软件工程个人作业03和psp记录
一、题目:四则运算3
老师提出了新的要求:
数据定义:
自然数:0, 1, 2, …。
真分数:1/2, 1/3, 2/3, 1/4, 1’1/2, …。
运算符:+, −, ×, ÷。
括号:(, )。
等号:=。
分隔符:空格(用于四则运算符和等号前后)
10点新要求:
1、定义参数控制生成题目的个数。
例如,参数n=10;则将生成10个题目。
2、定义参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围。
例如参数r= 10,将生成10以内(不包括10)的四则运算题目。该参数可以设置为1或其他自然数。
该参数必须给定,否则程序报错并给出帮助信息。
3、生成的题目中计算过程不能产生负数,也就是说算术表达式中如果存在形如e1 − e2的子表达式,那么e1 ≥ e2。
4、生成的题目中如果存在形如e1 ÷ e2的子表达式,那么其结果应是真分数。
5. 每道题目中出现的运算符个数不超过3个。
6、程序一次运行生成的题目不能重复,即任何两道题目不能通过有限次交换+和×左右的算术表达式变换为同一道题目
例如,23 + 45 = 和45 + 23 = 是重复的题目,6 × 8 = 和8 × 6 = 也是重复的题目。3+(2+1)和1+2+3这两个题目是重复的,由于+是左结合的,1+2+3等价于 (1+2)+3,也就是3+(1+2),也就是3+(2+1)。但是1+2+3和3+2+1是不重复的两道题,因为1+2+3等价于(1+2)+3,而3+2+1等价于(3+2)+1,它们之间不能通过有限次交换变成同一个题目
7.生成的题目存储到数据库中,
格式如下:
1. 四则运算题目1
2. 四则运算题目2
……
其中真分数在输入输出时采用如下格式,真分数五分之三表示为3/5,真分数二又八分之三表示为2’3/8。
8. 在生成题目的同时,计算出所有题目的答案,并存入数据库文件。
格式如下:
1. 答案1
2. 答案2
特别的,真分数的运算如下例所示:1/6 + 1/8 = 7/24。
9. 程序应能支持一万道题目的生成。
10. 程序支持对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计,
统计结果输出到数据表文件Grade,格式如下:
Correct: 5 (1, 3, 5, 7, 9)
Wrong: 5 (2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
其中“:”后面的数字5表示对/错的题目的数量,括号内的是对/错题目的编号。为简单起见,假设输入的题目都是按照顺序编号的符合规范的题目。
二、设计思路:
1.含多个运算符的题目如何生成,括号如何添加?
依据四则运算2来看,存在运算符最高只能产生7个,经过一个周末的看书和查阅资料,我放弃了之前的方法,采用先随机生成一个运算符+数字的数组,然后根据这个数组生成一棵二叉树。
/*-----------二叉树类——————————*/
public class BinaryTree {
private TreeNode root;
private int size;
private String[] data;
public BinaryTree(String[] array) {
this.data = array;
size = array.length;
root = createTree(0);
}
public String toString(){
String str = root.toString(); //当结点为根结点时的算术表达式
str = str.substring(1, str.length()-1); //去掉该表达式两边的括号
return str;
}
public String CalAndVal(){
return root.getResult();
}
/*创建二叉树*/
public TreeNode createTree(int index) {
if(index >= size)
return null;
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(data[index]);
node.setLchild(createTree(2*index + 1));
node.setRchild(createTree(2* index +2));
return node;
}
public TreeNode getRoot() { // 得到根节点
return root;
}
}
/*随机生成一个符号+数字的数组 */
public class CreatePro {
public String[] proArrary( int range, String hasMD, String hasFS){
int Num = (int) (2 + Math.random()* 2); //随机产生运算符个数,最少2个, 最多3个;
int Size = Num * 2 +1; // 在树中表示总结点个数,也是结点集的长度
String symbol[] = {"+","-","×","÷"};
String[] arrary = new String[Size];
ProperFra fractin = new ProperFra();
// 首先随机产生设置好的运算符,传入到数组中
for(int i =0 ; i< Num ; i++){
int symNum = 0;
if(hasMD.equals("Y") || hasMD.equals("y")) {
symNum = (int) (Math.random()* 4 );
}else if(hasMD.equals("N") || hasMD.equals("n")) {
symNum = (int) (Math.random()* 2 );
}
//int symNum=3;
arrary[i] = symbol[symNum];
}
//在将生成的整数或者分数传入到数组中
for(int i = Num; i< Size;i++ ){
int rand = 0;
if(hasFS.equals("Y") || hasFS.equals("y")) {
rand = (int) (Math.random() * 2);
}else if(hasFS.equals("N") || hasFS.equals("n")) {
rand = 0;
}
//int rand = 0;
String FS = fractin.createFS(range);
String ZS = fractin.createZS(range);
if(rand == 0) { //传入整数到数组
arrary[i] =ZS;
}else if(rand == 1) { //传入分数到数组
arrary[i] = FS;
}
}
return arrary;
}
2.如何将生成的数据存入数据库中?
