2017 SCNUCPC 解题报告
校内赛题目、解题思路、参考代码一览
A. Blackstorm’s Blackstore
Problem Description
Blackstorm is going to open a blackstore. He now need to transport some goods.
There are towns, numbered from to . Goods are now at Town while the destination is at Town . directed roads are connecting the towns, the th of which has values , meaning that this road connects from th town to th one, which can transport at most kilogram of goods at yuan per kilo. He wants to know how many goods can reach the destination with yuan.
Blackstorm is going to sleep. Can you help him solve this problem?
Input
Multiple test cases, process till end of file. For each case:
On the first line there are three numbers, , described as the description says.
Following are lines, on the th of which are four numbers .
All the numbers except are integers between . is integer between . It's also guaranteed that .
Output
For each test case, output "Case #: " (without quotes), where is the number of the cases, and is the maximum transporting mass with 4 digits after the decimal point.
Sample Input
3 3 5
1 3 1 1
1 2 1 5
2 3 1 5
Sample Output
Case \#1: 3.0000
Hint
One yuan on road 1->3, two on 1->2 and two on 2->3.
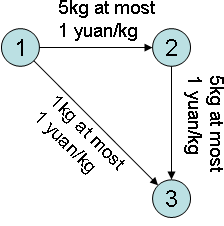
解题思路
- 网络流版题
参考代码
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 10000;
const int MAXM = 100000;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
struct Edge {
int to,next,cap,flow,cost;
} edge[MAXM];
int head[MAXN],tol;
int pre[MAXN],dis[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
int N;//节点总个数,节点编号从0~N-1
void init(int n) {
N = n;
tol = 0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
}
void addedge(int u,int v,int cap,int cost) {
edge[tol].to = v;
edge[tol].cap = cap;
edge[tol].cost = cost;
edge[tol].flow = 0;
edge[tol].next = head[u];
head[u] = tol++;
edge[tol].to = u;
edge[tol].cap = 0;
edge[tol].cost = -cost;
edge[tol].flow = 0;
edge[tol].next = head[v];
head[v] = tol++;
}
bool spfa(int s,int t) {
queue<int>q;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
dis[i] = INF;
vis[i] = false;
pre[i] = -1;
}
dis[s] = 0;
vis[s] = true;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for(int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) {
int v = edge[i].to;
if(edge[i].cap > edge[i].flow &&
dis[v] > dis[u] + edge[i].cost ) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + edge[i].cost;
pre[v] = i;
if(!vis[v]) {
vis[v] = true;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
if(pre[t] == -1)return false;
else return true;
}
int k;
//返回的是最大流,cost存的是最小费用
double minCostMaxflow(int s,int t) {
int flow = 0;
int cost = 0;
while(spfa(s,t)) {
int Min = INF;
for(int i = pre[t]; i != -1; i = pre[edge[i^1].to]) {
if(Min > edge[i].cap - edge[i].flow)
Min = edge[i].cap - edge[i].flow;
}
int costper = 0;
for(int i = pre[t]; i != -1; i = pre[edge[i^1].to]) {
edge[i].flow += Min;
edge[i^1].flow -= Min;
costper += edge[i].cost;
}
int tmpcost = cost + costper * Min;
if (tmpcost>=k) {
return flow + (k-cost)/(double)costper;
}
cost = tmpcost;
flow += Min;
}
return flow;
}
#include <cstdio>
int main() {
int n,m,i,T=0;
while (~scanf("%d%d%d", &n,&m,&k)) {
init (n+2);
for (i=0; i<m; i++) {
int a,b,p,c;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&p,&c);
addedge(a,b,c,p);
}
printf ("Case #%d: %.4f\n", ++T, minCostMaxflow(1,n));
}
}
### B. 龟兔慢跑
Problem Description
乌龟和兔子在绕圈跑,它们同时同地出发,问出发后第一次相遇的用时。圈长米,乌龟速度米/分钟,兔子速度米/分钟,且乌龟和兔子每跑米都会休息分钟再继续跑。
Input
首行一个整数代表组测试数据,接下来行每行4个整数分别是 。其中 ,
Output
每组测试数据输出一行一个整数,表示相遇时间。测试数据保证使得相遇时间为整数。
Sample Input
1
100 100 25 20
Sample Output
5
Hint
64位整型long long int请使用%lld输出
解题思路
- 模拟
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int n,m,t,w;
void solve()
{
int cycle=(m+t)*(m+w);
int ds=m*(t-w);
int cycle_num=0,dn=0;
if(n%ds==0)
dn=ds,cycle_num=n/ds-1;
else
dn=n%ds,cycle_num=n/ds;
long long int i=0,ans=1;
char stopw=0,stopt=0;
double dw=0,dt=0,mw=0,mt=0;
while(true)
{
i++;
if(stopw)
dw+=mw,stopw=0;
else if(mw+w>=m)
dw+=m-mw,mw=mw+w-m,stopw=1;
else
dw+=w,mw+=w;
if(stopt)
dt+=abs(mt),stopt=0;
else if(mt+t>=m)
dt+=m-mt,mt=mt+t-m,stopt=1;
else
dt+=t,mt+=t;
/*
printf("cycle=%d,cyclenum=%d,dn=%d,i=%I64d,dt=%f,dw=%f\n",cycle,cycle_num,dn,i,dt,dw);
if(i%10==0){
char s;
scanf("%c",&s);
}
*/
if(abs(dn+dw-dt)<0.00001 )
{
ans=i+(long long int)cycle_num*cycle;
break;
}
if(abs(dw-dt)<0.00001)
{
ans=i;
break;
}
}
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&t,&w);
solve();
}
return 0;
}
### C. Snake
解题思路
- 瞎模拟,原题。
参考代码
无
### D. Zyj pessimistic in competition
Problem Description
There's only 10 minutes left for the ACM competition(yes the contest you're having right now). Others have already packed their pack ready to leave, while Zyj is just opening his eyes. Zyj can see how many problems any one have done, and he decided to have his rank between . So how many ways are there for him? You can assume that others have penality less than 290min, so the rank of Zyj is totally decided by his answered problem, not his answering time.
