2017-2018-1 20155306 mypwd的实现
2017-2018-1 20155306 mypwd的实现
一.pwd的使用
- 功能:
Linux中用 pwd 命令来查看”当前工作目录“的完整路径。 - 命令格式:pwd [选项]
- 命令参数:
-L:当目录为连接路径时,显示连接路径
-P:显示实际物理路径,而非使用连接(link)路径
- 参数使用示例
1.:用 pwd 命令查看默认工作目录的完整路径
[root@localhost ~]# pwd
2.:使用 pwd 命令查看指定文件夹
[root@localhost ~]# cd /opt/soft/
[root@localhost soft]# pwd
/opt/soft
3.:显示当前目录的物理路径 pwd –P
[root@DB-Server init.d]# cd /etc/init.d
[root@DB-Server init.d]# pwd -P
/etc/rc.d/init.d
4.:显示当前目录的连接路径:pwd -L
[root@DB-Server networking]#cd/etc/init.d
[root@DB-Server init.d]# pwd -L
/etc/init.d
[root@DB-Server init.d]# pwd
/etc/init.d
注意:若当前目录被删除了,pwd命令仍然显示那个目录
二.pwd的实现
1. 实现要求
1 学习pwd命令
2 研究pwd实现需要的系统调用(man -k; grep),写出伪代码
3 实现mypwd
4 测试mypwd
2.:实现步骤
- 首先,我们了解到:目录其实也是一种文件,只不过这种文件比较特殊,它里面存储的是一张对应表,即文件名和i节点的对应关系表,而i节点才是记录此文件详细信息的结构,如文件大小,属性,权限,存在硬盘的那个块等。我们在一个目录创建文件就是在这张表里添加对应关系而已,使用某个文件时也是根据i节点确定在硬盘的实际存储位置的。

-然后, 有两个特殊的文件名“.” 和 “..”,“.”代表当前目录自身,".."代表包含当前目录的上一级目录。
- 最后我们考虑如何实现:每个目录都设置了一个指向自己的i节点入口,即".",还有一个指向其父目录i节点的入口,即”..",我们首先获取当前目录的i节点编号,但是并不能知道当前目录的名称,我们切换到其的父目录,在里面寻找当前i节点编号对应的文件名即可。这样我们就很容易联想到使用递归来实现,但是终止条件是什么呢?在Unix文件系统的根目录中,“."和“..”指向同一个i节点,我们可以以此判断是否发到达了根目录。(上课老师讲过)
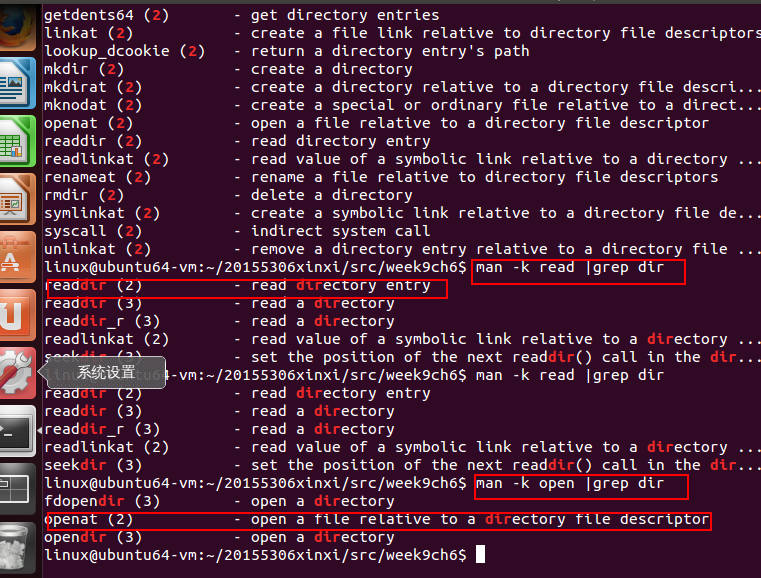
-同时,我们可以通过man命令和grep命令来获取我们所需要的系统调用函数信息。
man pwd:

man chdir:

man -k XX | grep XX
伪代码:
{
getinode(".");获取当前目录节点
getinode(".."); 获取父目录节点
记录当前节点的目录名;
只有当inode == up_inode时,打印。
}
产品代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
void printpath();
char *inode_to_name(int);
int getinode(char *);
int main()
{
printpath();
putchar('\n');
return ;
}
void printpath()
{
int inode,up_inode;
char *str;
inode = getinode(".");
up_inode = getinode("..");
chdir("..");
str = inode_to_name(inode);
if(inode == up_inode) {
// printf("/%s",str);
return;
}
printpath();
printf("/%s",str);
}
int getinode(char *str)
{
struct stat st;
if(stat(str,&st) == -1){
perror(str);
exit(-1);
}
return st.st_ino;
}
char *inode_to_name(int inode)
{
char *str;
DIR *dirp;
struct dirent *dirt;
if((dirp = opendir(".")) == NULL){
perror(".");
exit(-1);
}
while((dirt = readdir(dirp)) != NULL)
{
if(dirt->d_ino == inode){
str = (char *)malloc(strlen(dirt->d_name)*sizeof(char));
strcpy(str,dirt->d_name);
return str;
}
}
perror(".");
exit(-1);
}
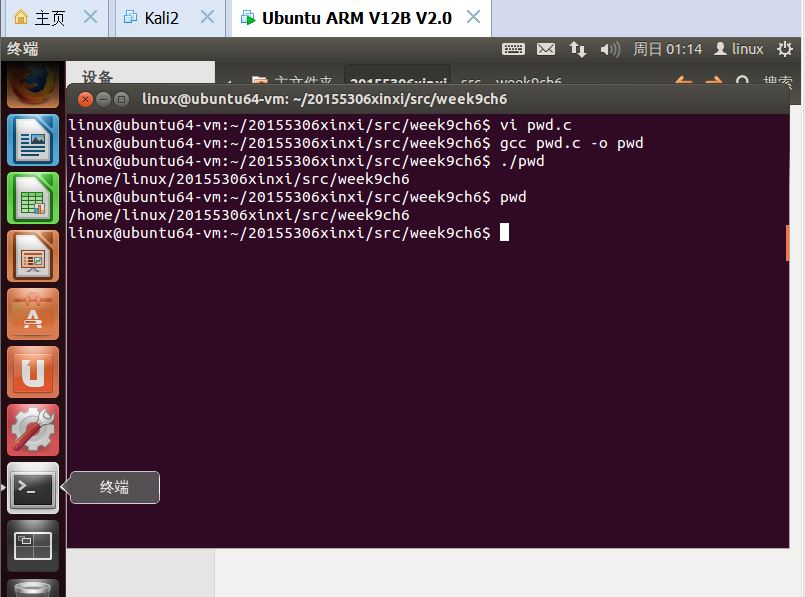
测试结果: