SpringMVC 3.1集成Spring Security 3.1
这篇算是一个入门文章,昨天看见有网友提问,spring mvc集成spring security 的时候出错,揣测了一下问题木有解决。我就帮忙给搭建了一个集成框架他说可以,他告诉我这样的文章网上少。今天我就分享在这里供入门学习。spring mvc我木有用过,所以我们这里重点讲解如何集成spring security ,spring security是一个非常好的开源权限框架(具体了解自己google,或者到spring 官网,这里我给一个DOC3.1:http://static.springsource.org/spring-security/site/docs/3.1.x/reference/springsecurity.html)。可以说不仅仅包含了权限,里面有一套完整的授权认证系统包括:权限、防止session攻击、支持信道安全、支持LDAP认证、支持OpenID、同时支持CAS集成单点登录等等,个人用过spring security 2.0基本大致一样,当时中文资源那个少啊,尤其集成SSH+spring security 更是少的可怜,最后还是硬着头皮上,最后拿下了这个框架,最起码了解了。当时就写了一个SSH+spring security的文章,还被某网站引用。好了废话不扯,我们今天在来集成一个springmvc3.1+spring security3.1.我们step by step go。
step1:搭建SpringMVC。
如果你会搭建或者搭建好了spring MVC那这一步可以略过了。首先下载spring mvc3.1 jar这个到官网下载或者google,需要的jar如图:
然后创建一个包新建一个spring mvc 的class、我的如下:
@Controller public class RestConstroller { public RestConstroller() {} @RequestMapping(value = "/welcome", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String registPost() { return "/hello"; } }
上面采用spring 注解方式实例化class,这个我不多讲,spring mvc也没用过不敢乱点。官网有例子你自己照着做。http://static.springsource.org/spring/docs/3.1.x/spring-framework-reference/html/validation.html#format-configuring-FormattingConversionService
接着新建了一个view试图放了一个hello.jsp
然后新建一个spring-servlet.xml 这个是spring mvc的一个配置文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 启动注解驱动的Spring MVC功能,注册请求url和注解POJO类方法的映射--> <mvc:annotation-driven /> <!-- 启动包扫描功能,以便注册带有@Controller、@Service、@repository、@Component等注解的类成为spring的bean --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.mvc.test" /> <!--这个包根据自己的项目来配置,我的是com.mvc.test--> <!-- 对模型视图名称的解析,在请求时模型视图名称添加前后缀 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" p:prefix="/WEB-INF/view/" p:suffix=".jsp" /> </beans> 然后配置web.xml: <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <!-- 应用上下文配置文件 --> <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-servlet.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- 配置spring核心servlet --> <servlet> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!-- url-pattern配置为/ 拦截 --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
项目具体结构:
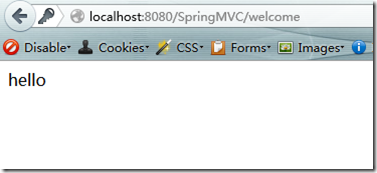
好了现在可以启动了,我这里启动的时候很不幸报错了,一看,缺少logger的jar,添加commons-logging-1.1.jar,ok启动访问http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/welcome成功、
到这里spring mvc配置完成。下面我们的重点集成spring security 3.1
step 2 spring mvc3.1集成spring security 3.1
首先要讲一点大版本集成要注意一点,大版本号要保持一直,第一位的往往都是大版本号,小版本号影响不大。为什么要这样讲,当时我在集成SSH 的时候spring 用的是spring 2.X,然后去下载了一个spring security 3.X的死活不成功。后来在一片老外的文章中发现了,具体地址我忘记了,spring 2.X +spring security 2.X才能集成功,spring 3.X +spring security 3.X才能集成成功。现在想想真够二的、哈哈,好了小插曲过后,我们继续。
首先下载spring security 3.1jar,地址:http://www.springsource.org/spring-community-download。我这里有曾今下载的,就不用了、jar结构如下:
红色的呢,是源码包,我们不用加入,蓝色圈中的是两个例子、你可以部署学习一下。其他的就是我们需要的jar,可以根据包名称发现各个包都是一个spring security 的特性,一般来说我们把jar都加进去,随着项目需要都会用到的。