Input
The first line contains an integer , representing the number of tests. For each test,
There are 4 numbers seperated by spaces, meaning that there are problems in this test( due to the number of letters) and participants other than Zyj himself. Zyj's rank should fall in .
The following line shows how many seconds Zyj needs to solve each problem(for each time , , and t have at most 6 digits after the decimal point).
Next are lines, each contain numbers, the th number on the th line showing whether the th man have solved the th problem, where 1 means he did and 0 means he didn't.
Output
For each test case, output Case #k: , which means that in the th case there are ways.
Sample Input
1
4 1 0 2
300 300 300 300
0 0 0 1
Sample Output
Case \#1: 6
Hint
For a rank in , or say the first, Zyj needs to solve 2 problems at least. Since he needs 5 minutes (300 s) to solve one, he can only solve 2 in 10 minutes. Thus there are ways.
解题思路
- 原题改改又是一年,二分。
参考代码
出题人的代码太丑了,我不敢放上来。
### E. How many LLM
Problem Description
LLM is also known as L2M. Find out how many of them are there.
Input
Multiple test cases, one per line.
On each line is a string. You need to find out how many LLM(L2M) are there. LLM(L2M)s needn't be continious, but any two can't overlap.
Output
One number per test cases, indicating how many LLM(L2M) are there at most.
Sample Input
LLL2MM
2LLLMM
Sample Output
2
1
解题思路
- 从后往前遍历,为每个M找L。如果先找到2可以当L用,凑够两个就消掉了。
参考代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
char str[10000007];
int main() {
while (gets(str)) {
int L=strlen(str), i, m=0, n=0, t=0;
for (i=L; i--; ) {
if (str[i] == 'M')
m++;
if (str[i] == '2' && m)
m--, t++;
if (str[i] == 'L') {
if (t) {
t--;
n++;
} else if (m)
t++, m--;
}
}
printf ("%d\n", n);
}
}
### F. Fabonacci
Problem Description
我们知道Fabonacci数组通项函数定义如下:
现在给你个各不相同的正整数,问你能不能找到一个正整数使得。
Input
第一行输入一个整数,表示有组测试数据。对于每一组测试数据,第一行是一个正整数,第二行是个正整数。
Output
输出有行,每一行对应一组测试数据。
对于每组测试数据,如果能找到满足的,则输出,否则输出。
Sample Input
2
2
4 5
3
4 5 6
Sample Output
6
-1
解题思路
- 首先注意:个不各不相同的正整数。如果存在相同,或者在模域上求,则是难度更大的解法。
- 性质:,即当有解时只可能为。
- 证明:
- 显而易见得,,且;
- ;
- ;
- 所以,根据夹逼法则,只可能存在唯一解。
- 推理:,可知若有解,则数列必须满足前两项相差,后面的项与前一项相差。
- 贪心:由于数列各不相同,设有序,则只有当时,和可加(否则不能解出);设相加结果为,同理只有当时其在上的像可加。因此每次取最小两个相加能得到全局解,若存在一次不可加(即最小两个相差大于),则调整前面任何一个都不能与之相加,选取后面不相邻的任何一个都不能与之相加;特殊情况时数列及其子数列可划分为两部分各自可加,由于前部分最大值和后部分最小值相差大于,因此两部分整体不可加,由此得证贪心法正确性。
- 时间复杂度:
出题人提供的题解
- 不失一般性的,我们可以假设。
- 由于
- 假设,则明显有,假设不成立。
- 假设,则只有时才成立。
- 假设,使满足的充分必要条件是。如此不断归约,问题最终会化为。
- 综合上面的式子,得到满足条件。即应该满足。
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
int main() {
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--) {
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) scanf("%d", a + i);
if(n < 2) printf("%d", a[0]);
else {
sort(a, a + n);
bool flag = true;
int ans;
if(a[0] == a[1] - 1) {
ans = a[1] + 1;
for(int i = 2; i < n; ++i)
if(ans == a[i] - 1)
ans = a[i] + 1;
else flag = false;
} else flag = false;
if(flag) printf("%d\n", ans);
else puts("-1");
}
}
return 0;
}
### G. 保龄球
Problem Description
Oyk开了一个保龄球馆,馆中有个保龄球瓶一字排开,每个保球瓶都有一个固定的权值,它们分别是。每次掷出一个保龄球只会打倒一个保龄球瓶,假如打倒的是第个保龄球瓶,则得到的分数为它与相邻两个没有被倒下的保龄球瓶共三个权重的乘积,即,然后第与第个保龄球瓶就变成相邻的了。(当然,打倒最前或最后的瓶得到的分数只有两个数的乘积,打倒剩下的最后一个瓶得到的分数即为它本身的权重)。现在给你个保龄球瓶的权重,问不同的打倒方案中能达到的最高得分是多少?
