MapReduce对交易日志进行排序的Demo(MR的二次排序)
1.日志源文件 (各个列分别是: 账户,营业额,花费,日期)
zhangsan@163.com 6000 0 2014-02-20
lisi@163.com 2000 0 2014-02-20
lisi@163.com 0 100 2014-02-20
zhangsan@163.com 3000 0 2014-02-20
wangwu@126.com 9000 0 2014-02-20
wangwu@126.com 0 200 2014-02-20
想要的结果: (计算出每个账户的总营业额和总花费,要求营业额排序降序,如果营业额相同则花费少的在上面)
zhangsan@163.com 9000 0 9000
wangwu@126.com 9000 200 8800
lisi@163.com 2000 100 1900
2.写代码:
InfoBean.java 对账户的后三个字段封装成一个Bean对象
1 import java.io.DataInput; 2 import java.io.DataOutput; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 6 7 //要和其他的InfoBean类型进行比较,所以此处泛型T为InfoBean 8 public class InfoBean implements WritableComparable<InfoBean> { 9 10 private String account; 11 private double income; 12 private double expenses; 13 private double surplus; 14 15 /* 16 *如果不写这个方法,封装InfoBean对象的时候就要分别set这个对象的各个属性. 17 */ 18 public void set(String account,double income,double expenses){ 19 this.account = account; 20 this.income = income; 21 this.expenses = expenses; 22 this.surplus = income -expenses; 23 } 24 @Override 25 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 26 out.writeUTF(account); 27 out.writeDouble(income); 28 out.writeDouble(expenses); 29 out.writeDouble(surplus); 30 } 31 32 @Override 33 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 34 this.account = in.readUTF(); 35 this.income = in.readDouble(); 36 this.expenses = in.readDouble(); 37 this.surplus = in.readDouble(); 38 } 39 40 @Override 41 public int compareTo(InfoBean o) { 42 if(this.income == o.getIncome()){ 43 return this.expenses > o.getExpenses() ? 1 : -1; 44 } else { 45 return this.income > o.getIncome() ? -1 : 1; 46 } 47 } 48 49 @Override 50 //toString()方法输出的格式最好和源文件trade_info.txt中的格式一样, 字段通过Tab键分隔. 51 //而且在SumReducer类输出k3,v3的时候会输出k3(context.write(key, v);) 所以这个地方没有必要再输出k3(account) 52 public String toString() { 53 // return "InfoBean [account=" + account + ", income=" + income 54 // + ", expenses=" + expenses + ", surplus=" + surplus + "]"; 55 return this.income + "\t" + this.expenses+"\t" + this.surplus; 56 } 57 public double getIncome() { 58 return income; 59 } 60 61 public void setIncome(double income) { 62 this.income = income; 63 } 64 65 public double getExpenses() { 66 return expenses; 67 } 68 69 public void setExpenses(double expenses) { 70 this.expenses = expenses; 71 } 72 73 public double getSurplus() { 74 return surplus; 75 } 76 77 public void setSurplus(double surplus) { 78 this.surplus = surplus; 79 } 80 81 public String getAccount() { 82 return account; 83 } 84 85 public void setAccount(String account) { 86 this.account = account; 87 } 88 89 }
SumStep.java
1 import java.io.IOException; 2 3 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 9 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 10 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 11 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 12 13 public class SumStep { 14 15 public static class SumMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, InfoBean>{ 16 private Text k = new Text(); 17 private InfoBean bean = new InfoBean(); 18 19 @Override 20 protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, InfoBean>.Context context) 21 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 22 23 String line = value.toString(); 24 String [] fields = line.split("\t"); 25 String account = fields[0]; 26 double income = Double.parseDouble(fields[1]); 27 double expenses = Double.parseDouble(fields[2]); 28 k.set(account); 29 bean.set(account, income, expenses); 30 context.write(k, bean); 31 } 32 } 33 public static class SumReducer extends Reducer<Text, InfoBean, Text, InfoBean>{ 34 private InfoBean v = new InfoBean(); 35 @Override 36 protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<InfoBean> values,Reducer<Text, InfoBean, Text, InfoBean>.Context context) 37 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 38 double sum_in = 0; 39 double sum_out = 0; 40 for(InfoBean bean : values){ 41 sum_in += bean.getIncome(); 42 sum_out += bean.getExpenses(); 43 } 44 /* 45 * 在crxy的流量统计的案例中 是如下的方式写出k3和v3的 在reduce方法中new这个封装好的对象. 46 * 但是如果数据量比较大的情况下 是可能会造成内存溢出的. 47 * TrafficWritable v3 = new TrafficWritable(t1, t2, t3, t4); 48 * context.write(k2, v3); 49 * 50 * 所以建议把这个封装的对象写在"脑袋顶上" 如上所示....private InfoBean v = new InfoBean(); 51 * 但是如果你Java基础比较好的话可能会说 在Java中是引用传递...所以后面的v会覆盖前面的v,造成最后只有最有一个v 52 * 其实这里是不会产生问题的,因为context.write()方法会直接把v3对应的InfoBean对象序列化. 53 * 虽然之前对象的引用确实覆盖了,但是之前对象的值等都保存了下来.是可以放在这个类的"脑袋顶上"的. 54 * 让这个类公用这个InfoBean对象. 55 */ 56 57 v.set(key.toString(),sum_in,sum_out); 58 context.write(key, v); 59 } 60 } 61 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 62 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 63 Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); 64 job.setJarByClass(SumStep.class); 65 66 job.setMapperClass(SumMapper.class); 67 //以下两行可以在满足一定条件的时候省略掉. 68 //在满足k2和k3,v2和v3一一对应的时候就可以省略掉. 看SumReducer类所在行的泛型. 69 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 70 job.setMapOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class); 71 72 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); 73 74 job.setReducerClass(SumReducer.class); 75 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 76 job.setOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class); 77 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); 78 job.waitForCompletion(true); 79 } 80 }
项目打成jar包放到Linux中,日志源文件上传到HDFS上.运行结果如下:
hadoop jar /root/itcastmr.jar itcastmr.SumStep /user/root/trade_info.txt /tradeout

但是这个结果并没有排序.还是按照账号的字典排序.
