STL容器之list
【1】list简介
实质上,list容器就是一个双向链表,可以高效地进行插入、删除操作。
【2】list链表常用方法
(1)构造、赋值、清空、删除、插入、判空等
应用示例代码如下:
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 // cbegin 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 9 // cend 返回指向最后一个元素之后位置的迭代器 10 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 11 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 12 { 13 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 } 17 18 void main() 19 { 20 // 构造函数(默认构造函数) 21 list<int> myList1; 22 23 // 构造函数(构建一个list,有10个元素,每个元素值都是10) 24 list<int> myList2(10, 10); 25 print(myList2); 26 27 // 拷贝构造函数 28 list<int> myList3(myList2); 29 print(myList3); 30 31 // 由区间内的值初始化list 32 int nArrayA[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; 33 list<int> myList4(nArrayA, nArrayA + 5); 34 print(myList4); 35 36 // 赋值assign(input_iterator start, input_iterator end); 37 myList1.assign(nArrayA, nArrayA + 4); 38 print(myList1); 39 40 // 赋值assign(size_type num, const Type & val); 41 myList1.assign(10, 100); 42 print(myList1); 43 44 // 返回对最后一个元素的引用 45 cout << myList4.back() << endl; 46 47 // 返回对第一个元素的引用 48 cout << myList4.front() << endl; 49 50 // 清空链表clear 51 myList4.clear(); 52 cout << myList4.empty() << endl; 53 54 // 删除元素erase(iterator pos) 55 list<int>::iterator iter = myList1.begin(); 56 for (; iter != myList1.end(); ) 57 { 58 myList1.erase(iter++); 59 } 60 cout << myList1.empty() << endl; 61 62 // 删除元素erase(iterator start, iterator end) 63 myList3.erase(myList3.begin(), myList3.end()); 64 cout << myList3.empty() << endl; 65 66 // 插入元素insert(iterator pos, const TYPE& val) 67 myList1.insert(myList1.begin(), 110); 68 print(myList1); 69 70 // 插入元素insert(iterator pos, size_type num, const TYPE &val) 71 myList1.insert(myList1.begin(), 10, 23); 72 print(myList1); 73 74 // 插入元素insert(iterator pos, input_iterator start, input_iterator end) 75 int nArrayB[4] = {7, 8, 9, 10}; 76 myList1.insert(myList1.begin(), nArrayB, nArrayB + 4); 77 print(myList1); 78 79 system("pause"); 80 } 81 82 // run out: 83 /* 84 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 85 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 86 10 20 30 40 50 87 10 20 30 40 88 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 89 50 90 10 91 1 92 1 93 1 94 110 95 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 110 96 7 8 9 10 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 110 97 请按任意键继续. . . 98 */
(2)merge方法
请看如下最常见的崩溃代码:
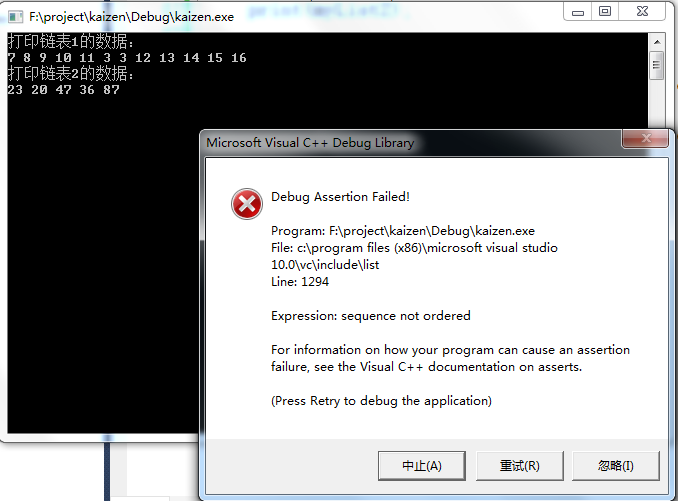
代码1:链表1无序,链表2无序。
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 // cbegin 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 9 // cend 返回指向最后一个元素之后位置的迭代器 10 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 11 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 12 { 13 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 } 17 18 void main() 19 { 20 // 构造函数(默认构造函数) 21 list<int> myList1, myList2; 22 // 赋值 23 myList1.assign(2, 3); 24 // 插入元素 25 int nArrayA[5] = {7, 8, 9, 10, 11}; 26 myList1.insert(myList1.begin(), nArrayA, nArrayA + 5); 27 // 追加元素 28 for (int i = 10; i < 15; ++i) 29 { 30 myList1.push_back(i + 2); 31 } 32 cout << "打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 33 print(myList1); 34 35 36 myList2.push_back(23); 37 myList2.push_back(20); 38 myList2.push_back(47); 39 myList2.push_back(36); 40 myList2.push_back(87); 41 cout << "打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 42 43 print(myList2); 44 45 myList1.merge(myList2); 46 cout << "合并后,打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 47 print(myList1); 48 cout << "合并后,打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 49 print(myList2); 50 51 system("pause"); 52 }
运行结果如下图:
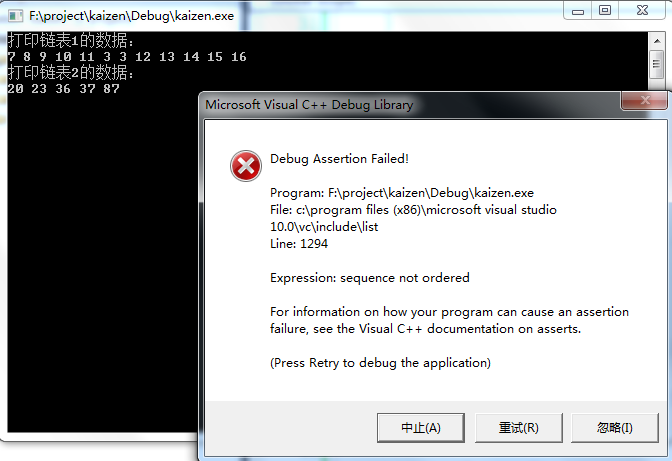
代码2:链表1无序,链表2升序。
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 // cbegin 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 9 // cend 返回指向最后一个元素之后位置的迭代器 10 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 11 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 12 { 13 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 } 17 18 void main() 19 { 20 // 构造函数(默认构造函数) 21 list<int> myList1, myList2; 22 // 赋值 23 myList1.assign(2, 3); 24 // 插入元素 25 int nArrayA[5] = {7, 8, 9, 10, 11}; 26 myList1.insert(myList1.begin(), nArrayA, nArrayA + 5); 27 // 追加元素 28 for (int i = 10; i < 15; ++i) 29 { 30 myList1.push_back(i + 2); 31 } 32 cout << "打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 33 print(myList1); 34 35 36 myList2.push_back(20); 37 myList2.push_back(23); 38 myList2.push_back(36); 39 myList2.push_back(37); 40 myList2.push_back(87); 41 cout << "打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 42 43 print(myList2); 44 45 myList1.merge(myList2); 46 cout << "合并后,打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 47 print(myList1); 48 cout << "合并后,打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 49 print(myList2); 50 51 system("pause"); 52 }
运行结果如下图:
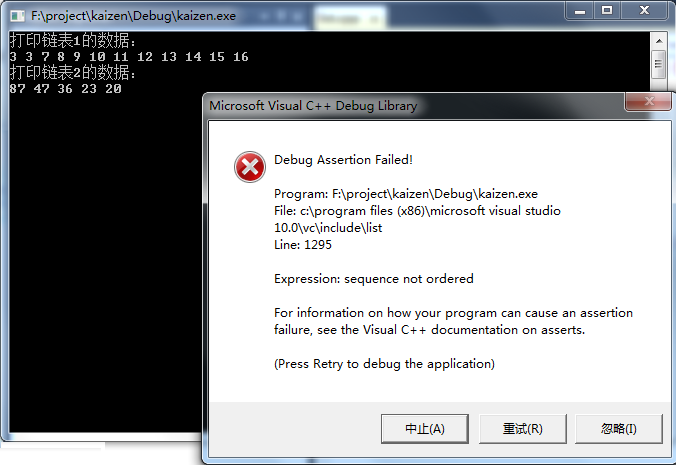
代码3:链表1升序,链表2降序。
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 // cbegin 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 9 // cend 返回指向最后一个元素之后位置的迭代器 10 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 11 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 12 { 13 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 } 17 18 void main() 19 { 20 // 构造函数(默认构造函数) 21 list<int> myList1, myList2; 22 // 赋值 23 myList1.assign(2, 3); 24 // 插入元素 25 int nArrayA[5] = {7, 8, 9, 10, 11}; 26 myList1.insert(myList1.end(), nArrayA, nArrayA + 5); 27 // 追加元素 28 for (int i = 10; i < 15; ++i) 29 { 30 myList1.push_back(i + 2); 31 } 32 cout << "打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 33 print(myList1); 34 35 myList2.push_back(87); 36 myList2.push_back(47); 37 myList2.push_back(36); 38 myList2.push_back(23); 39 myList2.push_back(20); 40 cout << "打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 41 42 print(myList2); 43 44 myList1.merge(myList2); 45 cout << "合并后,打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 46 print(myList1); 47 cout << "合并后,打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 48 print(myList2); 49 50 system("pause"); 51 }
运行结果如下图:
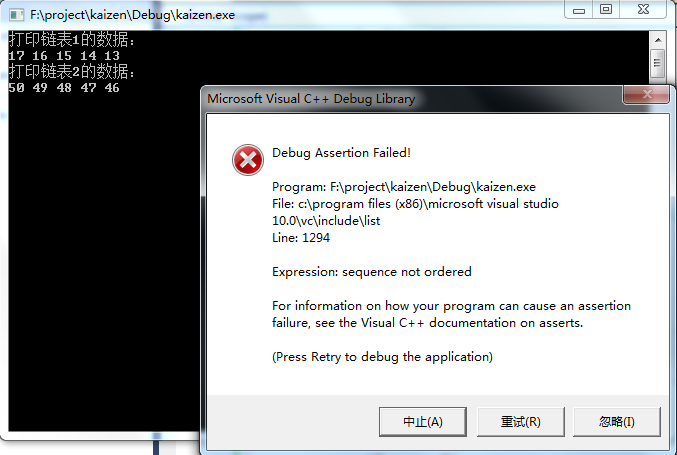
代码4:链表1降序,链表2降序。