Input
输入数据的第一行为一个正整数,代表着测试数据数量。对于每一个测试数据,第一行为一个正整数,代表着保龄球瓶的数量。第二行为个正整数,按顺序表示这个保龄球瓶的权重。
Output
输出数据总共有行,每一行对应一个测试数据。对于每一个测试数据,输出一个正整数,表示能达到的最大总得分。
Sample Input
1
4
1 2 2 1
Sample Output
10
解题思路
- DP。
- 时间复杂度:
参考代码(出题人的代码)
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[200];
int dp[200][200];
int main() {
int t, n;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--) {
scanf("%d", &n);
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
a[0] = a[n + 1] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d", a + i);
for(int k = 0; k < n; ++k)
for(int l = 1; l + k <= n; ++l) {
int r = l + k;
for(int mid = l; mid <= r; ++mid)
dp[l][r] = max(dp[l][r], dp[l][mid - 1] + a[l - 1] * a[mid] * a[r + 1] + dp[mid + 1][r]);
}
printf("%d\n", dp[1][n]);
}
return 0;
}
### H. 淹水
Problem Description
某地区有两个山峰。某年由于洪水,高的山峰被淹了两次,而低的山峰只被淹了一次。有可能吗?
答:有可能。在一次洪水淹了高的山峰,退去时低的山峰尚未露出水面,水位就又上升淹了高处山峰。
现在给出若干个山峰的高度和淹没次数,问这个次数可能出现吗?
Input
输入有多组数据,处理到文件尾。每组数据中,第一行为,山峰数量,下面行分别有两个数字,表示一座高度为的山峰被淹了次。
Output
如果可能,输出YES;否则输出NO。
Sample Input
2
7 2
3 1
Sample Output
YES
解题思路
- 水题。原定是签到题。
- 先从小到大排个序,1. 如果前面的山峰没被淹过,后面高的山峰就不可能被淹;2. 如果相同高度的山峰被淹次数不等,则不可能。
参考代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using std::sort;
int N;
struct Mountain {
int height, count;
bool operator<(const Mountain&c)const {
return height < c.height;
}
}mountain[10010];
void read() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
scanf("%d%d", &mountain[i].height, &mountain[i].count);
}
int judgeEqual(int idx) {
return mountain[idx].height != mountain[idx-1].height
|| mountain[idx].count == mountain[idx-1].count;
}
int judgeImpossible(int idx) {
return mountain[idx-1].count == 0 && mountain[idx].count > 0;
}
int work() {
sort(mountain, mountain+N);
int eqFlag = 1, impFlag = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < N; ++i) {
eqFlag = judgeEqual(i);
if (!eqFlag) return 0;
impFlag = judgeImpossible(i);
if (impFlag) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int main() {
while (~scanf("%d", &N)) {
read();
puts(work()? "YES": "NO");
}
return 0;
}
出题及解题总结
复盘
- 我没参与出题,因为我太蠢了。
- 想要复盘整个过程,也有很多话想说,最终还是按下了无数次退格。
- 嗨呀,大家都辛苦了啊!
建议、意见、吐槽
欢迎在下方评论区提出问题,4月内我都会回复and更新。
本文基于
知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议发布,欢迎引用、转载或演绎,但是必须保留本文的署名BlackStorm以及本文链接http://www.cnblogs.com/BlackStorm/p/SCNUCPC_2017_Solution.html,且未经许可不能用于商业目的。如有疑问或授权协商请与我联系。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义