sping AOP核心思想及实现原理
核心思想
aop的核心思想是目标对象初始化后创建其代理对象(cglib、jdk)。代理对象执行方法时走MethodInterceptor的invoke拦截方法,实现横切。
实现原理
首先我们先来看AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator(还有AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator),这是目标对象的代理对象创建者
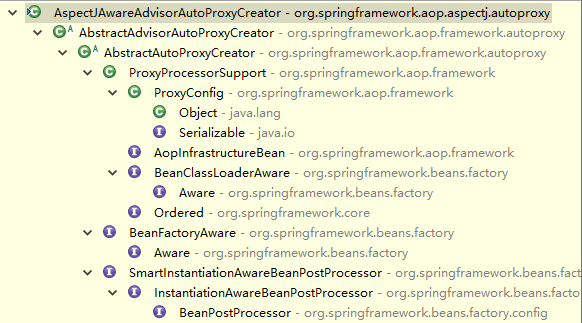
我们重点关注InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,BeanPostProcessor接口。
BeanPostProcessor
public interface BeanPostProcessor { /** * bean初始化前的后置处理*/ Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; /** * bean初始化后的后置处理*/ Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; }
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor继承了BeanPostProcessor
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor { /** * bean实例化之前的后只处理 */ Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException; /** * bean实例化后的后置处理 */ boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues( PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; }
也就是说AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator在bean实例化和初始化前后都会进行后置处理
spring注册并实例化AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator后,bean如GoodService实例化后初始化时就有了后置处理器的前置处理和后置处理,而后置处理就是为目标对象创建代理的过程。
AbstractBeanFactory执行creatBean()时,实例化前给后置处理器一个机会去创建自定义的代理对象,这个必须实现TargetSource接口
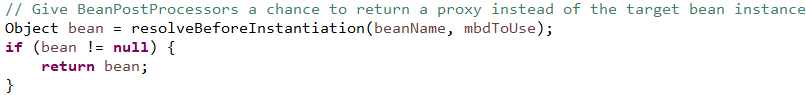
实例化bean后初始化时使用后置处理器去创建代理对象
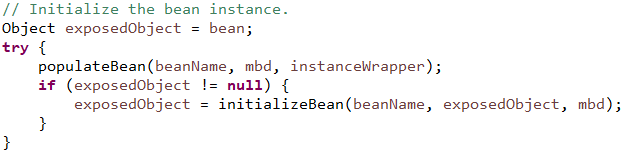
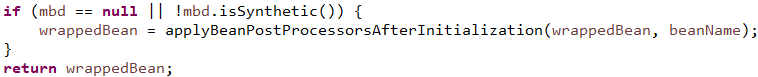
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean;
// 获得所有的bean后置处理器其中就包含AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { result = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (result == null) { return result; } } return result; }
AbstractAutoProxyCreator中执行
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; }
// 判断是Advice、Pointcut、Advisor等的实现类是的话不创建代理对象
// 判断是否需要跳过即判断该bean是否是切面类bean如com.wjz.service.Transaction,后文详解#1 if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } // 获得Advisor广播和Advice通知,后文详解#2 Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 创建目标对象的代理对象,后文详解#3 Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
书接前文#1
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { // 获得所有的广播 List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) { if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor) { if (((AbstractAspectJAdvice) advisor.getAdvice()).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) { return true; } } } return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName); }
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() { // Determine list of advisor bean names, if not cached already. String[] advisorNames = null; synchronized (this) { advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames; if (advisorNames == null) { // 获得所有的注册了的实现了Advisor接口的bean如<aop:before>标签对应的bean advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors( this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false); this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames; } } if (advisorNames.length == 0) { return new LinkedList<Advisor>(); } List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>(); for (String name : advisorNames) { if (isEligibleBean(name)) { if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(name)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping currently created advisor '" + name + "'"); } } else { try {
// 实例化那些广播bean(全局变量中有通知bean) advisors.add(this.beanFactory.getBean(name, Advisor.class)); } catch (BeanCreationException ex) { Throwable rootCause = ex.getMostSpecificCause(); if (rootCause instanceof BeanCurrentlyInCreationException) { BeanCreationException bce = (BeanCreationException) rootCause; if (this.beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(bce.getBeanName())) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Skipping advisor '" + name + "' with dependency on currently created bean: " + ex.getMessage()); } // Ignore: indicates a reference back to the bean we're trying to advise. // We want to find advisors other than the currently created bean itself. continue; } } throw ex; } } } } return advisors; }
这里我们需要说一下AspectJPointcutAdvisor的实例化过程是通过构造器反射完成的,他的构造函数如下
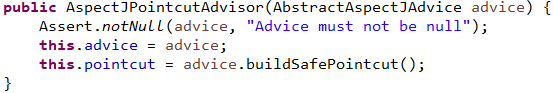
在实例化AspectJPointcutAdvisor之前我们知道得先实例化AbstractAspectJAdvice如AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice,后者的构造函数如下

我们可以看到他有三个参数,这三个参数都必须先初始化,他们的初始化过程就是普通的无参构造器反射
书接前文#2
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 获得广播和#1相同 List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 使用AspectJPointcutAdvisor中的ClassFilter和MethodMatcher匹配出符合的广播 List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
// pca.getPointcut()返回ComposablePointcut后者有ClassFilter和MethodMatcher return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions); }
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { // 获得AspectJExpressionPointcut并匹配bean的Class如com.wjz.service.GoodService,后文详解#2-1
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) { return false; } MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher(); if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) { // No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway... return true; } IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null; if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) { introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher; } Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass)); classes.add(targetClass); for (Class<?> clazz : classes) { Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz); for (Method method : methods) {
// 获得bean的所有方法使用MethodMatcher匹配方法,后文详解#2-2 if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null && introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) || methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) { return true; } } } return false; }
书接前文#2-1
public boolean matches(Class<?> targetClass) {