先定义一个连接数据库的工具类,方便我们每次需要连接数据库的时候直接调用就行,其次定义一个与数据库表中列名相同的一个JavaBean,数据产生后先将数据封装到javaBean中,然后调用写入到数据库中的方法,经过大量测试,生成一道题写入到数据库一道题耗时远远大于一次性把题全部插入到数据库
数据库连接工具类:
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JDBCUtils {
static Properties prop = null;
private JDBCUtils(){
}
//为了保证只读取一次配置文件,将读取步骤放在静态代码块中
static {
try {
prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileReader(JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResource("config.properties").getPath()));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//------------提供两个方法,连接数据库和关闭连接-----------------
/**
* 获取连接
* @return Connection对象
* @throws Exception
*/
public static Connection getConn() throws Exception{
Class.forName(prop.getProperty("driver"));
return DriverManager.getConnection(prop.getProperty("url"), prop.getProperty("user"), prop.getProperty("password"));
}
/**
* 关闭连接
* @param rs
* @param stat
* @param conn
*/
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement stat, Connection conn) {
if(rs != null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
rs = null;
}
}
if(stat != null){
try {
stat.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
stat = null;
}
}
if(conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
conn = null;
}
}
}
}
三、程序运行截图:


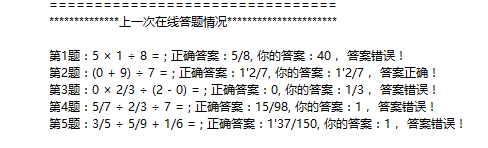
四、实验总结:
在程序设计的思路梳理上有了一定提高,但是在实际编写的时候却发现忽略的问题太多,还有就是在一些数学问题上存在空缺,需要日后不断提高
项目模块逻辑分块上有待提高。
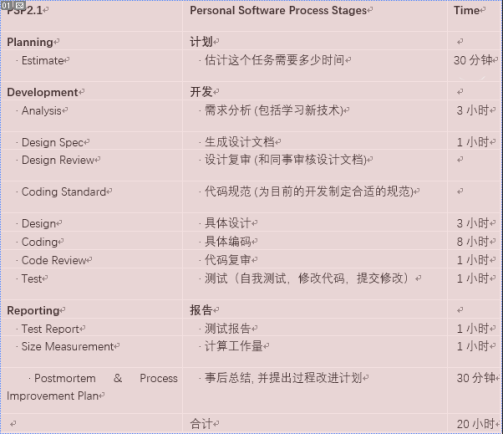
实现程序之前估计各个模块开发所花费的时间表:
实现程序之后再各个模块开发上所耗费的时间表:
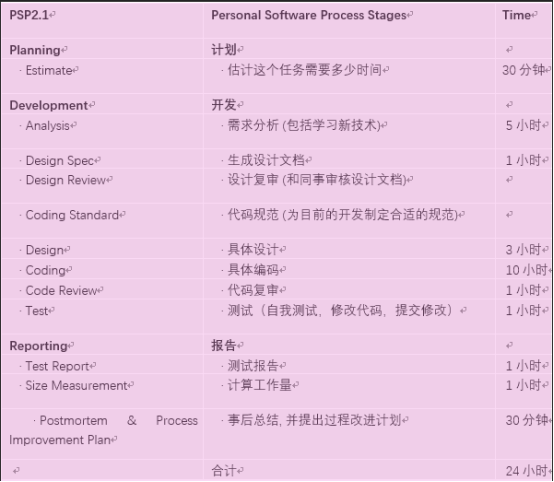
学到的东西:在程序设计的思路梳理上有了一定提高,但是在实际编写的时候却又会出现很多的问题,有些思路也不是很清晰,要善于先分析算法。项目模块逻辑以后要学习如何分类,类的划分也对程序很有帮助。