接下来我们需要新建一个applicationContext-security.xml文件,这个是spring security 配置必须的一个文件。内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <b:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security" xmlns:b="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.1.xsd"> <!-- 开启默认的拦截器 --> <http auto-config='true'> <!-- 允许访问的uri --> <intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER" /> </http> <!-- 权限管理者 --> <authentication-manager> <!-- 权限提供者 --> <authentication-provider> <!-- 可提供登陆访问的用户 --> <user-service> <user name="haha" password="haha" authorities="ROLE_USER, ROLE_ADMIN" /> <user name="xixi" password="xixi" authorities="ROLE_USER" /> </user-service> </authentication-provider> </authentication-manager> </b:beans>
里面大概解释了一下,其中http节点里面默认的开启的几个必须的拦截器,下面的user-service 就是可以登陆访问的用户列表,我们这里没有用数据库所以就这样配置了,如果使用数据库 配置一个dataSource即可,包括后面的authorities都是通过数据库管理用户权限的,这里我们暂时入门不做深入讲解。
然后我们需要一个spring security 的过滤器配置、web.xml完整配置。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app version="2.5" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <!-- 应用上下文配置文件 --> <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-servlet.xml,/WEB-INF/applicationContext-security.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- spring securit start --> <filter> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <!-- spring securit start --> <!-- 配置spring核心servlet --> <servlet> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!-- url-pattern配置为/,不带文件后缀,会造成其它静态文件(js,css等)不能访问。如配为*.do,则不影响静态文件的访问 --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> </web-app>
其中springSecurityFilterChain 过滤器必须放在最前面,因为spring security的安全机制是保护在web最外层的安全框架,所以你的任何访问都要经过spring security 投票机制授权才可以访问的,否则不允许访问。只有登陆用户才可以访问。
contextConfigLocation配置就是扫描我们的spring mvc和spring security配置文件。
具体完整的目录结构如下:
下面我们启动web看看会发生什么神奇的事情。下面我们访问http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/welcome
奇迹发生了,我们并没有创建登陆页面,那这个登陆页面哪里来的呢?哈哈,不要着急,慢慢来讲,看看url spring_security_login ,还记得我们前面配置的spring security 的配置文件的<http>这个配置默认会开启几个过滤器,其中有一个就是拦截发现我们没登陆然后查找登陆页面,但为什么自动出来呢?其是它为我们默认了一个登陆页面,登陆页面我们可以指定一个,前面我们没指定所以检查发现没有它就默认了一个登陆页面给我们,下面我们登陆看看会发生什么情况。(什么你不知道账号密码?其实就是我们spring security配置的那个账号密码)。
输入账号密码结果:
跳转到了我们刚刚要访问的uri了,中间还会检查我们的账号是否有权,有权才会访问成功,无权则会转到无权访问页面。好了,到这里spring mvc+spring security 集成就完成了,剩下的工作就是一步一步的慢慢学习spring security 来使用更多的完善的功能。简单吧,就这点东西。
到这里我们再试试如果登录一个不存在的账号会发生什么情况、我输入了一个admin、结果出现如下图:
spring security已经帮我们检查了,账号不存在,他会把我们继续重定向到登录页面,知道登录成功,否则你永远都面对的是这个登录页面。
好了今天主要分享的就这点,师傅引进门修行靠个人。不过我想了想,还是再分享一点有用的、有的人会想如果我的登录页面需要自定义怎么办?下面我们就讲讲。
首先自定义登陆,我们需要修改applicationContext-security.xml 配置文件,修改如下:
<!-- 开启默认的拦截器 --> <http auto-config='true'> <!-- 允许访问的uri --> <intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER" /> <!-- 登陆页面配置 --> <form-login login-page="/login.jsp" default-target-url="/index.jsp" authentication-failure-url="/login.jsp?error=true"/> </http> <!-- 权限管理者 --> <authentication-manager> <!-- 权限提供者 --> <authentication-provider> <!-- 可提供登陆访问的用户 --> <user-service> <user name="haha" password="haha" authorities="ROLE_USER, ROLE_ADMIN" /> <user name="xixi" password="xixi" authorities="ROLE_USER" /> </user-service> </authentication-provider> </authentication-manager>
其中就多加 了一个form 配置节点,从命名可以看出login-page就是你的登陆页面,default-target-url是默认的登陆成功后的页面,authentication-failure-url就是当你输入非法账号或者密码自动重定向到login.jsp.
