LeetCode 133. Clone Graph
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/description/
题目:
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity sake, each node's value is the same as the node's index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val = 1, the second node with val = 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
Adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
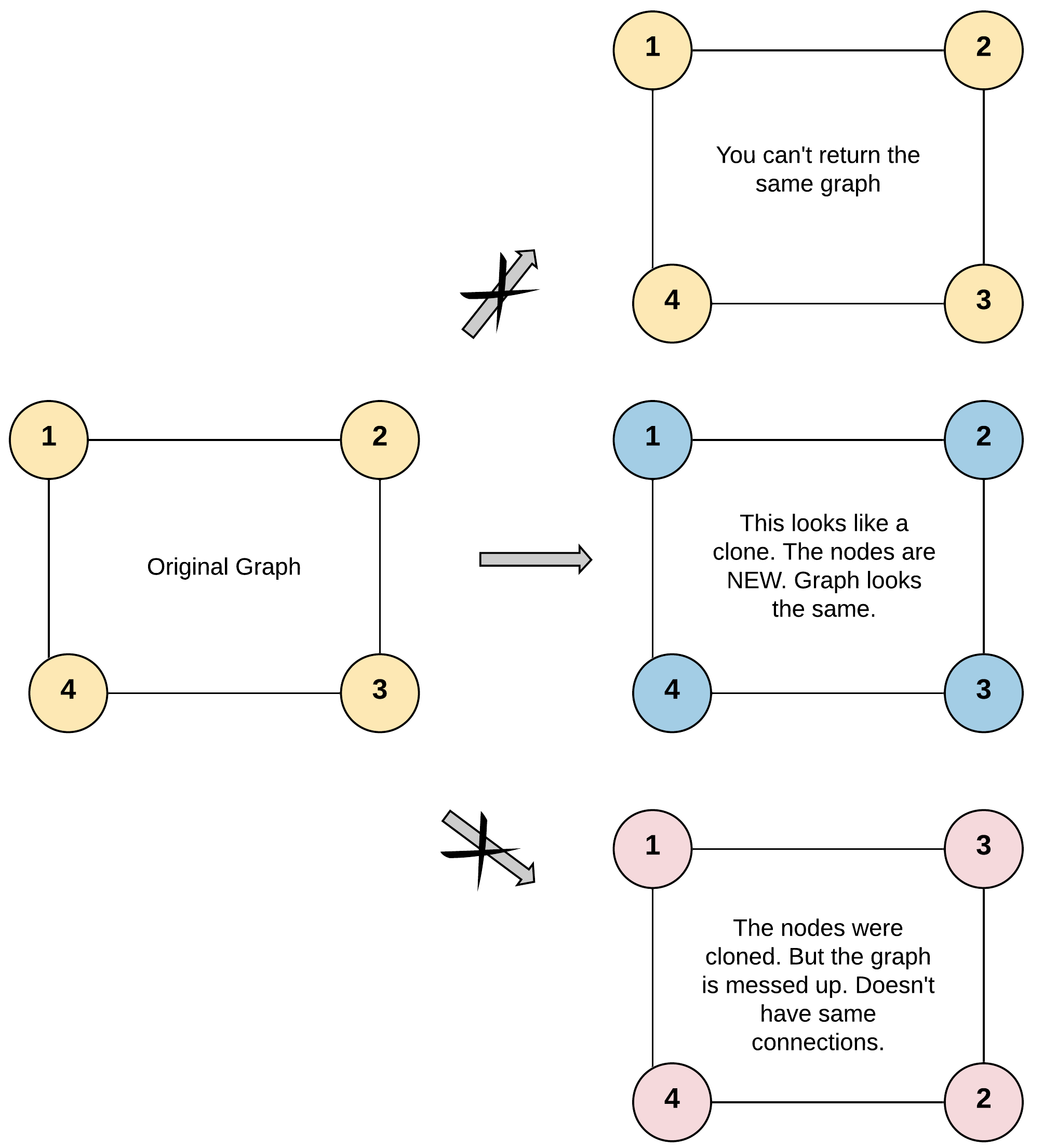
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
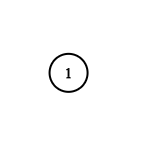
Input: adjList = [[]] Output: [[]] Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = [] Output: [] Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Example 4:
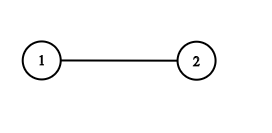
Input: adjList = [[2],[1]] Output: [[2],[1]]
Constraints:
1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.valis unique for each node.- Number of Nodes will not exceed 100.
- There is no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
题解:
复制原来的graph, 输入是一个graph node, 返回也是一个 graph node.
可以利用BFS, 同时维护HashMap hm 来记录visited 过的点. 以及 original node 和 copy node 的关系。
key存储原graph的node, value存用原node.label复制出来的node. 检查这个neighbor是不是已经在hm的key中了,如果已经在了就跳过,如果没在就加到queue中,并建立一个自身的copy组成键值对放入hm中。
同时更新当前节点currentNode 复制点 的neighbors list. 此时无论它的neighbor是否在hm中都应该把hm中对应这个heighbor key 的 value 放到 list中。
最后返回 以输入点的label复制的点。
Time Complexity: O(N+E). Space: O(N).
AC Java:
1 /** 2 * Definition for undirected graph. 3 * class UndirectedGraphNode { 4 * int label; 5 * List<UndirectedGraphNode> neighbors; 6 * UndirectedGraphNode(int x) { label = x; neighbors = new ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode>(); } 7 * }; 8 */ 9 public class Solution { 10 public UndirectedGraphNode cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode node) { 11 if(node == null){ 12 return node; 13 } 14 15 UndirectedGraphNode cloneNode = new UndirectedGraphNode(node.label); 16 HashMap<UndirectedGraphNode, UndirectedGraphNode> visited = new HashMap<UndirectedGraphNode, UndirectedGraphNode>(); 17 visited.put(node, cloneNode); 18 19 LinkedList<UndirectedGraphNode> que = new LinkedList<UndirectedGraphNode>(); 20 que.add(node); 21 while(!que.isEmpty()){ 22 UndirectedGraphNode cur = que.poll(); 23 for(UndirectedGraphNode neighbor : cur.neighbors){ 24 if(!visited.containsKey(neighbor)){ 25 UndirectedGraphNode cloneNeighbor = new UndirectedGraphNode(neighbor.label); 26 visited.put(neighbor, cloneNeighbor); 27 que.add(neighbor); 28 } 29 visited.get(cur).neighbors.add(visited.get(neighbor)); 30 } 31 } 32 33 return cloneNode; 34 } 35 }
也可以DFS.
Time Complexity: O(N+E). Space: O(N).
AC Java:
1 /* 2 // Definition for a Node. 3 class Node { 4 public int val; 5 public List<Node> neighbors; 6 7 public Node() { 8 val = 0; 9 neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>(); 10 } 11 12 public Node(int _val) { 13 val = _val; 14 neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>(); 15 } 16 17 public Node(int _val, ArrayList<Node> _neighbors) { 18 val = _val; 19 neighbors = _neighbors; 20 } 21 } 22 */ 23 class Solution { 24 HashMap<Integer, Node> visited = new HashMap<>(); 25 26 public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { 27 if(node == null){ 28 return node; 29 } 30 31 if(visited.containsKey(node.val)){ 32 return visited.get(node.val); 33 } 34 35 Node copy = new Node(node.val); 36 visited.put(node.val, copy); 37 38 for(Node nei : node.neighbors){ 39 copy.neighbors.add(cloneGraph(nei)); 40 } 41 42 return copy; 43 } 44 }