// 检查org.aspectj的PointcutExpression是否创建了 checkReadyToMatch();
// 这里使用了org.aspectj的API完成的 return this.pointcutExpression.couldMatchJoinPointsInType(targetClass); }
自定义实现横切过滤类功能
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import org.aspectj.weaver.tools.PointcutExpression;
import org.aspectj.weaver.tools.PointcutParameter;
import org.aspectj.weaver.tools.PointcutParser;
import org.aspectj.weaver.tools.PointcutPrimitive;
private static final Set<PointcutPrimitive> SUPPORTED_PRIMITIVES = new HashSet<PointcutPrimitive>(); private static final String expression = "execution(* com.wjz.service.*.*(..))"; private static final Class<?> clazz = GoodService.class; static { SUPPORTED_PRIMITIVES.add(PointcutPrimitive.EXECUTION); } public static void main(String[] args) { PointcutExpression pointcutExpression = null; PointcutParser parser = PointcutParser .getPointcutParserSupportingSpecifiedPrimitivesAndUsingSpecifiedClassLoaderForResolution( SUPPORTED_PRIMITIVES, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()); PointcutParameter[] pointcutParameters = new PointcutParameter[0]; pointcutExpression = parser.parsePointcutExpression(expression, null, pointcutParameters); System.out.println(pointcutExpression.couldMatchJoinPointsInType(clazz)); }
书接前文#2-2
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { return
// 判断目标方法是否是切入点方法如beginTransaction方法
MethodMatchers.matches(this.mm1, method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) && // 判断目标方法是否符合表达式,使用了org.aspectj的API完成的
MethodMatchers.matches(this.mm2, method, targetClass, hasIntroductions); }
public static boolean matches(MethodMatcher mm, Method method, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { return
// org.aspectj的API判断目标方法是否匹配表达式
((mm instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher &&
((IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) mm).matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions))
|| // 使用AdviceExcludingMethodMatcher判断目标方法是否是切入点方法
mm.matches(method, targetClass)); }
org.aspectj的API判断目标方法是否匹配表达式
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, boolean beanHasIntroductions) { // 检查是否创建了org.aspectj的PointcutExpression对象没有的话立即创建
checkReadyToMatch(); Method targetMethod = AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
// 获得org.aspectj的ShadowMatch对象 ShadowMatch shadowMatch = getShadowMatch(targetMethod, method);// 使用API判断是否匹配 if (shadowMatch.alwaysMatches()) { return true; }
return false;
}
自定义实现横切过滤方法功能
private static final Set<PointcutPrimitive> SUPPORTED_PRIMITIVES = new HashSet<PointcutPrimitive>(); private static final String expression = "execution(* com.wjz.service.*.*(..))"; private static final Class<?> clazz = GoodService.class; static { SUPPORTED_PRIMITIVES.add(PointcutPrimitive.EXECUTION); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { PointcutExpression pointcutExpression = null; PointcutParser parser = PointcutParser .getPointcutParserSupportingSpecifiedPrimitivesAndUsingSpecifiedClassLoaderForResolution( SUPPORTED_PRIMITIVES, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()); PointcutParameter[] pointcutParameters = new PointcutParameter[0]; pointcutExpression = parser.parsePointcutExpression(expression, null, pointcutParameters); Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("list"); ShadowMatch shadowMatch = pointcutExpression.matchesMethodExecution(method); System.out.println(shadowMatch.alwaysMatches()); }
使用AdviceExcludingMethodMatcher判断目标方法是否是切入点方法
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
// 方法比较 return !this.adviceMethod.equals(method); }
书接前文#3
这是核心部分,创建目标对象的代理对象
protected Object createProxy( Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) { if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) { AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass); } // 创建ProxyFactory对象并设置一些属性值 ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(); proxyFactory.copyFrom(this); // 判断bean是否已经是代理对象了 if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) { if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) { proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true); } else {
// 判断bean是否能创建代理对象 evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory); } } // 创建所有的广播,就是将specificInterceptors中的Advisor拿到 Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors); for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
// 将Advisor注入到ProxyFactory中 proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor); } // 将SingletonTargetSource注入到ProxyFactory中,前者包含bean的实例化对象 proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
// 自定义扩展ProxyFactory customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy); if (advisorsPreFiltered()) { proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true); } // 核心部分,获得bean对象的代理对象 return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader()); }
使用AopProxyFactory(DefaultAopProxyFactory)创建JdkDynamicAopProxy(JDK)或者是ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(cglib)对象,再创建代理对象
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader); }
判断创建jdk方式的代理还是cglib方式的代理
// 如果bean是接口或者已经是代理对象了则创建jdk方式的代理,否则创建cglib方式的
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
cglib方式创建代理对象
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {try { Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass(); Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy"); Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
// 判断是否是cglib代理对象 if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) { proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass(); Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces(); for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) { this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface); } } // 验证类,根据需要编写日志消息 validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader); // 创建cglib核心类Enhancer Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer(); if (classLoader != null) { enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader); if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && ((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) { enhancer.setUseCache(false); } } enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass); enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised)); enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE); enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareUndeclaredThrowableStrategy(classLoader)); // 获得回调即执行目标方法时的拦截方法,稍后详解 Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass); Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length]; for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) { types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass(); } // fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter( this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset)); enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types); // 生成代理类并创建一个代理实例 return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks); }
}
protected Object createProxyClassAndInstance(Enhancer enhancer, Callback[] callbacks) { enhancer.setInterceptDuringConstruction(false); enhancer.setCallbacks(callbacks); return (this.constructorArgs != null ? enhancer.create(this.constructorArgTypes, this.constructorArgs) : enhancer.create()); }
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception { // 用于优化选择的参数 boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy(); boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen(); boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic(); // 创建一个重要的动态aop拦截类,后文详解 Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised); Callback targetInterceptor; if (exposeProxy) { targetInterceptor = isStatic ? new StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()); } else { targetInterceptor = isStatic ? new StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()); } Callback targetDispatcher = isStatic ? new StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new SerializableNoOp(); Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] { aopInterceptor, // for normal advice targetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimized new SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to this targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher, new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised), new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised) }; Callback[] callbacks; if (isStatic && isFrozen) { Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods(); Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length]; this.fixedInterceptorMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(methods.length); // TODO: small memory optimisation here (can skip creation for methods with no advice) for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) { List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(methods[x], rootClass); fixedCallbacks[x] = new FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor( chain, this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(), this.advised.getTargetClass()); this.fixedInterceptorMap.put(methods[x].toString(), x); } callbacks = new Callback[mainCallbacks.length + fixedCallbacks.length]; System.arraycopy(mainCallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, mainCallbacks.length); System.arraycopy(fixedCallbacks, 0, callbacks, mainCallbacks.length, fixedCallbacks.length); this.fixedInterceptorOffset = mainCallbacks.length; } else { callbacks = mainCallbacks; } return callbacks; }
我们可以看到cglib设置了好几个CallBack用于拦截目标方法,我们详细看一下DynamicAdvisedInterceptor对象它拦截目标方法时做了什么?
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; Class<?> targetClass = null; Object target = null; try { if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; } target = getTarget(); if (target != null) { targetClass = target.getClass(); }
// 关键部分,获得所有的通知拦截如MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor、AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor,稍后详解 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); Object retVal; if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse); } else { // 创建方法调用,执行方法链 retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed(); }
// 处理返回结果 retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal); return retVal; } finally { if (target != null) { releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } }
public Object proceed() throws Throwable { // We start with an index of -1 and increment early. if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
// 调用methodProxy.invoke(target, arguments);执行目标方法 return invokeJoinpoint(); } Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex); if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) { InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice; if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) { return dm.interceptor.invoke(this); } else { return proceed(); } } else {// MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor、AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor等通知拦截器开始拦截 return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this); } }
前置通知拦截
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
// 前置通知拦截处理 this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis() );
// 调用拦截方法链 return mi.proceed(); }
后置通知拦截
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
// 调用拦截方法链 Object retVal = mi.proceed();
// 后置通知拦截处理 this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis()); return retVal; }
jdk方式创建代理对象
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource()); } Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true); findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces); return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this); }