接下来创建我们自定义的登陆页面,我的就是login.jsp,有人到这里会想,form接下来该如何写呢?怎么写才能被拦截呢?如下:
<h1>user login</h1> <form action="j_spring_security_check" method="post"> 用户名<input type="text" name="j_username"/><br/> 密码<input type="password" name="j_password"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="submit"/> </form>
action="j_spring_security_check"必须这样写,否则拦截器拦截不到。登陆的字段j_username j_password必须这样写,否则你的登陆拦截器获取不到value。当然你也可以自定义,但前提是你必须继承UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器去重写一下,这里我们就不麻烦了,而且一般情况下我们不需要重写,就用它提供的即可。好了,到这里我们可以启动服务器了。我们再次访问:http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/welcome看看会发生神马变化。如图:
咦?这是什么情况?url变了,是我们要访问的登陆地址。可是页面的登陆form呢?不要着急,这种情况我当时见多了,第一反应login.jsp没有被放行,拦截下来了、受保护的资源。前面我们不是讲过spring security 是保护在web最外层的,访问任何资源需要投票,授权才能访问的,这个也不例外。
好了,知道什么情况了,我们修改吧!修改如下部分片段即可:
<!-- 开启默认的拦截器 --> <http auto-config='true'> <!--对login.jsp放行,不用保护--> <intercept-url pattern="/login.jsp" filters="none" /> <!-- 允许访问的uri --> <intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER" /> <!-- 登陆页面配置 --> <form-login login-page="/login.jsp" default-target-url="/index.jsp" authentication-failure-url="/login.jsp?error=true"/> </http>
然后我们启动服务器再次访问http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/welcome
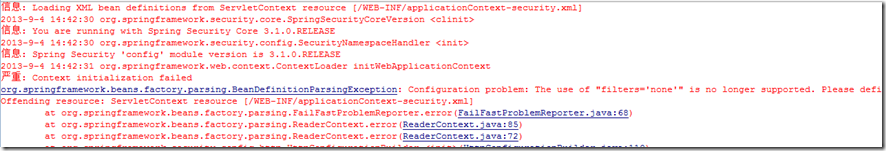
不幸的事情又发生了,控制台报错,服务器启动失败!如下图:
其实大概的意思是讲下面的这个配置作废了。
<!--对login.jsp放行,不用保护-->
<intercept-url pattern="/login.jsp" filters="none" />这个配置是spring security 2.X中的,3.X以后作废了,使用新的方式了。不过错误告诉我们怎么使用新的标签了,就是新建一个节点标签,属性security="none" 来放行,好了,我们修改一下。修改部分配置如下:
<!-- spring securit 3.X新的资源放行配置方式,不受保护的资源 --> <http pattern="/login.jsp" security="none"/> <!-- 开启默认的拦截器 --> <http auto-config='true'> <!-- 允许访问的uri --> <intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER" /> <!-- 登陆页面配置 --> <form-login login-page="/login.jsp" default-target-url="/index.jsp" authentication-failure-url="/login.jsp?error=true"/> </http>
在http节点上面再加一个节点,然后配置不需要拦截的。pattern属性的意思就是通过正则表达式来匹配的。security="none"就是不安全的,意思就是不受spring security保护的资源,这里还要提一点,就是.jpg、.gif、.swf、.css、.js/等等资源文件都会被拦截下来,即使他是包含在一个已经放行的jsp页面或者uri的request、怎么理解?就是比如:我们的login.jsp放行了,但是我们没有放行.jpg这样的图片资源,当我们访问login.jsp的时候图片是不显示的,因为它没有被放行,从这里可以看出spring security是非常严格的检查机制。假如我们要放行那些怎么办?
spring security 2.X中配置如下:
<http auto-config='true'> <!-- public 资源文件 –> <intercept-url pattern="/**/*.jpg" filters="none" /> <intercept-url pattern="/**/*.png" filters="none" /> <intercept-url pattern="/**/*.gif" filters="none" /> <intercept-url pattern="/**/*.ico" filters="none" /> <intercept-url pattern="/**/*.css" filters="none" /> <intercept-url pattern="/**/*.js" filters="none" /> <!-- 允许访问的uri --> <intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER" /> <!-- 登陆页面配置 --> <form-login login-page="/login.jsp" default-target-url="/index.jsp" authentication-failure-url="/login.jsp?error=true"/> </http>
当然我们这里讲spring security 3.X,所以3.X的如下:
<http pattern="/**/*.jpg" security="none"/> <http pattern="/**/*.png" security="none"/> <http pattern="/**/*.gif" security="none"/> <http pattern="/**/*.ico" security="none"/> <http pattern="/**/*.css" security="none"/> <http pattern="/**/*.js" security="none"/> <!-- spring securit 3.X新的资源放行配置方式,不受保护的资源 --> <http pattern="/login.jsp" security="none"/> <http auto-config='true'> <!-- 允许访问的uri --> <intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER" /> <!-- 登陆页面配置 --> <form-login login-page="/login.jsp" default-target-url="/index.jsp" authentication-failure-url="/login.jsp?error=true"/> </http>
上面的pattern="/**/*.jpg" 配置意思就是放行,项目中所有的.jpg资源,以后的以此类推的原理。你亦可以放行某一个文件下的,具体就是正则表达式的配置。
好了,我们还是回到刚刚修改的放行资源试试,再次启动服务器访问:http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/welcome
当我们再次访问的时候login.jsp已经出来了、这个时候我们登陆,成功后直接跳转到/welcome 的响应页面。结果如图;
这里我们没有配置用户资源访问权限,所以访问的资源直接可以访问,如果配置了访问权限登陆成功后,spring security还会检查是否有权访问,无权重定向。
好了到这里,今天分享的入门到此完毕。这个框架还是很值得学习的,功能比较强大,官方文档比较全面,可以好好研读一下,感谢抽宝贵的时间阅读。










 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号