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 // cbegin 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 9 // cend 返回指向最后一个元素之后位置的迭代器 10 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 11 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 12 { 13 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 } 17 18 void main() 19 { 20 // 构造函数(默认构造函数) 21 list<int> myList1, myList2; 22 // 追加元素 23 for (int i = 15; i > 10; --i) 24 { 25 myList1.push_back(i + 2); 26 } 27 cout << "打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 28 print(myList1); 29 30 myList2.push_back(50); 31 myList2.push_back(49); 32 myList2.push_back(48); 33 myList2.push_back(47); 34 myList2.push_back(46); 35 cout << "打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 36 37 print(myList2); 38 39 myList1.merge(myList2); 40 cout << "合并后,打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 41 print(myList1); 42 cout << "合并后,打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 43 print(myList2); 44 45 system("pause"); 46 }
运行结果如下图:
代码5:链表1升序,链表2升序。
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 // cbegin 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 9 // cend 返回指向最后一个元素之后位置的迭代器 10 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 11 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 12 { 13 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 } 17 18 void main() 19 { 20 // 构造函数(默认构造函数) 21 list<int> myList1, myList2; 22 // 赋值 23 myList1.assign(2, 3); 24 // 插入元素 25 int nArrayA[5] = {7, 8, 9, 10, 11}; 26 myList1.insert(myList1.end(), nArrayA, nArrayA + 5); 27 // 追加元素 28 for (int i = 10; i < 15; ++i) 29 { 30 myList1.push_back(i + 2); 31 } 32 cout << "打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 33 print(myList1); 34 35 myList2.push_back(20); 36 myList2.push_back(23); 37 myList2.push_back(36); 38 myList2.push_back(37); 39 myList2.push_back(87); 40 cout << "打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 41 42 print(myList2); 43 44 myList1.merge(myList2); 45 cout << "合并后,打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 46 print(myList1); 47 cout << "合并后,打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 48 print(myList2); 49 50 system("pause"); 51 }
运行结果如下图:

经过查资料及源码,发现问题是:
list链表合并merge方法注意事项:
1、合并的两个链表必须均默认升序的。即合并之前,两个链表就应该是由小到大顺序排列的。
2、合并完成后,被合并链表(myList2)数据元素被清空。
3、默认是按升序合并。比如上例4,若想按降序进行合并,需要指定降序。
修改后,如下代码:
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 // cbegin 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 9 // cend 返回指向最后一个元素之后位置的迭代器 10 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 11 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 12 { 13 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 } 17 18 void main() 19 { 20 // 构造函数(默认构造函数) 21 list<int> myList1, myList2; 22 // 追加元素 23 for (int i = 15; i > 10; --i) 24 { 25 myList1.push_back(i + 2); 26 } 27 cout << "打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 28 print(myList1); 29 30 myList2.push_back(50); 31 myList2.push_back(49); 32 myList2.push_back(48); 33 myList2.push_back(47); 34 myList2.push_back(46); 35 cout << "打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 36 37 print(myList2); 38 39 myList1.merge(myList2, greater<int>()); 40 cout << "合并后,打印链表1的数据:" << endl; 41 print(myList1); 42 cout << "合并后,打印链表2的数据:" << endl; 43 print(myList2); 44 45 system("pause"); 46 }