以这个MR的输出当做输入对其根据InfoBean对象进行排序.....
上代码SortStep.java:
1 import java.io.IOException; 2 3 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 9 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 10 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 11 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 12 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 13 14 public class SortStep { 15 //这个Mapper读取的HDFS文件是SumStep Reduce计算输出的文件. 16 public static class SortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, InfoBean, NullWritable>{ 17 private InfoBean k = new InfoBean(); 18 @Override 19 protected void map(LongWritable key,Text value,Mapper<LongWritable, Text, InfoBean, NullWritable>.Context context) 20 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 21 String line = value.toString(); 22 String [] fields = line.split("\t"); 23 String account = fields[0]; 24 double income = Double.parseDouble(fields[1]); 25 double expenses = Double.parseDouble(fields[2]); 26 k.set(account, income, expenses); 27 //现在是要求按照InfoBean对象中的规则排序(InfoBean中有compareTo方法)...所以InfoBean对象当做k2... 28 context.write(k,NullWritable.get());//不能传null,NullWritable.get() 是获得的this对象. 29 } 30 } 31 public static class SortReducer extends Reducer<InfoBean, NullWritable, Text, InfoBean>{ 32 private Text k = new Text(); 33 @Override 34 protected void reduce(InfoBean bean, Iterable<NullWritable> values,Reducer<InfoBean, NullWritable, Text, InfoBean>.Context context) 35 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 36 String account = bean.getAccount(); 37 k.set(account); 38 context.write(k, bean); 39 } 40 } 41 42 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 43 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 44 Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); 45 job.setJarByClass(SortStep.class); 46 47 job.setMapperClass(SortMapper.class); 48 //以下两行可以在满足一定条件的时候省略掉. 49 //在满足k2和k3,v2和v3一一对应的时候就可以省略掉. 看SumReducer类所在行的泛型. 50 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(InfoBean.class); 51 job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); 52 53 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); 54 55 job.setReducerClass(SortReducer.class); 56 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 57 job.setOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class); 58 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); 59 job.waitForCompletion(true); 60 } 61 }
打成jar包,然后运行命令....输入为上面SumStep.java的输出
hadoop jar /root/itcastmr.jar itcastmr.SortStep /tradeout /trade_sort_out
排序之后的结果:
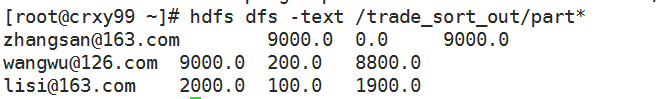
在MapReduce读取输入数据的时候,如果这个文件是以下划线开始的话,那么会不会读取这个文件中的内容...."_SUCCESS"文件就不会读取....
如果想对某个类进行排序,
1.这个类要实现WritableComparable接口,
2.还要重写compareTo方法. 根据自己的业务逻辑自定义排序.
只需要把要排序的类当做k2 就可以了...框架自动排序.
要排序对象的compareTo方法是框架调用的,框架在shuffle这个阶段会调用排序.
shuffle后面会讲,shuffle由很多很多的阶段组成,分区,排序,分组,combiner等等...把这些小的细节都讲完了之后再讲shuffle.
|
作者:SummerChill 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/DreamDrive/ 本博客为自己总结亦或在网上发现的技术博文的转载。 如果文中有什么错误,欢迎指出。以免更多的人被误导。 |




