Google Optimization Tools介绍
Google Optimization Tools(OR-Tools)是一款专门快速而便携地解决组合优化问题的套件。它包含了:
- 约束编程求解器。
- 简单而统一的接口,用于多种线性规划和混合整数规划求解,包括 CBC、CLP、GLOP、GLPK、Gurobi、CPLEX 和SCIP。
- 图算法 (最短路径、最小成本、最大流量、线性求和分配)。
- 经典旅行推销员问题和车辆路径问题的算法。
- 经典装箱和背包算法。
Google使用C++开发了OR-Tools库,但支持Python,C#,或Java语言调用。
安装Google OR-Tools
Google OR-Tools的源码在[Github] google/or-tools。其它开发环境下的安装如下。
Linux or Mac下安装
1. 确认使用了Python 2.7+,3.5+版本,以及pip 9.0.1+版本。
2. Mac OSX系统需要安装命令行工具Xcode,在Terminal中执行xcode-select --install。
Linux系统需要安装g++,在Terminal中执行sudo apt-get install g++ make。
如果使用C#请确认安装了Mono 4.2.0+的64位版本。
3. 在Terminal中执行pip install --upgrade ortools直接安装Python版本的OR-Tools包。C++/Java/C#版本的链接为:Mac, Ubuntu 17.04, Ubuntu 16.04, Ubuntu 14.04, CentOS 7, Debian 9 ,下载到指定目录后执行make all。
Windows下安装
Python版本的包的安装和Linux一样,可自行选用合适的开发工具。若是使用C++、C#,推荐使用64位版本的Windows10操作系统,并且使用Microsoft Visual Studio 2015 或者 2017作为开发工具,相应的库文件下载地址为: Visual Studio 2017 the Visual Studio 2015。
- C++使用lib/ortools.lib, 并且将or‑tools/include添加到项目引用。
- Java使用jar命令调用lib/com.google.ortools.lib的方式,并且将 ‑Djava.library.path=PATH_TO_or‑tools/lib添加到命令行。
- C#添加bin/Google.OrTools.dll到项目依赖,或者使用NuGet搜索Google.OrTools进行安装。
Demo
以下是几种支持语言的demo,运行一下验证是否安装正确。
C++ 代码
#include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h" #include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.pb.h" namespace operations_research { void RunTest( MPSolver::OptimizationProblemType optimization_problem_type) { MPSolver solver("Glop", optimization_problem_type); MPVariable* const x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, 1, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, 2, "y"); MPObjective* const objective = solver.MutableObjective(); objective->SetCoefficient(x, 1); objective->SetCoefficient(y, 1); objective->SetMaximization(); solver.Solve(); printf("\nSolution:"); printf("\nx = %.1f", x->solution_value()); printf("\ny = %.1f", y->solution_value()); } void RunExample() { RunTest(MPSolver::GLOP_LINEAR_PROGRAMMING); } } int main(int argc, char** argv) { operations_research::RunExample(); return 0; }
C# 代码
using System; using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver; public class my_program { private static void RunLinearProgrammingExample(String solverType) { Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("IntegerProgramming", solverType); Variable x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, 1.0, "x"); Variable y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, 2.0, "y"); Objective objective = solver.Objective(); objective.SetCoefficient(x, 1); objective.SetCoefficient(y, 1); objective.SetMaximization(); solver.Solve(); Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue()); Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue()); } static void Main() { RunLinearProgrammingExample("GLOP_LINEAR_PROGRAMMING"); } }
Python 代码
from __future__ import print_function from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp def main(): solver = pywraplp.Solver('SolveSimpleSystem', pywraplp.Solver.GLOP_LINEAR_PROGRAMMING) x = solver.NumVar(0, 1, 'x') y = solver.NumVar(0, 2, 'y') objective = solver.Objective() objective.SetCoefficient(x, 1) objective.SetCoefficient(y, 1) objective.SetMaximization() solver.Solve() print('Solution:') print('x = ', x.solution_value()) print('y = ', y.solution_value()) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
Java 代码
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable; public class my_program { static { System.loadLibrary("jniortools"); } private static MPSolver createSolver (String solverType) { return new MPSolver("my_program", MPSolver.OptimizationProblemType.valueOf(solverType)); } private static void runmy_program(String solverType, boolean printModel) { MPSolver solver = createSolver(solverType); MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, 1.0, "x"); MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, 2.0, "y"); MPObjective objective = solver.objective(); objective.setCoefficient(y, 1); objective.setMaximization(); solver.solve(); System.out.println("Solution:"); System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue()); System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue()); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { runmy_program("GLOP_LINEAR_PROGRAMMING", false); } }
执行结果如图:
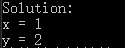
下一篇这个系列的文章,将具体介绍一种约束求解的应用场景。