按降序进行合并。前提必须两个链表均为降序有序排列。
(3)remove方法。删除链表中所有值为val的元素。
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 // cbegin 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 9 // cend 返回指向最后一个元素之后位置的迭代器 10 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 11 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 12 { 13 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 } 17 18 void main() 19 { 20 // 构造函数(默认构造函数) 21 list<int> myList1; 22 myList1.assign(3, 12); 23 myList1.insert(myList1.end(), 3, 34); 24 for (int i = 15; i > 10; --i) 25 { 26 myList1.push_back(12); 27 } 28 for (int i = 10; i < 15; ++i) 29 { 30 myList1.push_front(i + 5); 31 } 32 cout << "打印链表的数据:" << endl; 33 print(myList1); 34 35 cout << "删除12后,打印链表数据:"; 36 myList1.remove(12); 37 print(myList1); 38 39 cout << "删除34后,打印链表数据:"; 40 myList1.remove(34); 41 print(myList1); 42 43 system("pause"); 44 } 45 46 // run out: 47 /* 48 打印链表的数据: 49 19 18 17 16 15 12 12 12 34 34 34 12 12 12 12 12 50 删除12后,打印链表数据:19 18 17 16 15 34 34 34 51 删除34后,打印链表数据:19 18 17 16 15 52 请按任意键继续. . . 53 */
(4)remove_if方法。用一元函数判断是否删除元素,若函数返回true,则删除该元素。
应用示例代码如下:
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 9 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 10 { 11 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 12 } 13 cout << endl; 14 } 15 16 bool IsDel (int i) 17 { 18 return ((i % 2) == 1); 19 } 20 21 void main () 22 { 23 int myInts[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}; 24 list<int> myList(myInts, myInts + 10); 25 26 cout << "打印链表数据元素:" << endl; 27 print(myList); 28 myList.remove_if(IsDel); 29 cout << "删除(val % 2 == 1)后打印链表数据元素:" << endl; 30 print(myList); 31 32 system("pause"); 33 } 34 35 // run out: 36 /* 37 打印链表数据元素: 38 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 39 删除(val % 2 == 1)后打印链表数据元素: 40 2 4 6 8 10 41 请按任意键继续. . . 42 */
(5)unique方法。移除重复元素。
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 9 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 10 { 11 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 12 } 13 cout << endl; 14 } 15 16 void main() 17 { 18 list<int> myList; 19 myList.assign(5, 100); 20 for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) 21 { 22 myList.push_front(i + 2); 23 } 24 for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) 25 { 26 myList.push_back(10 + i); 27 } 28 myList.insert(myList.end(), 5, 45); 29 30 print(myList); 31 myList.unique(); // 移除重复元素 32 print(myList); 33 34 system("pause"); 35 } 36 37 // run out: 38 /* 39 6 5 4 3 2 100 100 100 100 100 10 11 12 13 14 45 45 45 45 45 40 6 5 4 3 2 100 10 11 12 13 14 45 41 请按任意键继续. . . 42 */
(6)splice 粘接方法的三种方式
应用示例代码如下:
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 9 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 10 { 11 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 12 } 13 cout << endl; 14 } 15 16 void main() 17 { 18 list<int> myList1, myList2, myList3, myList4; 19 myList1.assign(5, 10); 20 myList2.push_front(22); 21 cout << "打印myList2的数据:" << endl; 22 print(myList2); 23 cout << "打印myList1的数据:" << endl; 24 print(myList1); 25 // 粘接方法1:splice(iterator pos, list& lst) 26 // 将myList1链表元素粘接到myList2链表的第一个位置(pos及其后元素均后移) 27 myList2.splice(myList2.begin(), myList1); 28 cout << "粘接后,打印myList2的数据:" << endl; 29 print(myList2); 30 cout << "粘接后,打印myList1的数据:" << endl; 31 print(myList1); 32 33 // 粘接方法2:splice(iterator pos, list& lst, iterator del) 34 // 将myList1链表元素从第二个开始粘接到myList3链表的第一个位置 35 myList1.assign(2, 11); 36 myList3.assign(2, 22); 37 cout << endl << "打印myList3的数据:" << endl; 38 print(myList3); 39 cout << "打印myList1的数据:" << endl; 40 print(myList1); 41 myList3.splice(myList3.begin(), myList1, ++myList1.begin()); 42 cout << "粘接后,打印myList3的数据:" << endl; 43 print(myList3); 44 cout << "粘接后,打印myList1的数据:" << endl; 45 print(myList1); 46 47 // 粘接方法3:splice(iterator pos, list& lst, iterator start, iterator end) 48 // 将myList1链表元素从第二个开始粘接到myList4链表的第二个位置 49 myList1.push_back(12); 50 myList1.push_back(13); 51 myList1.push_back(14); 52 myList1.push_back(15); 53 myList4.assign(4, 44); 54 cout << endl << "打印myList4的数据:" << endl; 55 print(myList4); 56 cout << "打印myList1的数据:" << endl; 57 print(myList1); 58 myList4.splice(++myList4.begin(), myList1, ++myList1.begin(), myList1.end()); 59 cout << "粘接后,打印myList4的数据:" << endl; 60 print(myList4); 61 cout << "粘接后,打印myList1的数据:" << endl; 62 print(myList1); 63 64 system("pause"); 65 } 66 67 // run out: 68 /* 69 打印myList2的数据: 70 22 71 打印myList1的数据: 72 10 10 10 10 10 73 粘接后,打印myList2的数据: 74 10 10 10 10 10 22 75 粘接后,打印myList1的数据: 76 77 78 打印myList3的数据: 79 22 22 80 打印myList1的数据: 81 11 11 82 粘接后,打印myList3的数据: 83 11 22 22 84 粘接后,打印myList1的数据: 85 11 86 87 打印myList4的数据: 88 44 44 44 44 89 打印myList1的数据: 90 11 12 13 14 15 91 粘接后,打印myList4的数据: 92 44 12 13 14 15 44 44 44 93 粘接后,打印myList1的数据: 94 11 95 请按任意键继续. . . 96 */
(7)swap方法。交换两个链表中的元素。
应用示例代码如下:
1 #include <list> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // 打印链表数据信息 6 void print (const list<int> & tempList) 7 { 8 list<int>::const_iterator cIter = tempList.cbegin(); 9 for (; cIter != tempList.cend(); ++cIter) 10 { 11 cout << (*cIter) << " "; 12 } 13 cout << endl; 14 } 15 16 void main() 17 { 18 list<int> myList1, myList2; 19 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) 20 { 21 myList1.push_back(rand() % 100); 22 } 23 for (int j = 0; j < 10; ++j) 24 { 25 myList2.push_back(rand() % 200); 26 } 27 cout << "打印myList1的数据:" << endl; 28 print(myList1); 29 cout << "打印myList2的数据:" << endl; 30 print(myList2); 31 myList1.swap(myList2); 32 cout << "交换后,打印myList1的数据:" << endl; 33 print(myList1); 34 cout << "交换后,打印myList2的数据:" << endl; 35 print(myList2); 36 37 system("pause"); 38 } 39 // run out: 40 /* 41 打印myList1的数据: 42 41 67 34 0 69 24 78 58 62 64 43 打印myList2的数据: 44 105 145 81 27 161 91 195 142 27 36 45 交换后,打印myList1的数据: 46 105 145 81 27 161 91 195 142 27 36 47 交换后,打印myList2的数据: 48 41 67 34 0 69 24 78 58 62 64 49 请按任意键继续. . . 50 */
(8)待续。。。。
【3】list与vector区别总结
数组与链表的优缺点;
数组:
优点:访问效率高,内存为连续的区域。
缺点:添加、删除操作效率低。大小固定,不适合动态存储(不方便动态添加)。
链表:
优点:一般内存不连续。添加、删除效率高。大小可变。
缺点:只能通过指针顺序访问,查询效率低。
Good Good Study, Day Day Up.
顺序 选择 循环 总结



