))
my_print('分组聚合操作')
df2 = df.groupby(['colA']).sum().reset_index()
print(df2)
"""
colA colB colC colD
0 A X 100 90
1 A NaN 50 60
2 B Ya 30 60
3 C Xb 50 80
4 A Xa 20 50
********************分组聚合操作********************
colA colC colD
0 A 170 200
1 B 30 60
2 C 50 80
"""
加上排序
df = pd.DataFrame({'colA' : list('AABCA'), 'colB' : ['X',np.nan,'Ya','Xb','Xa'],'colC' : [100,50,30,50,20], 'colD': [90,60,60,80,50]})
print(df.head(10))
my_print('分组聚合排序操作')
df2 = df.groupby(['colA','colC']).sum().reset_index().sort_values(by=['colC'],ascending=True)
print(df2)
case when 操作
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def my_print(text,star_cnt=20):
stars = '*'*star_cnt
print('{stars}{text}{stars}'.format(stars=stars,text=text))
df = pd.DataFrame({'colA' : list('AABCA'), 'colB' : ['X',np.nan,'Ya','Xb','Xa'],'colC' : [100,50,30,50,20], 'colD': [90,60,60,80,50]})
print(df.head(10))
my_print('case when 操作')
df['colC_2'] = df['colC'].map(lambda x: '及格' if x>60 else '不及格')
print(df)
关联操作
df = pd.DataFrame({'colA' : list('AABCA'), 'colB' : ['X',np.nan,'Ya','Xb','Xa'],'colC' : [100,50,30,50,20], 'colD': [90,60,60,80,50]})
print(df.head(10))
my_print(' left join 操作')
df2 = pd.merge(df,df,how='left',on=['colA']) # left , right , outer, inner
print(df2.head(11))
print(len(df2[df2['colA'].str.contains(r'A')]))
union all 操作
df = pd.DataFrame({'colA' : list('AABCA'), 'colB' : ['X',np.nan,'Ya','Xb','Xa'],'colC' : [100,50,30,50,20], 'colD': [90,60,60,80,50]})
print(df.head(10))
my_print(' union all 操作')
df2 = pd.concat([df,df])
print(df2.head(10))
取唯一值操作
df = pd.DataFrame({'colA' : list('AABCA'), 'colB' : ['X',np.nan,'Ya','Xb','Xa'],'colC' : [100,50,30,50,20], 'colD': [90,60,60,80,50]})
print(df.head(10))
my_print(' 去重 操作')
df2 = df.loc[df['colB'].isnull(),'colA'].unique()
df2 = df['colA'][df['colB'].isnull()].unique()
print(df2)
仅对某几列进行操作, 可以延伸为对某几行操作
df = DataFrame ({'a' : np.random.randint(1,13),
'b' : ['foo', 'bar'] * 3,
'c' : np.random.randint(1,5)})
def my_test(a, b):
return a / b
print(df.head())
my_print("华丽的分割线")
df['Value'] = df.apply(lambda row: my_test(row['a'], row['c']), axis=1)
print(df.head())
"""
a b c
0 2 foo 4
1 2 bar 4
2 2 foo 4
3 2 bar 4
4 2 foo 4
******************** 华丽的分割线 ********************
a b c Value
0 2 foo 4 0.5
1 2 bar 4 0.5
2 2 foo 4 0.5
3 2 bar 4 0.5
4 2 foo 4 0.5
"""
无尽的试炼
源数据本身:
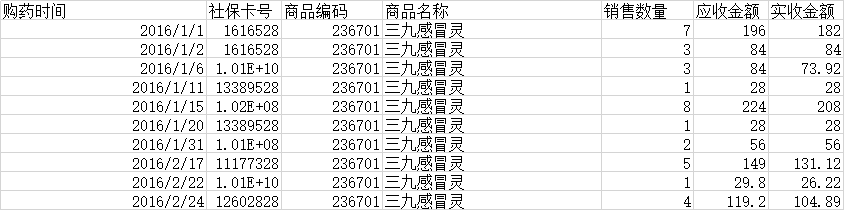
购药时间,社保卡号,商品编码,商品名称,销售数量,应收金额,实收金额
2016/1/1,1616528,236701,三九感冒灵,7,196,182
2016/1/2,1616528,236701,三九感冒灵,3,84,84
2016/1/6,10070343428,236701,三九感冒灵,3,84,73.92
2016/1/11,13389528,236701,三九感冒灵,1,28,28
2016/1/15,101554328,236701,三九感冒灵,8,224,208
2016/1/20,13389528,236701,三九感冒灵,1,28,28
2016/1/31,101464928,236701,三九感冒灵,2,56,56
2016/2/17,11177328,236701,三九感冒灵,5,149,131.12
2016/2/22,10065687828,236701,三九感冒灵,1,29.8,26.22
2016/2/24,12602828,236701,三九感冒灵,4,119.2,104.89
__author__ = 'Frank Li'
from pandas import DataFrame
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def my_print(text,star_cnt=20):
stars = '*'*star_cnt
print('{stars} {text} {stars}'.format(stars=stars,text=text))
df = pd.read_excel('cyyy2016.xls')
print(df.index)
print(df.head(10))
"""
"""
my_print("测试下下")
print(df.groupby(['商品名称']))
my_print("测试两下")
print(df.groupby('商品名称').agg({'销售数量':np.mean,'应收金额':np.size}).head(5))
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def my_print(text,star_cnt=20):
stars = '*'*star_cnt
print('{stars} {text} {stars}'.format(stars=stars,text=text))
df = pd.read_excel('cyyy2016.xls')
print(df.index)
print(df.head(10))
"""
"""
my_print("测试下下")
print(df.groupby(['商品名称']))
my_print("测试两下")
print(df.groupby(['商品名称','销售数量']).agg({'应收金额':[np.size,np.mean]}))
排名函数 over rank 的意思
from pandas import Series, DataFrame
import numpy as np
def pretty_print(text, star_cnt=20):
stars = '*'*star_cnt
print('{} {} {} '.format(stars,text,stars))
series = Series(np.random.random_sample(4))
pretty_print('排序前')
print(series)
pretty_print('排序后')
series = series.rank(method='first') # method 可以是 first , min ,max , dense, average(默认)
print(series)
"""
******************** 排名前 ********************
0 0.349426
1 0.786071
2 0.188400
3 0.786662
dtype: float64
******************** 排名后 ********************
0 2.0
1 3.0
2 1.0
3 4.0
dtype: float64
"""
where 后接 else , 如果内部 break ,或者异常则不会执行 else , continue 会执行 else
n = 0
while n<=10:
print(n)
n+=1
if n==5:
a = 1/0
else:
print('else...')
pandas 不同文本格式数据的读写
read_csv
read_table
read_fwf
read_clipboard
read_excel
read_hef
read_html
read_json
read_msgpack
read_pickle
read_sas
read_sql
read_stata
read_feather
如果有来生,一个人去远行,看不同的风景,感受生命的活力。。。


