PCA和白化练习之处理二维数据
在很多情况下,我们要处理的数据的维度很高,需要提取主要的特征进行分析这就是PCA(主成分分析),白化是为了减少各个特征之间的冗余,因为在许多自然数据中,各个特征之间往往存在着一种关联,为了减少特征之间的关联,需要用到所谓的白化(whitening).
首先下载数据pcaData.rar,下面要对这里面包含的45个2维样本点进行PAC和白化处理,数据中每一列代表一个样本点。
第一步 画出原始数据:
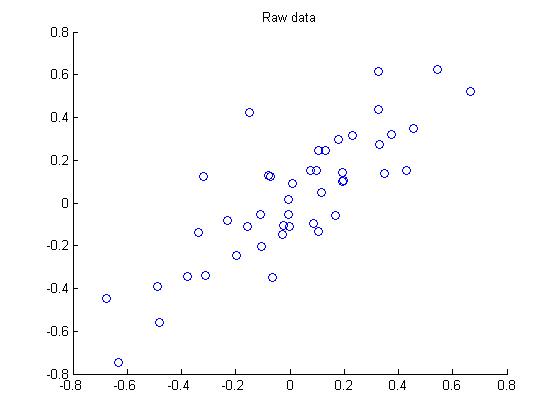
第二步:执行PCA,找到数据变化最大的方向:

第三步:将原始数据投射到上面找的两个方向上:

第四步:降维,此例中把数据由2维降维到1维,画出降维后的数据:

第五步:PCA白化处理:

第六步:ZCA白化处理:
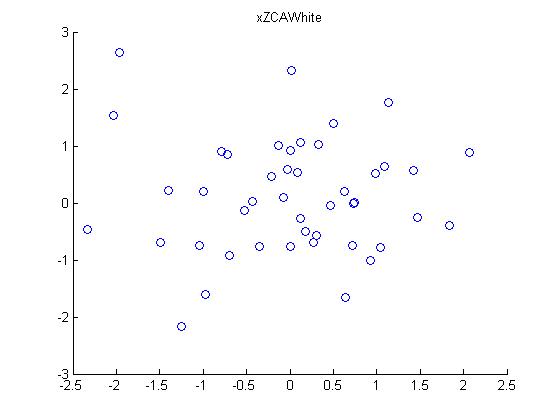
下面是程序matlab源代码:
1 close all;clear all;clc;
2
3 %%================================================================
4 %% Step 0: Load data
5 % We have provided the code to load data from pcaData.txt into x.
6 % x is a 2 * 45 matrix, where the kth column x(:,k) corresponds to
7 % the kth data point.Here we provide the code to load natural image data into x.
8 % You do not need to change the code below.
9
10 x = load('pcaData.txt','-ascii');
11 figure(1);
12 scatter(x(1, :), x(2, :));
13 title('Raw data');
14
15
16 %%================================================================
17 %% Step 1a: Implement PCA to obtain U
18 % Implement PCA to obtain the rotation matrix U, which is the eigenbasis
19 % sigma.
20
21 % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
22 u = zeros(size(x, 1)); % You need to compute this
23
24 sigma = x * x'/ size(x, 2);
25 [u,S,V] = svd(sigma);
26
27
28
29 % --------------------------------------------------------
30 hold on
31 plot([0 u(1,1)], [0 u(2,1)]);
32 plot([0 u(1,2)], [0 u(2,2)]);
33 scatter(x(1, :), x(2, :));
34 hold off
35
36 %%================================================================
37 %% Step 1b: Compute xRot, the projection on to the eigenbasis
38 % Now, compute xRot by projecting the data on to the basis defined
39 % by U. Visualize the points by performing a scatter plot.
40
41 % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
42 xRot = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
43 xRot = u' * x;
44
45 % --------------------------------------------------------
46
47 % Visualise the covariance matrix. You should see a line across the
48 % diagonal against a blue background.
49 figure(2);
50 scatter(xRot(1, :), xRot(2, :));
51 title('xRot');
52
53 %%================================================================
54 %% Step 2: Reduce the number of dimensions from 2 to 1.
55 % Compute xRot again (this time projecting to 1 dimension).
56 % Then, compute xHat by projecting the xRot back onto the original axes
57 % to see the effect of dimension reduction
58
59 % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
60 k = 1; % Use k = 1 and project the data onto the first eigenbasis
61 xHat = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
62 z = u(:, 1:k)' * x;
63 xHat = u(:,1:k) * z;
64
65 % --------------------------------------------------------
66 figure(3);
67 scatter(xHat(1, :), xHat(2, :));
68 title('xHat');
69
70
71 %%================================================================
72 %% Step 3: PCA Whitening
73 % Complute xPCAWhite and plot the results.
74
75 epsilon = 1e-5;
76 % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
77 xPCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
78
79 xPCAWhite = diag(1 ./ sqrt(diag(S) + epsilon)) * xRot;
80
81
82
83 % --------------------------------------------------------
84 figure(4);
85 scatter(xPCAWhite(1, :), xPCAWhite(2, :));
86 title('xPCAWhite');
87
88 %%================================================================
89 %% Step 3: ZCA Whitening
90 % Complute xZCAWhite and plot the results.
91
92 % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
93 xZCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
94
95 xZCAWhite = u * xPCAWhite;
96 % --------------------------------------------------------
97 figure(5);
98 scatter(xZCAWhite(1, :), xZCAWhite(2, :));
99 title('xZCAWhite');
100
101 %% Congratulations! When you have reached this point, you are done!
102 % You can now move onto the next PCA exercise. :)
请尊重原创知识,本人非常愿意与大家分享
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/90zeng/
作者:博客园-90Zeng



